##### #####
# # ###### #### # # ##### ###### # # # # #### #### #####
# # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # #
##### ##### # # # # # ##### ##### ###### # # # # #
# # # # # ##### # # # # # # # # #
# # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # #
##### ###### #### #### # # ###### ##### # # #### #### #
- Purpose: Docker and Kubernetes network troubleshooting can become complex. With proper understanding of how Docker and Kubernetes networking works and the right set of tools, you can troubleshoot and resolve these networking issues. The
secureshootcontainer has a set of powerful networking tshooting tools that can be used to troubleshoot Docker networking issues. Along with these tools come a set of use-cases that show how this container can be used in real-world scenarios.
Network Namespaces: Before starting to use this tool, it's important to go over one key topic: Network Namespaces. Network namespaces provide isolation of the system resources associated with networking. Docker uses network and other type of namespaces (pid,mount,user..etc) to create an isolated environment for each container. Everything from interfaces, routes, and IPs is completely isolated within the network namespace of the container.
Kubernetes also uses network namespaces. Kubelets creates a network namespace per pod where all containers in that pod share that same network namespace (eths,IP, tcp sockets...etc). This is a key difference between Docker containers and Kubernetes pods.
Cool thing about namespaces is that you can switch between them. You can enter a different container's network namespace, perform some troubleshooting on its network's stack with tools that aren't even installed on that container. Additionally, secureshoot can be used to troubleshoot the host itself by using the host's network namespace. This allows you to perform any troubleshooting without installing any new packages directly on the host or your application's package.
-
Container's Network Namespace: If you're having networking issues with your application's container, you can launch
secureshootwith that container's network namespace like this:$ docker run --rm -it --tty --net container:<container_name> ghcr.io/lordoverlord/secureshoot:main -
Host's Network Namespace: If you think the networking issue is on the host itself, you can launch
secureshootwith that host's network namespace:$ docker run --rm -it --tty --net host ghcr.io/lordoverlord/secureshoot:main -
Network's Network Namespace: If you want to troubleshoot a Docker network, you can enter the network's namespace using
