Overview • Branch roadmap • Environment: docker • Install CKAN • CKAN images • Extending guide • Applying patches • Addons • Info & Backups • API
Requirements:
Contains Docker images for the different components of CKAN Cloud and a Docker compose environment (based on ckan) for development and testing Open Data portals.
Tip
- Use the deploy in 5 minutes to see
ckan-dockerin 5 minutes ⏱! - Or use Codespaces to test
ckan-dockerin your browser:
Important
This is a custom installation of Docker Compose with specific extensions for spatial data and GeoDCAT-AP/INSPIRE metadata profiles. For official installations, please have a look: CKAN documentation: Installation.
Available components:
- CKAN custom multi-stage build with spatial capabilities from ckan-docker-spatial1, an image used as a base and built from the official CKAN repo. The following versions of CKAN are available:
| CKAN Version | Type | Base image | Docker tag | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.9.x | custom spatial image | alpine:3.15 |
ghcr.io/mjanez/ckan-spatial:ckan-2.9.8, ghcr.io/mjanez/ckan-spatial:ckan-2.9.8, ghcr.io/mjanez/ckan-docker:ckan-2.9.9, ghcr.io/mjanez/ckan-docker:ckan-2.9.10, ghcr.io/mjanez/ckan-docker:ckan-2.9.11 |
Stable official versions of CKAN 2.9.8, 2.9.10 and 2.9.11 |
| 2.10.x | custom spatial image | python:3.10-slim-bookworm |
ghcr.io/mjanez/ckan-docker:2.10.5 |
From 2.10 images only Debian-based official Python images rather than Alpine-based images will be provided. |
| 2.11.x | custom spatial image | python:3.10-slim-bookworm |
ghcr.io/mjanez/ckan-docker:2.11.0 |
CKAN's latest official version. Only Debian-based official Python images. |
| master | custom spatial image | python:3.10-slim-bookworm |
ghcr.io/mjanez/ckan-docker:master |
Latest image available. Not for use in production. |
The non-CKAN images are as follows:
- PostgreSQL: Custom image based on official PostgreSQL image. Database files are stored in a named volume.
- Solr: Custom image based on official CKAN pre-configured Solr image. The index data is stored in a named volume and has a custom spatial schema upgrades. 2
- Redis: Standard Redis image
- NGINX: Latest stable nginx image that includes SSL and Non-SSL endpoints.
- ckan-pycsw: Custom image based on pycsw CKAN harvester ISO19139 for INSPIRE Metadata CSW Endpoint.
Optional HTTP Endpoint (samples/docker-compose/):
docker-compose.apache.yml&docker-compose.dev.apache.yml:- Apache HTTP Server: Custom image based on official latest stable httpd image. Configured to serve multiple routes for the ckan-pycsw CSW endpoint (
{CKAN_SITE_URL}/csw) and CKAN ({CKAN_SITE_URL}/catalog). Only HTTP.
- Apache HTTP Server: Custom image based on official latest stable httpd image. Configured to serve multiple routes for the ckan-pycsw CSW endpoint (
| Compose files | Repository | Type | Docker tag | Size | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
docker-compose.yml / docker-compose.apache.yml |
CKAN 2.10.5 | custom image | mjanez/ckan-docker:ckan-2.10.5 |
1.27 GB | Custom Dockerfile: ckan/Dockerfile |
docker-compose.yml / docker-compose.apache.yml |
PostgreSQL 15 | base image | postgres/postgres:15-alpine |
243 MB | Custom Dockerfile: postgresql/Dockerfile |
docker-compose.yml / docker-compose.apache.yml |
Solr 9 | custom image | ckan/ckan-solr:2.9-solr9-spatial |
584 MB | CKAN's pre-configured spatial Solr image. |
docker-compose.yml / docker-compose.apache.yml |
Redis 7 | base image | redis/redis:7-alpine |
41.2 MB | - |
docker-compose.yml |
NGINX stable | base image | nginx:stable-alpine |
43.2 MB | Custom Dockerfile: nginx/Dockerfile |
docker-compose.yml / docker-compose.apache.yml |
pycsw CKAN harvester ISO19139 | custom image | mjanez/ckan-pycsw:latest |
418 MB | Custom Dockerfile: ckan-pycsw/Dockerfile |
docker-compose.apache.yml |
Apache HTTP Server 2.4 | custom image | httpd/httpd:2.4 |
62.9 MB | Custom Dockerfile: apache/Dockerfile |
The site is configured using environment variables that you can set in the .env file for an NGINX and ckan-pycsw deployment (default .env.example), or replace it with the .env.apache.example for a Apache HTTP Server deployment using the Docker Compose file: docker-compose.apache.yml.
