RLPortfolio is a Python package which provides several features to implement, train and test reinforcement learning agents that optimize a financial portfolio:
- A training simulation environment that implements the state-of-the-art mathematical formulation commonly used in the research field.
- Two policy gradient training algorithms that are specifically built to solve the portfolio optimization task.
- Four cutting-edge deep neural networks implemented in PyTorch that can be used as the agent policy.
Click here to access the library documentation!
Note: This project is mainly intended for academic purposes. Therefore, be careful if using RLPortfolio to trade real money and consult a professional before investing, if possible.
This library is composed by the following components:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| rlportfolio.algorithm | A compilation of specific training algorithms to portfolio optimization agents. |
| rlportfolio.data | Functions and classes to perform data preprocessing. |
| rlportfolio.environment | Training reinforcement learning environment. |
| rlportfolio.policy | A collection of deep neural networks to be used in the agent. |
| rlportfolio.utils | Utility functions for convenience. |
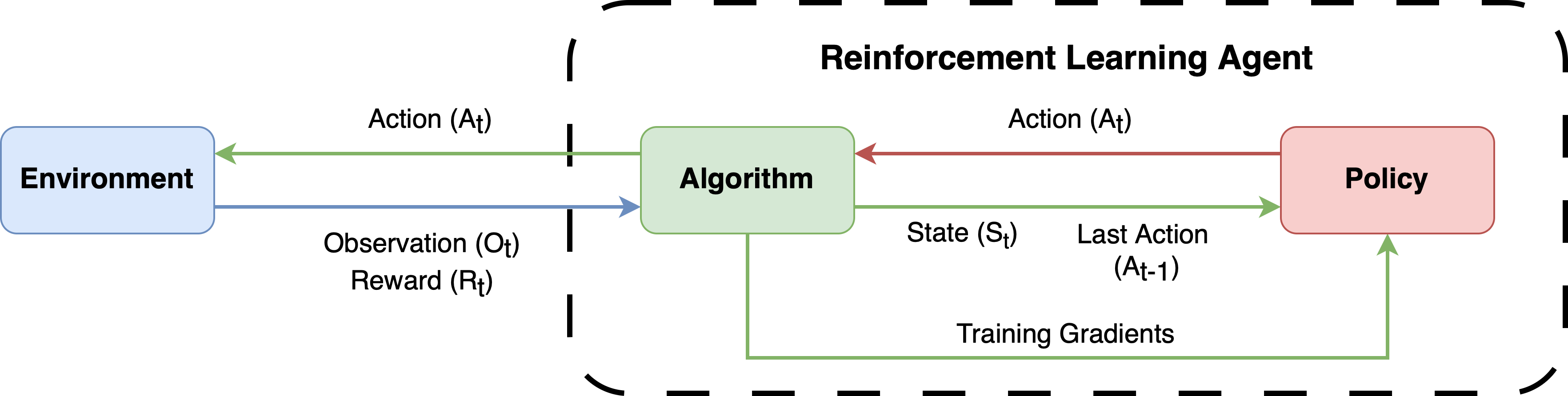
RLPortfolio is implemented with a modular architecture in mind so that it can be used in conjunction with several other libraries. To effectively train an agent, you need three constituents:
- A training algorithm.
- A simulation environment.
- A policy neural network (depending on the algorithm, a critic neural network might be necessary tools).
The figure below shows the dynamics between those components. All of them are present in this library, but users are free to use other libraries or custom implementations.
Differently than other implementations of the research field, this library utilizes modern versions of libraries (PyTorch, Gymnasium, Numpy and Pandas) and follows standards that allows its utilization in conjunction with other libraries.
RLPortfolio aims to be easy to use and its code is heavily documented using Google Python Style so that users can understand how to utilize the classes and functions. Additionaly, the training components are very customizable and, thus, different training routines can be run without the need to directly modify the code.
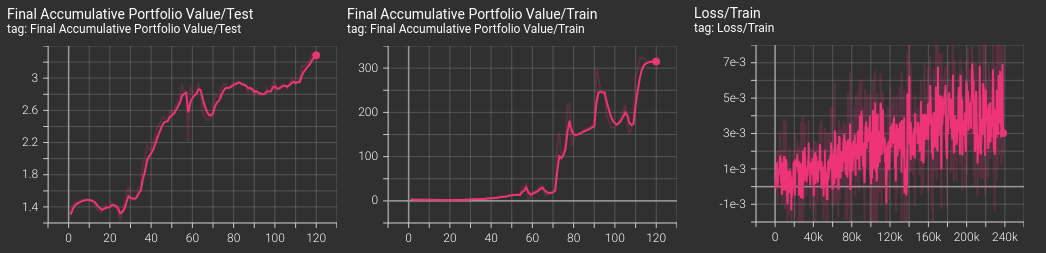
The algorithms implemented in the package are integrated with Tensorboard, automatically providing graphs of the main metrics during training, validation and testing.
In order to be as reliable as possible, this project has a strong focus in implementing unit tests for new implementations. Therefore, RLPortfolio can be easily used to reproduce and compare research studies.
You can install this package using pip with:
$ pip install rlportfolioAdditionally, you can also install it by cloning this repository and running the following command:
$ pip install .RLPortfolio's interface is very easy to use. In order to train an agent, you need to instantiate an environment object. The environment makes use of a dataframe which contains the time series of price of stocks.
import pandas as pd
from rlportfolio.environment import PortfolioOptimizationEnv
# dataframe with training data (market price time series)
df_train = pd.read_csv("train_data.csv")
environment = PortfolioOptimizationEnv(
df_train, # data to be used
100000 # initial value of the portfolio
)Then, it is possible to instantiate the policy gradient algorithm to generate an agent that actuates in the created environment.
from rlportfolio.algorithm import PolicyGradient
algorithm = PolicyGradient(environment)Finally, you can train the agent using the defined algorithm through the following method:
# train the algorithm for 10000
algorithm.train(10000)It's now possible to test the agent's performance in another environment which contains data of a different time period.
# dataframe with testing data (market price time series)
df_test = pd.read_csv("test_data.csv")
environment_test = PortfolioOptimizationEnv(
df_test, # data to be used
100000 # initial value of the portfolio
)
# test the agent in the test environment
algorithm.test(environment_test)The test function will return a dictionary with the metrics of the test.