nsenter. This is explained in thensentersection below. -
Vanilla Docker usage: If you wanna use it in docker desktop
$ docker run --rm -it --tty --volume /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock:ro -it ghcr.io/lordoverlord/secureshoot:main
You can easily deploy secureshoot using Docker Compose using something like this:
version: "3.6"
services:
tcpdump:
image: ghcr.io/lordoverlord/secureshoot
depends_on:
- nginx
command: tcpdump -i eth0 -w /data/nginx.pcap
network_mode: service:nginx
volumes:
- $PWD/data:/data
nginx:
image: nginx:alpine
ports:
- 80:80
-
If you want to spin up a throw away container for debugging.
$ kubectl run secureshoot --rm -it --tty --image ghcr.io/lordoverlord/secureshoot:main -
if you want to spin up a container on the host's network namespace.
$ kubectl run secureshoot --rm -it --tty --overrides='{"spec": {"hostNetwork": true}}' --image ghcr.io/lordoverlord/secureshoot:main -
if you want to use secureshoot as a sidecar container to troubleshoot your application container
$ cat secureshoot-sidecar.yaml apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: ngisecureshootoot labels: app: secureshoottshoot spec: replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: apsecureshoot-netshoot template: metadata: labels: secureshootinx-netshoot spec: containers: - name: nginx image: nginx:1.14.2 ports: - containerPort: 80 secureshoot name: netshoot secureshoot lordoverlord/netshoot command: ["/bin/bash"] args: ["-c", "while true; do ping localhost; sleep 60;done"] secureshootctl apply -f netshoot-sidecar.yaml secureshootment.apps/nginx-secureshoot created $ kubectl get pod NAME READY STATsecureshootSTARTS AGE nginx-netshoot-7f9c6957f8-kr8q6 2/2 Running 0 4m27 $kubectl exec -it ngsecureshoothoot-7f9c6957f8-kr8q6 -c netshoot -- /bin/bash nginx-secureshoot-7f9c6957f8-kr8q6 $
'''
Network Problems
Many network issues could result in application performance degradation. Some of those issues could be related to the underlying networking infrastructure(underlay). Others could be related to misconfiguration at the host or Docker level. Let's take a look at common networking issues:
- latency
- routing
- DNS resolution
- firewall
- incomplete ARPs
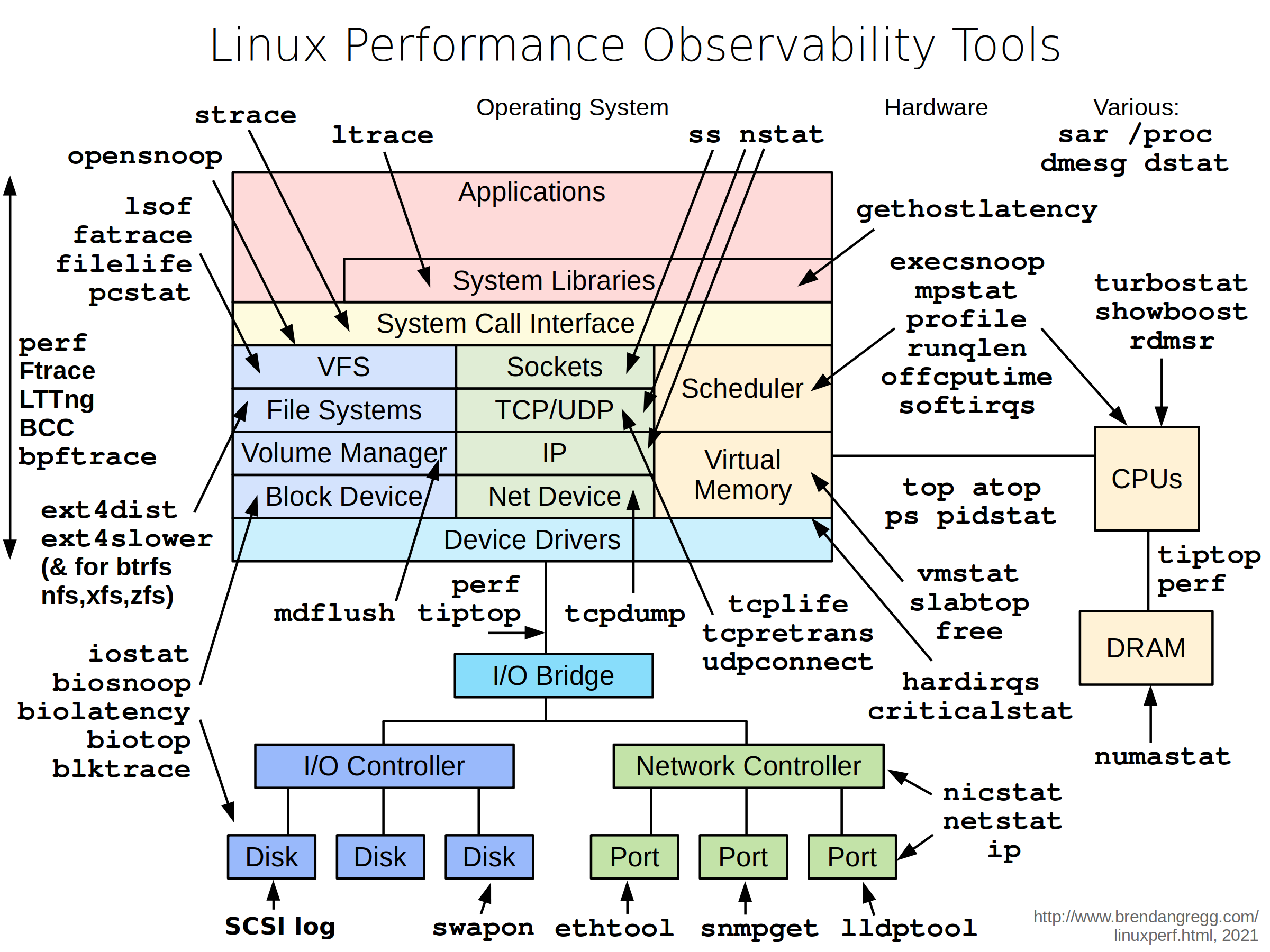
To troubleshoot these issues, secureshoot includes a set of powerful tools as recommended by this diagram.
Included Packages: The following packages are included isecureshootoot`. We'll go over some with some sample use-cases.
bash
busybox-extras
curl
drill
file
iftop
iperf3
jq
mtr
openjdk11
openssl
tcptraceroute
git
htop
kafka
confluent
Purpose: test networking performance between two containers/hosts.