Information about extensions installed in the main image. More info described in the Extending the base images
Note
Switch branches to see the roadmap for other projects: ckan-docker/branches
| Element | Description | version | Status | DEV3 | PRO4 | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Core | CKAN | 2.10.5 | Stable | ✔️ | ✔️ | Stable installation for version 2.10.5 (Production & Dev images) via Docker Compose based on official images). Initial configuration, basic customisation and operation guide. |
| Core + | Datastore | 2.10.5 | Stable | ✔️ | ✔️ | Stable installation (Production & Dev images) via Docker Compose. |
| Core + | 0.0.19 | Deprecated | ❌ | ❌ | Updated to xloader, an express Loader - quickly load data into DataStore. | |
| Extension | ckanext-xloader | 1.0.1-stable | 🚧 WIP | ✔️ | ✔️ | Custom development from ckan/ckanext-xloader, a replacement for DataPusher because it offers ten times the speed and more robustness |
| Extension | ckanext-harvest | v1.5.6 | 🚧 WIP | ✔️ | ✔️ | Forked, remote harvest extension for CKAN to protect private harvest methods (API keys, DB logins, ...) |
| Extension | ckanext-geoview | 0.0.20 | Stable | ✔️ | ✔️ | Stable installation. |
| Extension | ckanext-spatial | v2.1.1 | Stable | ✔️ | ✔️ | Stable installation, required for implementing custom harvesters: (ckanext-schemingdcat/harvesters) |
| Extension | ckanext-dcat | v1.8.0 | 🚧 WIP | ✔️ | ✔️ | Latest stable version of vanilla ckanext-dcat with minor fixes, includes base DCAT-AP 2/3 profiles extended by ckanext-schemingdcat |
| Extension | ckanext-scheming | release-3.0.0 | Stable | ✔️ | ✔️ | Provides a way to configure and share metadata schemas using a YAML or JSON schema description. Custom validation and template snippets for editing and display are supported. |
| Extension | ckanext-resourcedictionary | v1.0.1 | 🚧 WIP | ✔️ | ✔️ | This extension extends the default CKAN Data Dictionary functionality by adding possibility to create data dictionary before actual data is uploaded to datastore. |
| Extension | ckanext-pages | v0.5.2 | Stable | ✔️ | ✔️ | This extension gives you an easy way to add simple pages to CKAN. |
| Extension | ckanext-pdfview | 0.0.8 | Stable | ✔️ | ✔️ | This extension provides a view plugin for PDF files using an html object tag. |
| Extension | ckanext-schemingdcat | 4.2.3 | 🚧 WIP | ✔️ | ✔️ | Custom development to provide functions and templates specifically designed to extend ckanext-scheming and ckanext-dcat. Customized ckanext schema5 and profiles based on the Spanish Metadata Core with the aim of completing the minimum metadata elements contained in the current datasets according to GeoDCAT-AP and INSPIRE. Also includes DCAT profile improvements and several enhancements like multilang for datasets, orgs and groups, themes, CLI, ... |
| Extension | ckanext-openapi | 1.0.0 | 🚧 WIP | ✔️ | ✔️ | Custom development to integrates and displays OpenAPI endpoints directly in the CKAN catalog. |
| Extension | ckanext-fluent | v1.0.1 | 🚧 WIP | ✔️ | ✔️ | Multilingual fields for CKAN, custom version with fixes and enhancements. |
| Software | ckan-pycsw | main | 🚧 WIP | ✔️ | ✔️ | PyCSW Endpoint of Open Data Portal with docker compose config. Harvest the CKAN catalogue in a CSW endpoint based on existing spatial datasets in the open data portal. |
All Docker Compose commands in this README will use the V2 version of Compose ie: docker compose. The older version (V1) used the docker-compose command. Please see Docker Compose for
more information.
Follow the installation instructions for your environment to install Docker Engine.
To verify a successful Docker installation, run docker run hello-world and docker version. These commands should output
versions for client and server.
Note
Learn more about Docker/Docker Compose basic commands.
Before starting the deployment, you'll need to set up a .env file. This file is crucial as it contains environment variables that the application needs to run properly. These variables include site urls, credentials, API keys, and other configuration details that should not be hard-coded into the application's source code for security reasons.
-
Clone project
cd /path/to/my/project git clone https://github.com/mjanez/ckan-docker.git & cd ckan-docker
-
Copy the
.env.exampletemplate (or use another from/samples/) and modify the resulting.envto suit your needs.cp .env.example .env
Adjust the
HTTP/HTTPSports as necessary:# Common proxy server for Apache or NGINX. PROXY_SERVER_HTTP_PORT_HOST=81 PROXY_SERVER_HTTPS_PORT_HOST=8443
Next, modify the variables related to the site URL or locations if needed. If you don't require
PROXY_SERVER_URL_PORT_HOST(e.g., if it's set to80) or you're using a domain without the NGINX deployment service, edit thePROXY_SERVER_URL, remove:${PROXY_SERVER_URL_PORT_HOST}or set it to your desired domain.Lines 43 to 50 in 39763db
Note
Please note that when accessing CKAN directly (via a browser) ie: not going through Apache/NGINX you will need to make sure you have "ckan" set up to be an alias to localhost in the local hosts file. Either that or you will need to change the .env entry for CKAN_SITE_URL
For more information about the `.env' file, see .env docs
Warning
Using the default values on the .env file will get you a working CKAN instance. There is a sysadmin user created by default with the values defined in CKAN_SYSADMIN_NAME and CKAN_SYSADMIN_PASSWORD (ckan_admin and test1234 by default). All envvars with API_TOKEN are automatically regenerated when CKAN is loaded, no editing is required.
This should be obviously changed before running this setup as a public CKAN instance.
You are now ready to proceed with deployment.
Use this if you are a maintainer and will not be making code changes to CKAN or to CKAN extensions.
- Build the images:
docker compose build
Note
You can use a deploy in 5 minutes if you just want to test the package.
- Start the containers:
docker compose up
This will start up the containers in the current window. By default the containers will log direct to this window with each container
using a different colour. You could also use the -d "detach mode" option ie: docker compose up -d if you wished to use the current
window for something else.
Note
- Or
docker compose up --buildto build & up the containers. - Or
docker compose -f ./samples/docker-compose/docker-compose.apache.yml up -d --buildto use the Apache HTTP Server version.
