This is an example application to run a CLIP inference on a video in real-time. The image embeddings are accelerated by the Hailo-8/8L AI processor, while the text embeddings run on the host. Text embeddings are sparse and should be calculated only once per text. If they do not need to be updated in real-time, they can be saved to a JSON file and loaded on the next run.
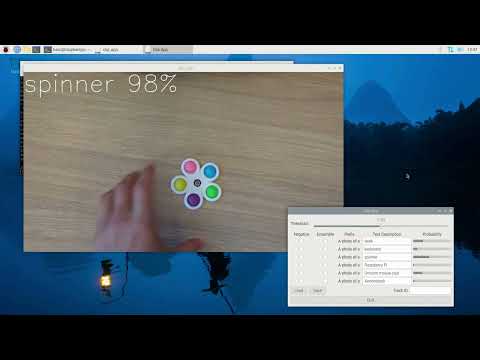
Click the image below to watch the demo on YouTube.
This application is compatible with x86 and RPi5 (8GB) systems.
This example has been tested with the following Hailo TAPPAS versions:
- v3.30.0
- v3.31.0
Please ensure that one of these versions is installed on your system.
hailo-tappas-core: TAPPAS core installation using a.debfile orapt install(Raspberry Pi platforms).hailo_tappas: For full TAPPAS installation. See instructions in our TAPPAS repository.
This repo uses Hailo Apps Infra repository. It will be installed automatically to your virtualenv when running the installation script. You can also clone it manually see instructions in the Hailo Apps Infra repository.
To install the application, clone the repository and run the installation script:
./install.shIt will prepare a virtual environment and install the required dependencies.
To prepare the environment, run the following command:
source setup_env.shRun the example:
python clip_application.py --input demoOn the first run, CLIP will download the required models. This will happen only once.
Watch the Hailo CLIP Zero Shot Classification Tutorial
python clip_application.py -h- Default mode (
--detector none): Runs CLIP inference on the entire frame, which is the intended use for CLIP and provides the best results. - Person mode (
--detector person): Runs CLIP inference on detected persons. CLIP acts as a person classifier and runs every second per tracked person. This interval can be adjusted in the code. - Face mode (
--detector face): Runs CLIP inference on detected faces. This mode may not perform as well as person mode due to cropped faces being less represented in the dataset. Experiment to see if it fits your application.
Before running the application, ensure a camera is connected to your device. Use the --input flag to specify the camera device, defaulting to /dev/video0.
You can check which USB webcam device is connected by running the following command:
get-usb-cameraIf you see the camera feed, the device is supported. If not, try /dev/video2, /dev/video4, etc. (devices are usually mapped to an even number).
Once you identify your camera device, you can run the application as follows:
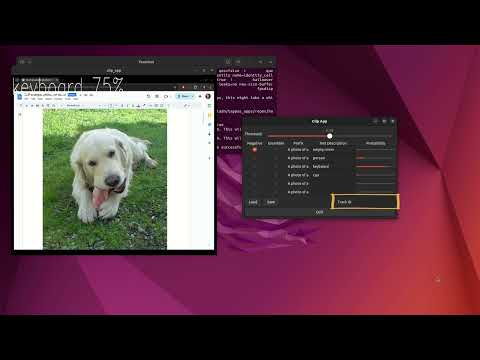
python clip_application.py --input /dev/video0python clip_application.py --input rpi- Threshold Slider: Adjusts the threshold for CLIP classification. Classifications with probabilities lower than this threshold will be ignored.
- Negative Checkbox: Marks the classification as a negative prompt. It will be included in the Softmax calculation but will not be shown in the output.
- Ensemble Checkbox: Enables ensemble mode, where the prompt text embedding is calculated with variations to improve results. See
ensemble_templateintext_image_matcher.pyfor more details. - Text Description: The text prompt for CLIP classification.
- Probability Bars: Displays the probability of various classifications in real-time.
- Load Button: Loads the text embeddings from a JSON file specified by the
--json-pathflag. - Save Button: Saves the text embeddings to a JSON file specified by the
--json-pathflag. - Track ID: Displays the classification probabilities for a specific person in person mode. The track ID appears in the bottom left corner of the bounding box.
- Quit Button: Exits the application.
