- Flume是向Hadoop批量导入基于事件的海量数据,例如利用Flume从一组Web服务器中搜集日志文件,然后把这些文件转移到一个新的HDFS汇总文件中以做进一步处理,其终点(或者sink)通常为HDFS。
- Flume也支持导入其他系统比如HBase或Solr。
- 基于流式架构,灵活简单。
- 支持动态配置,定时拉取flume-ng配置,配置热更新。
- 使用Flume需要
运行Flume代理,Flume代理是由持续运行的source、sink以及channel(用于连接source和sink)构成的Java进程 - Flume的
sourcgite产生事件,并将其传输给channel,channel存储这些事件直至转发给sink。 - 可以把source-channel-sink的组合视为基本的Flume构件。
JVM进程,以事件的形式将数据从source sink到目的地。- 包含Souce、Channel、Sink是哪个部分
Souce复制接收数据到FLume Agent的组件。SOuce组件支持处理多种类型多种格式的日志数据,包括avro、thrift、exec、jms、spooling directory、netcat、sequence generator、syslog、http、legacy。
- Sink不断地轮询Channel中的事件且批量地移除它们,并将这些事件批量写入到存储或索引系统、或者被发送到另一个Flume Agent.
- Sink组件目的地包括
hdfs、logger、avro、thrift、ipc、file、HBase、solr、自定义。
- Channel是位于
Source和Sink之间的缓冲区。因此,Channel允许Source和Sink运作在不同的速率。Channel是线程安全的,可以同时处理几个Source的写入操作和几个Sink的读取操作。 - 自带Channel:
Memory和File以及KafkaChannel。 - Memory Channel是内存中的队列。File Channel是将所有事件写到磁盘。
- 传输单元,Flume数据传输的基本单元,以Event的形式将数据从源头送至目的地。Event由
Header和Body两部分组成,Header用来存放该event的一些属性,为K-V结构,Body用来存放该条数据, 形式为字节数组。
http://www.apache.org/dyn/closer.lua/flume/1.9.0/apache-flume-1.9.0-bin.tar.gz
# 解压
tar -zxvf apache-flume-1.9.0-bin.tar.gz
# 配置环境变量
#Flume环境
export FLUME_HOME=/Users/babywang/Documents/reserch/studySummary/bigdata/flume/apache-flume-1.9.0
export PATH=$PATH:$FLUME_HOME/bin
# 配置JAVA HOME
# export JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-8-oracle
export JAVA_HOME=/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_221.jdk/Contents/Home- Flume-ng启动代理查看是否安装成功
# example.conf: A single-node Flume configuration
# Name the components on this agent
# a1为agent的名称
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
# Describe/configure the source
# 配置agent a1的source配置
a1.sources.r1.type = netcat
a1.sources.r1.bind = localhost
a1.sources.r1.port = 9999
# Describe the sink
# 配置agent a1的sink配置
a1.sinks.k1.type = logger
# Use a channel which buffers events in memory
# 配置agent a1的channel配置
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
# 绑定source和channel,sink和channel,channel和sink为1对n,source和channel为1对多
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1flume-ng agent -n a1 -c $FLUME_HOME/conf -f netcat-flume-logger.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console- -n: 指定运行的agent名称
- -c:指定flume配置文件目录
- -f:运行的Job
nc localhost 9999- 实时监控Zookeeper日志,并上传到HDFS中
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
# 配置source -F失败后会重试 -f直接读取后面的数据
a1.sources.r1.type = exec
a1.sources.r1.command = tail -f /Users/babywang/Documents/reserch/studySummary/module/hadoop-2.8.5/logs/hadoop-babywang-namenode-research.log
# 配置sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = logger
# 配置agent a1的channel配置
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# source绑定channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel=c1- 启动flume-ng
flume-ng agent -n a1 -c $FLUME_HOME/conf -f file-flume-logger.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console- 将Hadoop相关jar拷贝至Flume lib目录下
#从hadoop/shared目录下拷贝
hadoop-auth-2.8.5.jar
hadoop-common-2.8.5.jar
hadoop-hdfs-2.8.5.jar
commons-io-2.4.jar
commons-configuration-1.6.jar
htrace-core4-4.0.1-incubating.jar- 配置
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
# 配置source -F失败后会重试 -f直接读取后面的数据
a1.sources.r1.type = exec
a1.sources.r1.command = tail -f /Users/babywang/Documents/reserch/studySummary/module/hadoop-2.8.5/logs/hadoop-babywang-namenode-research.log
# 配置sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = hdfs
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.path = hdfs://hadoop:8020/hadoop/logs/%y-%m-%d/%H%M/%S
# 上传文件前缀
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.filePrefix = namenode-
# 上传文件后缀
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.fileSuffix = log