Note
Learn more about configuring this ckan docker:
At the end of the container start sequence there should be 6 containers running.
After this step, CKAN should be running at https://${PROXY_SERVER_URL}${PROXY_CKAN_LOCATION} and ckan-pycsw at https://{PROXY_SERVER_URL}/{PROXY_PYCSW_LOCATION}, i.e:
- https://localhost:8443/catalog or https://localhost:8443/csw
- http://localhost:81/catalog or http://localhost:81/csw
| CONTAINER ID | IMAGE | COMMAND | CREATED | STATUS | PORTS | NAMES |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0217537f717e | ckan-docker-nginx/ckan-docker-apache | /docker-entrypoint.… | 6 minutes ago | Up 4 minutes | 80/tcp,0.0.0.0:80->80/tcp,0.0.0.0:8443->443/tcp | ckan-docker-nginx-1/ckan-docker-apache-1 |
| 7b06ab2e060a | ckan-docker-ckan | /srv/app/start_ckan… | 6 minutes ago | Up 5 minutes (healthy) | 0.0.0.0:5000->5000/tcp | ckan-docker-ckan-1 |
| 1b8d9789c29a | redis:7-alpine | docker-entrypoint.s… | 6 minutes ago | Up 4 minutes (healthy) | 6379/tcp | ckan-docker-redis-1 |
| 7f162741254d | ckan/ckan-solr:2.9-solr9-spatial | docker-entrypoint.s… | 6 minutes ago | Up 4 minutes (healthy) | 8983/tcp | ckan-docker-solr-1 |
| 2cdd25cea0de | ckan-docker-db | docker-entrypoint.s… | 6 minutes ago | Up 4 minutes (healthy) | 5432/tcp | ckan-docker-db-1 |
| 9cdj25dae6gr | ckan-docker-pycsw | docker-entrypoint.s… | 6 minutes ago | Up 4 minutes (healthy) | 8000/tcp | ckan-docker-pycsw-1 |
If you just want to test the package and see the general functionality of the platform, you can use the ckan-docker image from the Github container registry:
# Edit the envvars in the .env as you like and start the containers.
docker compose -f docker-compose.ghcr.yml up -d --build Note
It will download the pre-built image and deploy all the containers. Remember to use your own domain by changing localhost in the .env file.
Select this mode when making modifications to CKAN code, either by developing new extensions or updating existing ones. This mode uses the .env configuration file to manage configuration options. For an example configuration, see samples/.env.dev.example.
To develop local extensions use the docker compose.dev.yml file:
To build the images:
bash docker compose -f docker-compose.dev.yml build
To start the containers:
bash docker compose -f docker-compose.dev.yml up
See CKAN images for more details of what happens when using development mode.
Tip
To enable the Flask tool console, you need to enable tool debugging mode. This is done by setting the tool logging level to DEBUG in the CKAN configuration file, ckan.ini. Here is the code snippet you need to add to your ckan.ini file:
[logger_werkzeug]
level = DEBUGYou can use the ckan extension instructions to create a CKAN extension, only executing the command inside the CKAN container and setting the mounted src/ folder as output:
docker compose -f docker-compose.dev.yml exec ckan-dev /bin/sh -c "ckan -c /srv/app/ckan.ini generate extension --output-dir /srv/app/src_extensions"Then, answer the prompts to configure the plugin:
Extension's name [must begin 'ckanext-']: ckanext-newextension
Author's name []: Joe Bloggs
Author's email []: [email protected]
Your Github user or organization name []: joebloggs
Brief description of the project []: test creating a new extension
List of keywords (separated by spaces) [CKAN]: ckanext-newextension
Do you want to include code examples? [y/N]: y
Written: /srv/app/src_extensions/ckanext-newextensionThe new extension files and directories are created in the /srv/app/src_extensions/ folder in the running container. They will also exist in the local src/ directory as local /src directory is mounted as /srv/app/src_extensions/ on the ckan container. You might need to change the owner of its folder to have the appropiate permissions.
Sometimes is useful to run your local development instance under HTTPS, for instance if you are using authentication extensions like ckanext-saml2auth. To enable it, set the following in your .env file:
USE_HTTPS_FOR_DEV=True
## ckan-pycsw unverified mode (True/False). SSL certificate from host will download if SSL_UNVERIFIED_MODE=True, to avoid SSL error when certificate was self-signed.
SSL_UNVERIFIED_MODE=Trueand update the site URL setting:
CKAN_SITE_URL=https://localhost:5000After recreating the ckan-dev container, you should be able to access CKAN at https://localhost:5000
The Docker image config files used to build your CKAN project are located in the ckan/ folder. There are two Docker files:
-
Dockerfile: this is based onmjanez/ckan-base-spatial:<version>, a base image located in the Github Package Registry, that has CKAN installed along with all its dependencies, properly configured and running on uWSGI (production setup) -
Dockerfile.dev: this is based onmjanez/ckan-base-spatial:<version>-devalso located located in the Github Package Registry, and extendsmjanez/ckan-base-spatial:<version>to include:- Any extension cloned on the
./srcfolder will be installed in the CKAN container when booting up Docker Compose (docker compose -f docker-compose.dev.yml up). This includes installing any requirements listed in arequirements.txt(orpip-requirements.txt) file and runningpython setup.py develop. You can clone all the extensions explained insrc/READMEwith their tag, reqs and autocrlf using a bash script. - CKAN is started running this:
/usr/bin/ckan -c /srv/app/ckan.ini run -H 0.0.0.0. - Make sure to add the local plugins to the
CKAN__PLUGINSenv var in the.envfile.