Create Overlay network:
$ docker network create -d overlay perf-test
Launch two containers:
🐳 → docker service create --name perf-test-a --network perf-test lordoverlord/secureshoot iperf3 -s -p 9999
7dkcckjs0g7b4eddv8e5ez9nv
🐳 → docker service create --name perf-test-b --network perf-test lordoverlord/secureshoot iperf3 -c perf-test-a -p 9999
2yb6fxls5ezfnav2z93lua8xl
🐳 → docker service ls
ID NAME REPLICAS IMAGE COMMAND
2yb6fxls5ezf perf-test-b 1/1 lordoverlord/secureshoot iperf3 -c perf-test-a -p 9999
7dkcckjs0g7b perf-test-a 1/1 nicolasecureshootoot iperf3 -s -p 9999
🐳 → docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
ce4ff40a5456 lordoverlord/secureshoot:latest "iperf3 -s -p 9999" 31 seconds ago Up 30 seconds iperf3 -test- .1.bil2mo8inj3r9nyrss1g15qav
🐳 → docker logs ce4ff40a5456
------------------------------------------------------------
Server listening on TCP port 9999
TCP window size: 85.3 KByte (default)
------------------------------------------------------------
[ 4] local 10.0.3.3 port 9999 connected with 10.0.3.5 port 35102
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth
[ 4] 0.0-10.0 sec 32.7 GBytes 28.1 Gbits/sec
[ 5] local 10.0.3.3 port 9999 connected with 10.0.3.5 port 35112
Purpose: iftop does for network usage what top does for CPU usage. It listens to network traffic on a named interface and displays a table of current bandwidth usage by pairs of hosts.
Continuing the iperf3 example.
→ docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
ce4ff40a5456 lordoverlord/secureshoot:latest "iperf3 -s -p 9999" 5 minutes ago Up 5 minutes perf-test-a.1.bil2mo8inj3r9nyrss1g15qav
🐳 → docker run -it --net container:perf-test-a.1.bil2mo8inj3r9nyrss1g15qav lordoverlord/secureshoot iftop -i eth0
Purpose: drill is a tool to designed to get all sorts of information out of the DNS.
Continuing the iperf example, we'll use drill to understand how services' DNS is resolved in Docker.
🐳 → docker run -it --net container:perf-test-a.1.bil2mo8inj3r9nyrss1g15qav lordoverlord/secureshoot drill -V 5 perf-test-b
;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, rcode: NOERROR, id: 0
;; flags: rd ; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 0, AUTHORITY: 0, ADDITIONAL: 0
;; QUESTION SECTION:
;; perf-test-b. IN A
;; ANSWER SECTION:
;; AUTHORITY SECTION:
;; ADDITIONAL SECTION:
;; Query time: 0 msec
;; WHEN: Thu Aug 18 02:08:47 2016
;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 0
;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, rcode: NOERROR, id: 52723
;; flags: qr rd ra ; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 1, AUTHORITY: 0, ADDITIONAL: 0
;; QUESTION SECTION:
;; perf-test-b. IN A
;; ANSWER SECTION:
perf-test-b. 600 IN A 10.0.3.4 <<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<< Service VIP
;; AUTHORITY SECTION:
;; ADDITIONAL SECTION:
;; Query time: 1 msec
;; SERVER: 127.0.0.11 <<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<< Local resolver
;; WHEN: Thu Aug 18 02:08:47 2016
;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 56
ctop is a free open source, simple and cross-platform top-like command-line tool for monitoring container metrics in real-time. It allows you to get an overview of metrics concerning CPU, memory, network, I/O for multiple containers and also supports inspection of a specific container.
To get data into ctop, you'll need to bind docker.sock into the secureshoot container.
`/ # `docker run -it --rm -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock lordoverlord/secureshoot ctop``
It will display running and existed containers with useful metrics to help troubleshoot resource issues; hit "q" to exit.
Feel free to provide to contribute troubleshooting tools and use-cases by opening PRs. If you would like to add any package, please follow these steps:
-
In the PR, please include some rationale as to why this tool is useful to be included in secureshoot.
Note: If the functionality of the tool is already addressed by an existing tool, I might not accept the PR
-
Change the Dockerfile to include the new package/tool
-
If you're building the tool from source, make sure you leverage the multi-stage build process and update the
build/fetch_binaries.shscript -
Update the README's list of included packages AND include a section on how to use the tool
-
If the tool you're adding supports multi-platform, please make sure you highlight that.