# 是否按照实际滚动文件夹
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.round = true
# 多少时间单位创建一个新的文件夹
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundValue = 1
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundUnit = hour
# 是否使用本地时间戳
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp = true
# 积攒多少个Event才flush到HDFS一次
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.batchSize = 1000
# 设置文件类型,可支持压缩
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.fileType = DataStream
# 多久生成一个文件
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollInterval = 60
# 设置每个文件的滚动大小
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollSize = 134217700
# 文件的滚动与Event数量无关
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollCount = 0
# 配置agent a1的channel配置
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 3000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 2000
# source绑定channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel=c1- 启动脚本
flume-ng agent -n a1 -c $FLUME_HOME/conf -f file-flume-hdfs.conf- 使用Spooling Directory Source
a1.sources = s1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
# sources
a1.sources.s1.type = TAILDIR
a1.sources.s1.positionFile = /Users/babywang/Documents/reserch/studySummary/module/flume-1.9.0/job/taildir_position.json
a1.sources.s1.filegroups = f1 f2
a1.sources.s1.filegroups.f1 = /Users/babywang/Documents/reserch/studySummary/module/test/file1.txt
a1.sources.s1.filegroups.f2 = /Users/babywang/Documents/reserch/studySummary/module/test/file2.txt
# sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = logger
# channels
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactitionCapacity = 100
# binds
a1.sources.s1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1- 启动脚本
flume-ng agent -n a1 -c $FLUME_HOME/conf -f dir-flume-hdfs.conf- 无法使用Exec source因为Exec无法保证数据不丢失,Spooldir Source能够保证数据不丢失,且能够实现断点续传,存在延迟,不能实时监控;Taildir Source支持断点续传,也可以保证数据不丢失并且低延迟支持实时监控。
- Flume使用
两个独立的事务分别负责从source到channel以及从channel到sink的事件传递 - 一旦事务中的所有事件全部传递到channel且提交成功,那么source就将该文件标记为已完成。如果
事件失败就会回滚保存在channel中等待重新传递。
- file channel,
具有持久性,只要事件被写入channel,即使代理重新启动,事件也不会丢失 - memory channel,
事件缓冲在存储器中,不具有持久存储能力。
- Flume在有可能的情况下尽量以
事务为单位来批量处理事件,而不是逐个事件进行处理。批量处理有利于提高file channel的性能,因为每个事务只需要写一次本地磁盘和调用一次fsync函数。 批量的大小取决于组件的类型,并且大多数情况下是配置的。
a1.sources = r1
a1.channels = c1 c2 c3 c4
a1.sources.r1.selector.type = multiplexing
a1.sources.r1.selector.header = state
# 如果header中包含state CZ选择c1channel,包含state US选择c2 c3默认选择c4
a1.sources.r1.selector.mapping.CZ = c1
a1.sources.r1.selector.mapping.US = c2 c3
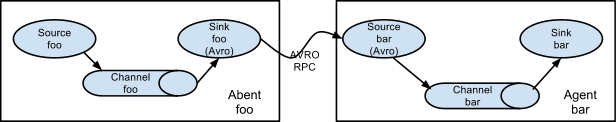
a1.sources.r1.selector.default = c4- 这种模式是将多个flume顺序连接起来,从最初的source开始到最终sink传送的目的存储系统。不适合桥接过多的flume数量,flume数量过多会导致传送速度变慢和系统稳定性。
- Flume支持将事件流向一个或多个目的地。这种模式可以将相同数据复制到多个channel中,或者将不同数据分发到不同channel中,sink可以选择传送到不同的目的地。
flume-1.sources = s1
flume-1.sinks = k1 k2
flume-1.channels = c1 c2
# source
flume-1.sources.s1.type = TAILDIR
flume-1.sources.s1.positionFile = /Users/babywang/Documents/reserch/studySummary/module/flume-1.9.0/job/position.json
flume-1.sources.s1.filegroups = f1
flume-1.sources.s1.filegroups.f1 = /Users/babywang/Documents/reserch/studySummary/module/hadoop-2.8.5/logs/hadoop-babywang-namenode-research.log
# sinks
## k1
flume-1.sinks.k1.type = avro
flume-1.sinks.k1.hostname = hadoop
flume-1.sinks.k1.port = 4545
## k2
flume-1.sinks.k2.type = avro
flume-1.sinks.k2.hostname = hadoop
flume-1.sinks.k2.port = 4546
# channels
## c1
flume-1.channels.c1.type = memory
flume-1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
flume-1.channels.c1.transactitionCapacity = 100
## c2
flume-1.channels.c2.type = memory