- Any extension cloned on the
-
Any custom changes to the scripts run during container start up can be made to scripts in the
setup/directory. For instance if you wanted to change the port on which CKAN runs you would need to make changes to the Docker Compose yaml file, and thestart_ckan.sh.overridefile. Then you would need to add the following line to the Dockerfile ie:COPY setup/start_ckan.sh.override ${APP_DIR}/start_ckan.sh. Thestart_ckan.shfile in the locally built image would override thestart_ckan.shfile included in the base image
Tip
If you get an error like doesn't have execute permissions:
Daemon error response: failed to create shim task: OCI runtime create failed: runc create failed: unable to start container process: exec: "/srv/app/start_ckan.sh": permission denied: unknown
It may be necessary to give execute permissions to the file in the Dockerfile:
...
# Override start_ckan.sh
COPY setup/start_ckan.sh.override ${APP_DIR}/start_ckan.sh
RUN chmod +x ${APP_DIR}/start_ckan.sh
...You can modify the docker files to build your own customized image tailored to your project, installing any extensions and extra requirements needed. For example here is where you would update to use a different CKAN base image ie: ckan/ckan-base-spatial:<new version>
To perform extra initialization steps you can add scripts to your custom images and copy them to the /docker-entrypoint.d folder (The folder should be created for you when you build the image). Any *.sh and *.py file in that folder will be executed just after the main initialization script (prerun.py) is executed and just before the web server and supervisor processes are started.
For instance, consider the following custom image:
ckan
├── docker-entrypoint.d
│ └── setup_validation.sh
├── Dockerfile
└── Dockerfile.devWe want to install an extension like ckanext-validation that needs to create database tables on startup time. We create a setup_validation.sh script in a docker-entrypoint.d folder with the necessary commands:
#!/bin/bash
# Create DB tables if not there
ckan -c /srv/app/ckan.ini validation init-db And then in our Dockerfile.dev file we install the extension and copy the initialization scripts:
FROM ckan/ckan-base-spatial:2.10.5
RUN pip install -e git+https://github.com/frictionlessdata/ckanext-validation.git#egg=ckanext-validation && \
pip install -r https://raw.githubusercontent.com/frictionlessdata/ckanext-validation/master/requirements.txt
COPY docker-entrypoint.d/* /docker-entrypoint.d/Tip
There are a number of extension examples commented out in the Dockerfile.dev file
When building your project specific CKAN images (the ones defined in the ckan/ folder), you can apply patches
to CKAN core or any of the built extensions. To do so create a folder inside ckan/patches with the name of the
package to patch (ie ckan or ckanext-??). Inside you can place patch files that will be applied when building
the images. The patches will be applied in alphabetical order, so you can prefix them sequentially if necessary.
For instance, check the following example image folder:
ckan
├── patches
│ ├── ckan
│ │ ├── 01_datasets_per_page.patch
│ │ ├── 02_groups_per_page.patch
│ │ ├── 03_or_filters.patch
│ └── ckanext-harvest
│ └── 01_resubmit_objects.patch
├── setup
├── Dockerfile
└── Dockerfile.devNote
Git diff is a command to output the changes between two sources inside the Git repository. The data sources can be two different branches, commits, files, etc.
- Show changes between working directory and staging area:
git diff > [file.patch] - Shows any changes between the staging area and the repository:
git diff --staged [file]
To apply patches in development mode, you would need to follow these steps:
-
Ensure that your patches are placed in the
ckan/patchesdirectory. The patches should be organized into subdirectories named after the package they are intended to patch (e.g.,ckanorckanext-??). Each patch file should end with the .patch extension.For example, your directory structure might look like this:
ckan ├── patches │ ├── ckan │ │ ├── 01_datasets_per_page.patch │ │ ├── 02_groups_per_page.patch │ │ ├── 03_or_filters.patch │ └── ckanext-harvest │ └── 01_resubmit_objects.patch ├── setup ├── Dockerfile └── Dockerfile.dev
-
Navigate to the
/srcdirectory. -
Apply the patches using the patch command:
find /path/to/ckan/patches -name '*.patch' -exec patch -p1 < {} \;
This command will recursively search the
/path/to/ckan/patchesdirectory for files ending with.patchand apply them using the patch command. Replace/path/to/ckan/patcheswith the actual path to yourckan/patchesdirectory.
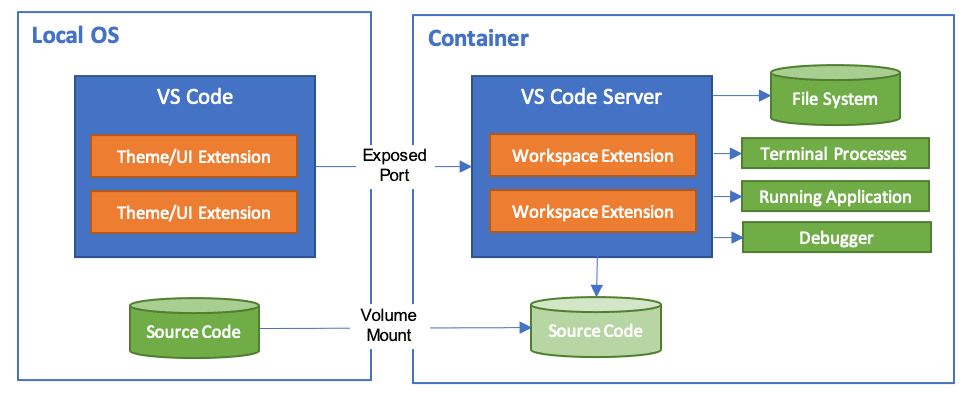
The Visual Studio Code Dev Containers extension is a powerful tool that enables developers to use a container as a complete development environment. With this extension, developers can open any folder inside a container and take advantage of the full range of features provided by Visual Studio Code. To do this, developers create a devcontainer.json file in their project that specifies how to access or create a development container with a predefined tool and runtime stack. This allows developers to work in an isolated environment, ensuring that the development environment is consistent across team members and that project dependencies are easy to manage.