- Keep in mind that the network was trained on image + caption pairs. Your text description should be somewhat similar. For example, a text description of "A photo of a cat" will give a better score than "cat".
- The app has a pre-defined "prefix" of "A photo of a" which you can change in the
TextImageMatcherclass. - The pipeline output will select one of the classes as "the best one". There is no
backgroundclass. You should define a "negative" prompt (or prompts) to be used asbackground. When set asnegative, the class will be used in the "best match" algorithm but will not be shown in the output. - You can also use
thresholdto fine-tune detection sensitivity. However, usingnegativeprompts is better for detecting specific classes. - Negative prompts should be used to "peel off" similar classifications to your target. For example, "a man with a red shirt" will have a high score for just a man or a shirt of a different color. Add negative prompts like "a man with a blue shirt" to ensure you do not get lots of false classifications.
- Play around with prompts to see what works best for your application.
You can integrate your code in the clip_application.py file. This file includes a user-defined app_callback function that is called after the CLIP inference and before the display. You can use it to add your logic to the app. The app_callback_class will be passed to the callback function and can be used to access the app's data.
- The application will run the text embeddings on the host, allowing you to change the text on the fly. This mode might not work on weak machines as it requires a host with enough memory to run the text embeddings model (on CPU). See Offline Text Embeddings for more details.
- You can set which JSON file to use for saving and loading embeddings using the
--json-pathflag. If not set,embeddings.jsonwill be used. - If you wish to load/save your JSON, use the
--json-pathflag explicitly.
- To run without online text embeddings, you can set the
--disable-runtime-promptsflag. This will speed up the load time and save memory. Additionally, you can use the app without thetorchandtorchvisiondependencies. This might be suitable for final application deployment. - You can save the embeddings to a JSON file and load them on the next run. This will not require running the text embeddings on the host.
- If you need to prepare text embeddings on a weak machine, you can use the
text_image_matchertool. This tool will run the text embeddings on the host and save them to a JSON file without running the full pipeline. This tool assumes the first text is a 'positive' prompt and the rest are negative.
text_image_matcher -h
usage: text_image_matcher [-h] [--output OUTPUT] [--interactive] [--image-path IMAGE_PATH] [--texts-list TEXTS_LIST [TEXTS_LIST ...]] [--texts-json TEXTS_JSON]
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--output OUTPUT output file name default=text_embeddings.json
--interactive input text from interactive shell
--image-path IMAGE_PATH
Optional, path to image file to match. Note image embeddings are not running on Hailo here.
--texts-list TEXTS_LIST [TEXTS_LIST ...]
A list of texts to add to the matcher, the first one will be the searched text, the others will be considered negative prompts. Example: --texts-list "cat" "dog" "yellow car"
--texts-json TEXTS_JSON
A json of texts to add to the matcher, the json will include 2 keys negative and positive, the values are going to be lists of texts.
Example: resources/texts_json_example.json
Some CPP code is used in this app for post-processing and cropping. This code should be compiled before running the example. It uses Hailo pkg-config to find the required libraries.
The compilation script is compile_postprocess.sh. You can run it manually, but it will be executed automatically when installing the package. The post-process .so files will be installed under the resources directory.
When running with TAPPAS docker, you might encounter this error:
ImportError: cannot import name 'packaging' from 'pkg_resources'
This is a known issue with setuptools version 70.0.0 and above. To fix it, either downgrade setuptools to version 69.5.1:
pip install setuptools==69.5.1Or upgrade setuptools to the latest version:
pip install --upgrade setuptoolsThe Hailo Apps Infra repository containes the infrastructure of hailo applications and pipelines. You can find it here see the Hailo Apps Infra.
We welcome contributions from the community. You can contribute by:
- Contribute to our Community Projects.
- Reporting issues and bugs.
- Suggesting new features or improvements.
- Joining the discussion on the Hailo Community Forum.
This project is licensed under the MIT License. See the LICENSE file for details.
This code example is provided by Hailo solely on an “AS IS” basis and “with all faults.” No responsibility or liability is accepted or shall be imposed upon Hailo regarding the accuracy, merchantability, completeness, or suitability of the code example. Hailo shall not have any liability or responsibility for errors or omissions in, or any business decisions made by you in reliance on this code example or any part of it. If an error occurs when running this example, please open a ticket in the "Issues" tab.