flume-1.channels.c2.capacity = 1000
flume-1.channels.c2.transactitionCapacity = 100
# 将数据流复制给所有channel
flume-1.sources.s1.selector.type = replicating
# bind
flume-1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
flume-1.sinks.k2.channel = c2
flume-1.sources.s1.channels = c1 c2flume-2.sources = s1
flume-2.sinks = k1
flume-2.channels = c1
# source
flume-2.sources.s1.type = avro
flume-2.sources.s1.bind = hadoop
flume-2.sources.s1.port = 4546
# sinks
flume-2.sinks.k1.type = logger
# channels
flume-2.channels.c1.type = memory
flume-2.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
flume-2.channels.c1.transactitionCapacity = 100
# bind
flume-2.sinks.k1.channel = c1
flume-2.sources.s1.channels = c1flume-3.sources = s1
flume-3.sinks = k1
flume-3.channels = c1
# source
flume-3.sources.s1.type = avro
flume-3.sources.s1.bind = hadoop
flume-3.sources.s1.port = 4545
# sinks
flume-3.sinks.k1.type = hdfs
flume-3.sinks.k1.hdfs.path = hdfs://hadoop:8020/hadoop/logs/%y-%m-%d/%H%M/%S
# 上传文件前缀
flume-3.sinks.k1.hdfs.filePrefix = namenode-
# 上传文件后缀
flume-3.sinks.k1.hdfs.fileSuffix = log
# 是否按照实际滚动文件夹
flume-3.sinks.k1.hdfs.round = true
# 多少时间单位创建一个新的文件夹
flume-3.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundValue = 1
flume-3.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundUnit = hour
# 是否使用本地时间戳
flume-3.sinks.k1.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp = true
# 积攒多少个Event才flush到HDFS一次
flume-3.sinks.k1.hdfs.batchSize = 100
# 设置文件类型,可支持压
flume-3.sinks.k1.hdfs.fileType = DataStream
# 多久生成一个文件
flume-3.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollInterval = 60
# 设置每个文件的滚动大小
flume-3.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollSize = 134217700
# 文件的滚动与Event数量无关
flume-3.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollCount = 0
# channels
flume-3.channels.c1.type = memory
flume-3.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
flume-3.channels.c1.transactitionCapacity = 200
# bind
flume-3.sinks.k1.channel = c1
flume-3.sources.s1.channels = c1- 先启动下游Flume Ng,在启动上游Flume-Ng
- 将多个sink逻辑上分到一个sink组,sink组配合不同的SinkProcessor可以实现负载均衡和故障转移。
# flume1
a1.sources = s1
a1.sinks = k1 k2
a1.channels = c1
a1.sinkgroups = g1
# sources
a1.sources.s1.type=netcat
a1.sources.s1.bind=hadoop
a1.sources.s1.port=9999
# sinks
a1.sinks.k1.type=avro
a1.sinks.k1.hostname=hadoop
a1.sinks.k1.port=4000
a1.sinks.k2.type=avro
a1.sinks.k2.hostname=hadoop
a1.sinks.k2.port=4001
# sink groups
a1.sinkgroups.g1.sinks = k1 k2
a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.type = failover
a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.priority.k1 = 5
a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.priority.k2 = 10
a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.maxpenalty = 10000
# channels
a1.channels.c1.type=memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity=1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity=100
# bind
a1.sources.s1.channels=c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel=c1
a1.sinks.k2.channel=c1
# sink1-flume2
a2.sources = s2
a2.sinks = k2
a2.channels = c2
# sources
a2.sources.s2.type=avro
a2.sources.s2.bind=hadoop
a2.sources.s2.port=4000
# sinks
a2.sinks.k2.type=logger
# channels
a2.channels.c2.type=memory
a2.channels.c2.capacity=1000
a2.channels.c2.transactionCapacity=100
# bind
a2.sources.s2.channels=c2
a2.sinks.k2.channel=c2
# sink2-flume3
a3.sources = s3
a3.sinks = k3
a3.channels = c3
# sources
a3.sources.s3.type=avro
a3.sources.s3.bind=hadoop
a3.sources.s3.port=4001
# sinks
a3.sinks.k3.type=logger
# channels
a3.channels.c3.type=memory
a3.channels.c3.capacity=1000
a3.channels.c3.transactionCapacity=100
# bind
a3.sources.s3.channels=c3