To set this up:
-
Install VSCode.
-
Install the Remote Development extension for VSCode.
-
In your project directory, create a
devcontainer.jsonfile. This file will contain the configuration for your development container. -
In the
devcontainer.jsonfile, specify the Docker image for your development container and any additional configuration settings, such as environment variables, ports to expose, and startup commands. -
Enable
debugpyfor your development instance in your.envfile:
USE_DEBUGPY_FOR_DEV=true-
Start the containers in development mode and launch VS Code.
-
Install the "Dev Container" extension: press
CTRL+SHIFT+X, type "dev container", click "install". -
Click the
Open a Remote Windowbutton in the bottom-left of the VS Code window. -
Click
Attach to Running Container...and select your ckan-dev container, e.g.ckan-docker-ckan-dev-1. -
Click the
Run and Debugicon on the left panel thencreate a launch.json, selectPython Debugger,Remote Attach, hostlocalhostand port5678. -
Press
F5or click theRunmenu andStart Debugging.
You can now set breakpoints and remote debug your CKAN development instance using VSCode Dev Containers and debugpy.
Add these lines to the ckan-dev service in the docker compose.dev.yml file
stdin_open: true
tty: trueDebug with pdb (example) - Interact with docker attach $(docker container ls -qf name=ckan)
command: python -m pdb /usr/lib/ckan/venv/bin/ckan --config /srv/app/ckan.ini run --host 0.0.0.0 --passthrough-errors
The default Docker Compose configuration (docker-compose.yml) uses an NGINX image as the front-end (ie: reverse proxy). It includes HTTPS running on port number 8443 and an HTTP port (81). A "self-signed" SSL certificate is generated beforehand and the server certificate and key files are included. The NGINX server_name (ENV: PROXY_SERVER_NAME) directive and the CN field in the SSL certificate have been both set to 'localhost'. This should obviously not be used for production.
The proxy locations, ports and other NGINX options can be modified in the .env file:
# Host Ports
NGINX_PORT_HOST=81
NGINX_SSLPORT_HOST=8443
# NGINX
NGINX_PORT=80
NGINX_SSLPORT=443
NGINX_LOG_DIR=/var/log/nginx
# Check CKAN__ROOT_PATH and CKANEXT__DCAT__BASE_URI. If you don't need to use domain locations, it is better to use the nginx configuration. Leave blank or use the root `/`.
PROXY_SERVER_NAME=localhost
PROXY_CKAN_LOCATION=/catalog
PROXY_PYCSW_LOCATION=/cswThe base Docker Compose configuration uses an NGINX image as the front-end (ie: reverse proxy). It includes HTTPS running on port number 8443. A "self-signed" SSL certificate is generated as part of the ENTRYPOINT. The ENV PROXY_SERVER_NAME, NGINX server_name directive and the CN field in the SSL certificate have been both set to 'localhost'. This should obviously not be used for production.
Creating the SSL cert and key files as follows:
openssl req -new -newkey rsa:4096 -days 365 -nodes -x509 -subj "/C=DE/ST=Berlin/L=Berlin/O=None/CN=localhost" -keyout ckan-local.key -out ckan-local.crt
The ckan-local.* files will then need to be moved into the nginx/setup/ directory
The Docker Compose configuration (docker-compose.apache.yml) uses an httpd image as the front-end. It has two routes for the ckan (default location: /catalog) and ckan-pycsw (default location: /csw) services.
The proxy locations, ports and other Apache Web Server options can be modified in the .env file:
# Host Ports
APACHE_PORT_HOST=81
# Apache HTTP Server
APACHE_VERSION=2.4-alpine
APACHE_PORT=80
APACHE_LOG_DIR=/var/log/apache
# Check CKAN__ROOT_PATH and CKANEXT__DCAT__BASE_URI. If you don't need to use domain locations, it is better to use the nginx configuration. Leave blank or use the root `/`.
PROXY_SERVER_NAME=localhost
PROXY_CKAN_LOCATION=/catalog
PROXY_PYCSW_LOCATION=/cswThe ckanext-envvars extension is used in the CKAN Docker base repo to build the base images. This extension checks for environmental variables conforming to an expected format and updates the corresponding CKAN config settings with its value.
For the extension to correctly identify which env var keys map to the format used for the config object, env var keys should be formatted in the following way:
All uppercase
Replace periods ('.') with two underscores ('__')
Keys must begin with 'CKAN' or 'CKANEXT', if they do not you can prepend them with 'CKAN___'
For example:
CKAN__PLUGINS="envvars image_view text_view recline_view datastore datapusher"CKAN__DATAPUSHER__CALLBACK_URL_BASE=http://ckan:5000CKAN___BEAKER__SESSION__SECRET=CHANGE_ME
These parameters can be added to the .env file
For more information please see ckanext-envvars
Warning
When deploying under a proxy, such as in a corporate environment, to avoid errors when resolving urls with container_names/hostnames associated with the container on internal networks, use the no_proxy' variable, in lower case, with the names of the services/containers, the IP of the Docker network, etc. e.g: no_proxy="127.0.0.1,192.168.192.0/23,172.0.0.0/0,redis,solr,${DB_CONTAINER_NAME}"`
The Datastore database and user is created as part of the entrypoint scripts for the db container.
This deployment replaces DataPusher with XLoader using Supervisor, more info about other alternatives on the wiki page for this: https://github.com/ckan/ckan-docker/wiki/Replacing-DataPusher-with-XLoader
ckan-pycsw is a docker compose environment (based on pycsw) for development and testing with CKAN Open Data portals.5
Available components:
- pycsw: The pycsw app. An OARec and OGC CSW server implementation written in Python.
- ckan2pycsw: Software to achieve interoperability with the open data portals based on CKAN. To do this, ckan2pycsw reads data from an instance using the CKAN API, generates ISO-19115/ISO-19139 metadata using pygeometa, or a custom schema that is based on a customized CKAN schema, and populates a pycsw instance that exposes the metadata using CSW and OAI-PMH.
ckanext-harvest supervisor allows you to harvest metadata from multiple sources on a production deployment. Here it is deployed by a worker consumers in the ckan container, also the ckanext-harvest extension and other custom harvesters (ckanext-schemingdcat or ckanext-dcat) are included in the CKAN docker images.
![TIP] To enable harvesters you need to set up in the
.envfile theCKAN__PLUGINSvariable with theharvestplugin:Lines 126 to 127 in a18e0c8
PostgreSQL offers the command line tools pg_dump and pg_restore for dumping and restoring a database and its content to/from a file.
-
Create a new file called
ckan_backup_custom.shand open it in your preferred text editor. -
Add the following code to the script, replacing the placeholders with your
.envvalues:#!/bin/bash # Set the necessary variables DB_CONTAINER_NAME="ckan-docker-db-1" CKAN_DB="ckandb" POSTGRES_USER="postgres" POSTGRES_PASSWORD="your_postgres_password" BACKUP_DIRECTORY="/path/to/your/backup/directory" DATE=$(date +%Y%m%d%H%M%S) MONTH=$(date +%m) YEAR=$(date +%Y) # Create the monthly backup directory if it doesn't exist mkdir -p "$BACKUP_DIRECTORY/monthly/$YEAR-$MONTH" # Run the backup command docker exec -e PGPASSWORD=$POSTGRES_PASSWORD $DB_CONTAINER_NAME pg_dump -U $POSTGRES_USER -Fc $CKAN_DB > "$BACKUP_DIRECTORY/monthly/$YEAR-$MONTH/ckan_backup_$DATE.dump" # Compress the dump files into a zip archive cd "$BACKUP_DIRECTORY/monthly/$YEAR-$MONTH" || exit zip "backup_${YEAR}-${MONTH}.zip" *.dump # Remove the original dump files rm -f *.dump
-
Replace the following placeholders with your actual values:
your_postgres_password: The password for the PostgreSQL user./path/to/your/backup/directory: The path to the directory where you want to store the backup files.
Warning
If you have changed the values of the PostgreSQL container, database or user, change them too.
Check that zip package is installed: sudo apt-get install zip
-
Save and close the file.
-
Make the script executable:
chmod +x ckan_backup_custom.sh
-
Open the crontab for the current user:
crontab -e
-
Add the following line to schedule the backup to run daily at midnight (adjust the schedule as needed):
0 0 * * * /path/to/your/script/ckan_backup_custom.sh
Note
Replace /path/to/your/script with the actual path to the ckan_backup_custom.sh script.
- Save and close the file.
The cronjob is now set up and will backup your CKAN PostgreSQL database daily at midnight using the custom format. The backups will be stored in the specified directory with the timestamp in the filename.
Note
Sample scripts for backing up CKAN: doc/scripts
If need to use a backup, restore it:
-
First clean the database. Caution, this will delete all data from your CKAN database!
docker exec -it ckan /bin/bash -c "export TERM=xterm; exec bash" # Delete everything in the CKAN database, including the tables, to start from scratch ckan -c $CKAN_INI db clean
-
After cleaning the database you must do either initialize it or import a previously created dump.
docker exec -i -e PGPASSWORD=$POSTGRES_PASSWORD $DB_CONTAINER_NAME pg_restore -U $POSTGRES_USER --clean --if-exists -d $CKAN_DB < /path/to/your/backup/directory/ckan.dump
-
Restart the
ckancontainer.