a3.sinks.k3.channel=c3# source端
a1.sources = s1
a1.sinks = k1 k2
a1.channels = c1
a1.sinkgroups = g1
# sources
a1.sources.s1.type=netcat
a1.sources.s1.bind=hadoop
a1.sources.s1.port=9999
# sinks
a1.sinks.k1.type=avro
a1.sinks.k1.hostname=hadoop
a1.sinks.k1.port=4000
a1.sinks.k2.type=avro
a1.sinks.k2.hostname=hadoop
a1.sinks.k2.port=4001
# sink groups
a1.sinkgroups.g1.sinks = k1 k2
a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.type = load_balance
a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.backoff = true
a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.selector = round_robin
# channels
a1.channels.c1.type=memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity=1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity=100
# bind
a1.sources.s1.channels=c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel=c1
a1.sinks.k2.channel=c1
# sink1
a2.sources = s2
a2.sinks = k2
a2.channels = c2
# sources
a2.sources.s2.type=avro
a2.sources.s2.bind=hadoop
a2.sources.s2.port=4000
# sinks
a2.sinks.k2.type=logger
# channels
a2.channels.c2.type=memory
a2.channels.c2.capacity=1000
a2.channels.c2.transactionCapacity=100
# bind
a2.sources.s2.channels=c2
a2.sinks.k2.channel=c2
# sink2
a3.sources = s3
a3.sinks = k3
a3.channels = c3
# sources
a3.sources.s3.type=avro
a3.sources.s3.bind=hadoop
a3.sources.s3.port=4001
# sinks
a3.sinks.k3.type=logger
# channels
a3.channels.c3.type=memory
a3.channels.c3.capacity=1000
a3.channels.c3.transactionCapacity=100
# bind
a3.sources.s3.channels=c3
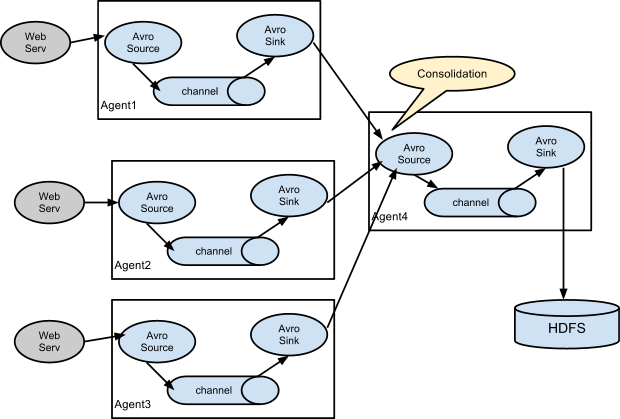
a3.sinks.k3.channel=c3- 收集web应用日志分布式方式手机多个web服务器的日志然后汇总到一台最终sink到存储系统。
- 实现
org.apache.flume.interceptor.Interceptor接口
/**
* @fileName: TypeInterceptor.java
* @description: 自定义Flume拦截器
* @author: by echo huang
* @date: 2020-07-31 00:12
*/
public class TypeInterceptor implements Interceptor {
/**
* 添加过头的事件
*/
private List<Event> addHeaderEvents;
@Override
public void initialize() {
this.addHeaderEvents = Lists.newArrayList();
}
/**
* 单个事件拦截
*
* @param event
* @return
*/
@Override
public Event intercept(Event event) {
Map<String, String> headers = event.getHeaders();
String body = new String(event.getBody());
//如果event的body包含hello则向header添加一个标签
if (body.contains("hello")) {
headers.put("type", "yes");
} else {
headers.put("type", "no");
}
return event;
}
/**
* 批量事件拦截
*
* @param list
* @return
*/
@Override
public List<Event> intercept(List<Event> list) {
this.addHeaderEvents.clear();
list.forEach(event -> addHeaderEvents.add(intercept(event)));
return this.addHeaderEvents;
}
@Override
public void close() {
}
public static class InterceptorBulder implements Builder {
@Override
public Interceptor build() {
return new TypeInterceptor();
}
/**
* 传递配置,可以将外部配置传递至内部
*
* @param context 配置上下文
*/
@Override
public void configure(Context context) {
}
}
}-
打包将jar包上传至flume的lib下
-
添加flume配置interceptors
# interceptor
a2.sources.s1.interceptors = i1
a2.sources.s1.interceptors.i1.type = org.research.flume.interceptor.TypeInterceptor$InterceptorBulder
# channel selector
a2.sources.s1.selector.type=multiplexing
a2.sources.s1.selector.header=type
a2.sources.s1.selector.mapping.yes=c1
a2.sources.s1.selector.mapping.no=c2- 继承
AbstractSource类,实现Configurable和PollableSource接口
public class OssSource extends AbstractSource implements Configurable, PollableSource {
private String prefix;
private String suffix;
@Override
public void configure(Context context) {
this.prefix = context.getString("prefix");
this.suffix = context.getString("suffix", "suffix");
}
/**
* 1.接受数据(读取OSS数据)
* 2.封装事件
* 3.将事件传递给Channel
*
* @return
* @throws EventDeliveryException
*/
@Override
public Status process() throws EventDeliveryException {
Status status = null;