To perform a backup, follow these steps:
-
Replicate the
ckancoredocker exec -it <container_id> bash -c "curl http://localhost:8983/solr/ckan/replication?command=backup&wt=json"
Replace
<container_id>with the id of yoursolr-1container. -
In the container, navigate to the Solr data directory:
docker exec -it <container_id> bash
solr@12d91jdkas:/opt/solr-9.7.0$ cd /var/solr/data/ckan/
# Backup data (e.g. snapshot.20241015102836306)
solr@12d91jdkas:/var/solr/data/ckan$ tar -czvf /tmp/snapshots_backup.tgz data/snapshot.20241015102836306
# Backup conf
tar -czvf /tmp/conf_backup.tgz conf- Export it to the host
docker cp <container_id>:/tmp/snapshots_backup.tgz ./snapshots_backup.tgz
docker cp <container_id>:/tmp/conf_backup.tgz ./conf_backup.tgz-
Create a new user directly by a sysadmin in the
{ckan_site_url}/user/registerendpoint -
Create new user accounts via the API
user_create -
Create a new user from the Docker host, for example to create a new user called
user_exampledocker exec -it <container-id> ckan -c ckan.ini user add user_example email=user_example@localhost # Admin user docker exec -it <container-id> ckan -c ckan.ini sysadmin add admin_example email=admin_example@localhost name=admin_example
To delete the 'user_example' user
docker exec -it <container-id> ckan -c ckan.ini user remove user_example`
-
Create a new user from within the ckan container. You will need to get a session on the running container
ckan -c ckan.ini user add user_example email=user_example@localhost`To delete the 'user_example' user
ckan -c ckan.ini user remove user_example`
For more information about Docker and Docker Compose's basic commands and post-installation procedures, see Docker/Docker Compose Info
To have Docker Compose run automatically when you reboot a machine, you can follow the steps below:
-
Create a systemd service file for Docker Compose. You can create a file named
ckan-docker-compose.servicein the/etc/systemd/system/folder with the following content:[Unit] Description=CKAN Docker Compose Application Service Requires=docker.service After=docker.service [Service] User=docker Group=docker Type=oneshot RemainAfterExit=yes WorkingDirectory=/path/to/project/ckan-docker/ ExecStart=/bin/docker compose up -d ExecStop=/bin/docker compose down TimeoutStartSec=0 [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
-
Replace
/path/to/project/ckan-docker/with the path where your project'sdocker-compose.ymlfile is located and and check the path to the docker compose binary on execution and stop:/bin/docker. Also change theUser/Groupto execute the service. -
Load the systemd service file with the following command:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
-
Enables the service to start automatically when the machine boots up:
sudo systemctl enable ckan-docker-compose -
You can now start the service with the following command:
sudo systemctl start ckan-docker-compose
-
If you want to stop or check the status of the service, use the following commands:
# Stop the service sudo systemctl stop ckan-docker-compose # Check the status sudo systemctl status ckan-docker-compose
To prevent bots and crawlers from overloading your CKAN API and causing service disruptions, it is essential to properly configure the robots.txt file in the root directory of your server. This file provides instructions to web crawlers about which parts of your site they are allowed to access and crawl.
-
Create or Edit
nginx/setup/robots.txtin the Root Directory: Ensure that therobots.txtfile is located in the root directory of your server. This is crucial because bots typically look for this file at the root level. -
Disallow Specific Bots: To prevent specific bots, such as the SEMrushBot, from crawling certain parts of your site, add the following lines to your
robots.txtfile:User-agent: SemrushBot Disallow: /catalogo
-
Set Crawl Delay: To reduce the load on your server, you can set a crawl delay for bots. This instructs the bot to wait a specified number of seconds between requests. For example, to set a 10-second delay for SEMrushBot, add:
User-agent: SemrushBot Crawl-delay: 10
-
General Disallow Rules: You can also add general rules to disallow all bots from accessing specific directories or files. For example:
User-agent: * Disallow: /catalog/ Disallow: /csw/ -
Example
robots.txtFile: Here is an example of a completerobots.txtfile that includes the above configurations:# Disallow SEMrushBot from accessing the /catalogo directory User-agent: SemrushBot Disallow: /catalogo Crawl-delay: 10 # General disallow rules for all bots User-agent: * Disallow: /private/ Disallow: /tmp/
-
Verify
robots.txtConfiguration: After updating therobots.txtfile, verify that it is correctly configured by accessing it via your browser. For example, navigate tohttps://{ckan_site_url}/robots.txtand ensure that the rules are as expected. -
Monitor Bot Activity: Continuously monitor your server logs to ensure that bots are adhering to the rules specified in the
robots.txtfile. If you notice any bots ignoring the rules, you may need to take additional measures, such as blocking their IP addresses.
Note
params: Parameters to pass to the action function. The parameters are specific to each action function.
-
fl(text): Fields of the dataset to return. The parameter controls which fields are returned in the solr query.flcan beNoneor a list of result fields, such as:id,name,extras_custom_schema_field.Example: All datasets with the fields
id,name,titleand a custom schema fieldextras_inspire_id:{ckan-instance}/api/3/action/package_search?fl=id,name,title,extras_inspire_id -
fq(text): Any filter queries to apply. Example: All datasets that have tageconomy: http://demo.ckan.org/api/3/action/package_search?fq=tags:economy -