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
SimpleEvent event = new SimpleEvent();
event.setBody((prefix + "--" + i + "--" + suffix).getBytes());
//传递数据给Channel
getChannelProcessor().processEvent(event);
status = Status.READY;
}
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (Exception e) {
status = Status.BACKOFF;
}
return status;
}
@Override
public long getBackOffSleepIncrement() {
return 0;
}
@Override
public long getMaxBackOffSleepInterval() {
return 0;
}
}- 配置自定义source
a1.sources = s1
a1.sinks =k1
a1.channels=c1
# source
a1.sources.s1.type=org.research.flume.source.OssSource
a1.sources.s1.prefix=hello
a1.sources.s1.suffix=world
# sinks
a1.sinks.k1.type=logger
# channels
a1.channels.c1.type=memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity=1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity=100
# bind
a1.sources.s1.channels=c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel=c1- 继承
AbstractSink实现Configurable接口,Sink是完全事务性的,从Channel批量删除数据之前,每个SInk用Channel启动一个事务,批量事件一旦成功写出则利用Channel提交事务。事务一旦提交,该Channel从自己的内部缓冲区删除事件。
public class CustomSink extends AbstractSink implements Configurable {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(CustomSink.class);
private String prefix;
private String suffix;
@Override
public Status process() throws EventDeliveryException {
Status status = null;
Channel channel = getChannel();
//拿到channel事务
Transaction transaction = channel.getTransaction();
transaction.begin();
try {
Event take = channel.take();
String body = new String(take.getBody(), Charsets.UTF_8);
LOGGER.info("result:{}", prefix + body + suffix);
transaction.commit();
status = Status.READY;
} catch (Exception e) {
transaction.rollback();
status = Status.BACKOFF;
} finally {
transaction.close();
}
return status;
}
@Override
public void configure(Context context) {
this.prefix = context.getString("prefix");
this.suffix = context.getString("suffix", "on the road");
}
}- flume配置
a1.sources = s1
a1.sinks =k1
a1.channels=c1
# source
a1.sources.s1.type = netcat
a1.sources.s1.bind = hadoop
a1.sources.s1.port = 9999
# sinks
a1.sinks.k1.type=org.research.flume.sink.CustomSink
a1.sinks.k1.prefix=hello
a1.sinks.k1.suffix=world
# channels
a1.channels.c1.type=memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity=1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity=100
# bind
a1.sources.s1.channels=c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel=c1- 替换yum源
mv /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo.backup
curl -o /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/Centos-7.repo
sed -i -e ‘/mirrors.cloud.aliyuncs.com/d‘ -e ‘/mirrors.aliyuncs.com/d‘ /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo- 安装httpd服务与php
sudo yum -y install httpd php - 安装其他依赖
sudo yum -y install rrdtool perl-rrdtool rrdtool-devel
sudo yum -y install apr-devel- 安装ganglia
mv /etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo /etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo.backup
mv /etc/yum.repos.d/epel-testing.repo /etc/yum.repos.d/epel-testing.repo.backup
curl -o /etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/epel-7.repo
sudo yum -y install ganglia-gmetad
sudo yum -y install ganglia-web
sudo yum -y install ganglia-gmond- ganglia配置
sudo vim /etc/httpd/conf.d/ganglia.confAlias /ganglia /usr/share/ganglia
<Location /ganglia>
# Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
# AllowOverride None
Require all granted
# Order deny,allow
# Deny from all
Allow from all
# Require local
# Require ip 10.1.2.3
# Require host example.org
</Location>- gmetad配置修改数据源
sudo vim /etc/ganglia/gmetad.conf# A list of machines which service the data source follows, in the
# format ip:port, or name:port. If a port is not specified then 8649
# (the default gmond port) is assumed.
# default: There is no default value
#
# data_source "my cluster" 10 localhost my.machine.edu:8649 1.2.3.5:8655
# data_source "my grid" 50 1.3.4.7:8655 grid.org:8651 grid-backup.org:8651
# data_source "another source" 1.3.4.7:8655 1.3.4.8
data_source "hadoop" 192.168.1.12- 修改/etc/ganglia/gmond.conf
cluster {
name = "hadoop"
owner = "unspecified"
latlong = "unspecified"
url = "unspecified"
}
/* The host section describes attributes of the host, like the location */
host {
location = "unspecified"
}
/* Feel free to specify as many udp_send_channels as you like. Gmond
used to only support having a single channel */
udp_send_channel {
#bind_hostname = yes # Highly recommended, soon to be default.
# This option tells gmond to use a source address
# that resolves to the machine‘s hostname. Without
# this, the metrics may appear to come from any
# interface and the DNS names associated with
# those IPs will be used to create the RRDs.
# mcast_join = 239.2.11.71
host = 192.168.1.12
port = 8649
ttl = 1
}
/* You can specify as many udp_recv_channels as you like as well. */
udp_recv_channel {
# mcast_join = 239.2.11.71
port = 8649
bind = 192.168.1.12
retry_bind = true
# Size of the UDP buffer. If you are handling lots of metrics you really
# should bump it up to e.g. 10MB or even higher.
# buffer = 10485760
}- 关闭selinux,临时关闭
sudo setenforce 0 - 修改ganglia权限
sudo chmod -R 777 /var/lib/ganglia- 启动ganglia
stytemctl start httpd
stytemctl start gmetad
stytemctl start gmond
- 访问ganglia页面
http://locahost/ganglia
- 使用ganglia实时监控,或者修改源码通过pushgateway将数据push至普罗米修斯中,通过granfa来监控。
- 收集数据,可以处理各种类型、各种格式的日志数据。
- 采集到的数据进行缓存,可以存放到Memory或File中。
- 使用
file channel可以设置多个dataDirs目录,checkpoint和backcheckpoint可以放在不同的磁盘上。
- 用于将数据发送到目的地的组件,目的地包括HDFS、Logger、avro等
- 监控后台日志:tairDir(支持多文件监控、支持断点续传、支持position容错checkpoint)、exec
- 监控后台产生日志端口:netcat、exec、tairDir
- Replicating Channel Selector(default)和Multiplexing Channel Selectors(通过映射选择将不同的 header数据传输到不同的channel)
- Source端增加BatchSize批次大小
- channel增大event容量并且增大事务容量,根据业务选择memory方式。
- Sink使用负载均衡的方式,增大batchSize个数,一次处理多条消息。
- Flume使用两个独立的事务分别负责从Source到Channel(put事务),以及从channel到SInk的事务(task事务)。
- Source到Channel不会丢失数据,Channel到Sink也不会丢失数据,但是如果channel是memory类型的会丢失数据,并且agent宕机导致数据丢失或者channel存储数据已满导致SOurce不可写入,未写入的数据丢失。
Flume会导致数据重复,因为FLume保证的语义为at least once,比如因为网络原因导致source发送数据到channel一直没有响应,但是数据已经写出了,此时source重发就会导致数据重复。