rows(int): The maximum number of matching rows (datasets) to return. (optional, default:10, upper limit:1000unless set in site’s configurationckan.search.rows_max)
More info: CKAN API Documentation and data.gov.uk
Request: {ckan-instance}/api/3/action/package_search?fl=id,extras_publisher_name
Response:
{
"help": "{ckan-instance}/api/3/action/help_show?name=package_search",
"success": true,
"result": {
"count": 32,
"facets": {},
"results": [
{
"id": "e4a607d0-0875-4043-b8c7-36f731ba5ca8",
"publisher_name": "Example publisher"
},
{
"id": "5319a6b3-f439-4f53-9732-71699b9f62c8",
"publisher_name": "Example publisher"
},
{
"id": "02a30269-7665-4f6a-a43d-c288003f5cbb",
"publisher_name": "Example publisher"
}
],
"sort": "score desc, metadata_modified desc",
"search_facets": {}
}
}Request: {ckan-instance}/api/3/action/package_search?fq=organization:iepnb&fl=id,name,extras_alternate_identifier&rows=100
Response:
{
"help": "{ckan-instance}/api/3/action/help_show?name=package_search",
"success": true,
"result": {
"count": 56,
"facets": {},
"results": [
{
"id": "fe757d64-436c-482d-b65b-f24348139fd6",
"name": "example_dataset_1",
"alternate_identifier": "IDEXAMPLEDATASET1"
},
{
"id": "fc21c1a5-4c02-4157-9d2f-9a2cd200f908",
"name": "example_dataset_2",
"alternate_identifier": "IDEXAMPLEDATASET2"
},
{
"id": "fb326c11-18d4-4ee1-aa23-a40cb90cf8d8",
"name": "example_dataset_3",
"alternate_identifier": "IDEXAMPLEDATASET3"
}
],
"sort": "score desc, metadata_modified desc",
"search_facets": {}
}
}Request: {ckan-instance}/api/3/action/package_search?q=name:"spa_example_dataset_1_2023"
Response:
{
"help": "https://demo.ckan.org/api/3/action/help_show?name=package_search",
"success": true,
"result": {
"count": 1,
"facets": {},
"results": [
{
"author": "Test Author",
"author_email": "[email protected]",
"creator_user_id": "47c7f1b1-0ef5-4d7b-b43c-811c51c9e349",
"id": "c322307a-b871-44fe-a602-32ee8437ff04",
"isopen": true,
"license_id": "cc-by",
"license_title": "Creative Commons Attribution",
"license_url": "http://www.opendefinition.org/licenses/cc-by",
"maintainer": "Test Maintainer",
"maintainer_email": "[email protected]",
"metadata_created": "2021-04-09T11:39:37.657233",
"metadata_modified": "2022-05-20T09:20:43.998956",
"name": "sample-dataset-1",
"notes": "A CKAN Dataset is a collection of data resources (such as files), together with a description and other information (what is known as metadata), at a fixed URL. \r\n\r\n",
"num_resources": 9,
"num_tags": 8,
"organization": {
"id": "1fa89238-ee96-4439-a885-22d15244d070",
"name": "sample-organization",
"title": "Sample Organization",
"type": "organization",
"description": "This is a sample organization.",
"image_url": "2022-05-20-084702.929838siurana.jpg",
"created": "2021-04-09T14:27:17.753798",
"is_organization": true,
"approval_status": "approved",
"state": "active"
},
"owner_org": "1fa89238-ee96-4439-a885-22d15244d070",
"private": false,
"state": "active",
"title": "Sample Dataset",
"type": "dataset",
"url": "",
"version": "1.0",
"groups": [
{
"description": "",
"display_name": "Test Group",
"id": "5d423f6b-137e-4d15-a156-868763fa7a64",
"image_display_url": "https://demo.ckan.org/uploads/group/2021-04-21-153504.571229064c7c.png",
"name": "test-group",
"title": "Test Group"
}
],
"resources": [
{
"cache_last_updated": null,
"cache_url": null,
"created": "2021-04-09T14:31:09.032858",
"datastore_active": true,
"description": "This is a sample resource added via url.",
"format": "CSV",
"hash": "",
"id": "e687245d-7835-44b0-8ed3-0827de123895",
"last_modified": null,
"metadata_modified": "2021-04-09T14:31:09.021596",
"mimetype": "text/csv",
"mimetype_inner": null,
"name": "sample-linked.csv",
"package_id": "c322307a-b871-44fe-a602-32ee8437ff04",
"position": 0,
"resource_type": null,
"size": null,
"state": "active",
"url": "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/datopian/CKAN_Demo_Datasets/main/resources/org1_sample.csv",
"url_type": null
},
{
"cache_last_updated": null,
"cache_url": null,
"created": "2021-04-09T14:31:45.092631",
"datastore_active": true,
"description": "Sample csv (uploaded).",
"format": "CSV",
"hash": "",
"id": "b53c9e72-6b59-4cda-8c0c-7d6a51dad12a",
"last_modified": "2021-04-09T16:13:57.353205",
"metadata_modified": "2021-04-09T16:13:57.367140",
"mimetype": "application/csv",
"mimetype_inner": null,
"name": "sample.csv",
"package_id": "c322307a-b871-44fe-a602-32ee8437ff04",
"position": 1,
"resource_type": null,
"size": 6731,
"state": "active",
"url": "https://demo.ckan.org/dataset/c322307a-b871-44fe-a602-32ee8437ff04/resource/b53c9e72-6b59-4cda-8c0c-7d6a51dad12a/download/sample.csv",
"url_type": "upload"
}
],
"tags": [
{
"display_name": "csv",
"id": "b5e651dd-8f42-445c-b9c4-2f09a3268427",
"name": "csv",
"state": "active",
"vocabulary_id": null
},
{
"display_name": "economy",
"id": "0c4f9ad5-a372-4bda-a59b-e560cf264b0f",
"name": "economy",
"state": "active",
"vocabulary_id": null
}
],
"extras": [],
"relationships_as_subject": [],
"relationships_as_object": []
}
],
"sort": "score desc, metadata_modified desc",
"search_facets": {}
}
}
This material is copyright (c) 2006-2023 Open Knowledge Foundation and contributors.
It is open and licensed under the GNU Affero General Public License (AGPL) v3.0 whose full text may be found at:
http://www.fsf.org/licensing/licenses/agpl-3.0.html
Footnotes
-
Official CKAN repo: https://github.com/ckan/ckan-docker-base ↩
-
Contains fields needed for the ckanext-spatial geo search ↩
-
Development environment, check the
src/README↩ -
Production environment, check the
ckan/Dockerfile↩ -
ckan_geodcatap, more info: https://github.com/mjanez/ckanext-scheming/pull/1 ↩ ↩2