- 객체를 특정 클래스에 결합하지 않고 복제할 수 있게 하는 생성 디자인 패턴
- 동일한 타입의 새로운 객체를 필요에 따라 생성
- 어떤 클래스의 인스턴스를 만드는 것이 복잡하거나 자원/시간이 많이 소요되는 경우
- 외부에선 객체를 완전히 알 수 없다 - 객체가 private 필드를 가지면 완벽한 복사본을 만들 수 없을 수 있음
- 객체를 복사하려면 객체의 클래스를 알아야 하기 때문에, 클래스에 의존하게 됨
- 기존 인스턴스를 복사해서 새로운 인스턴스를 만들기
- 클라이언트 코드가 어떤 클래스의 인스턴스를 만드는지 몰라도 인스턴스를 만들 수 있음
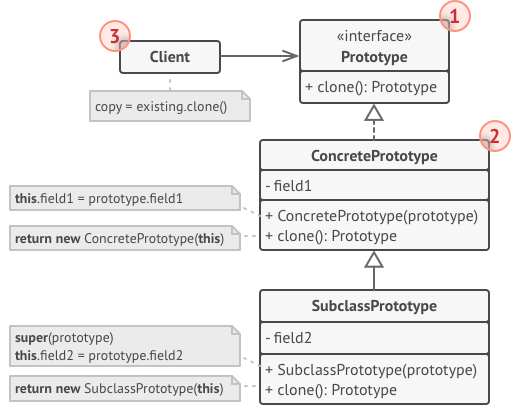
- 복제 대상 객체에 복제 프로세스를 위임. 이 객체를 프로토타입이라고 부름
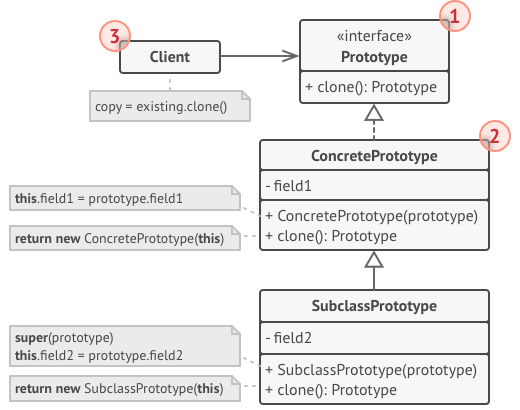
- 프로토타입: 복제 메서드 선언 (clone)
- ⇒ 클라이언트 코드는 Prototype.clone 인터페이스만 알면 객체의 구상 클래스를 몰라도 복제할 수 있다
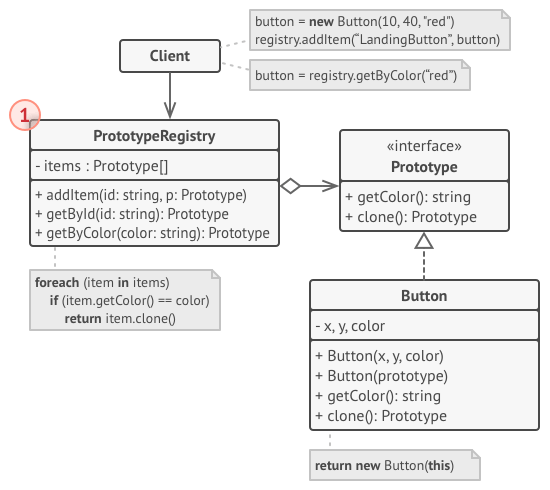
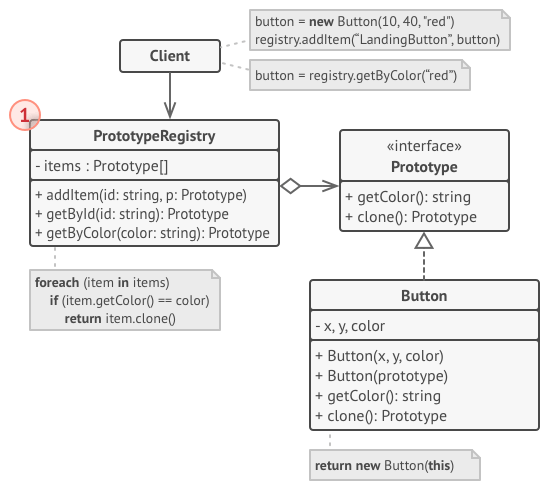
- 프로토타입 레지스트리: 자주 사용하는 프로토타입에 쉽게 접근할 수 있게 제공
as-is
const tree = new Composite();
const branch1 = new Composite();
branch1.add(new Leaf());
branch1.add(new Leaf());
tree.add(branch1);
const branch2 = new Composite();
branch2.add(new Leaf());
tree.add(branch2);
// tree를 똑같이 복사하려면 ??
const clonedTree = new Composite();
// children이 private이라 알 수 없다..
// 생성한 그대로 기억했다가 재생성..?
const clonedBranch1 = new Composite();
clonedBranch1.add(new Leaf());
clonedBranch1.add(new Leaf());
clonedTree.add(clonedBranch1);
const clonedBranch2 = new Composite();
clonedBranch2.add(new Leaf());
clonedTree.add(clonedBranch2);
to-be
abstract class Component {
/** ... **/
public abstract clone(): Component;
}
export class Composite extends Component {
private children: Set<Component> = new Set<Component>();
/** ... **/
public override clone(): Composite {
const clone = new Composite();
this.children.forEach((child) => {
clone.add(child.clone());
});
return clone;
}
}
export class Leaf extends Component {
/** ... **/
public override clone(): Leaf {
const clone = new Leaf();
clone.setParent(this.parent);
return clone;
}
}
// 클라이언트 코드
const tree = new Composite();
const branch1 = new Composite();
branch1.add(new Leaf());
branch1.add(new Leaf());
tree.add(branch1);
const branch2 = new Composite();
branch2.add(new Leaf());
tree.add(branch2);
const clonedTree = tree.clone();
- 클라이언트에서 인스턴스 생성 과정을 몰라도 된다
- 클라이언트가 구체적인 형식을 몰라도 객체를 생성할 수 있다
- 객체를 새로 생성하는 것보다 복사하는 것이 효율적일 수 있다
- 상속 대신 사용 - 일부 설정이 공통되는 자식 클래스를 만드는 대신, 프로토타입을 사용해 복제하게 할 수 있다
- 객체를 복사하는 것이 복잡한 경우가 있을 수 있다 (순환 참조 등)
- 데코레이터, 복합체 등 복잡한 구조를 만들어야 할 때 다시 생성하는 대신 프로토타입을 통해 복제할 수 있음
- 커맨드 패턴의 복사본을 저장해야 할 때 유용
public class Circle implements Cloneable {
private double radius;
public Circle(double radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
public void setRadius(double radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
public double getRadius() {
return radius;
}
@Override
public Circle clone() {
try {
return (Circle) super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
throw new AssertionError();
}
}
}
Cloneable 인터페이스에는 메서드가 선언되어 있지 않지만, 이 인터페이스를 구현하지 않은 클래스에서 clone()을 사용하려고 하면 CloneNotSupportedException 발생Object.clone() 메서드는 얕은 복사를 수행
- 스프링 빈은 일반적으로 싱글톤 빈
- 프로토타입 스코프로 지정하면, 빈 요청이 있을 때마다 새로운 객체가 생성됨
- 자바스크립트는 '클래스'라는 추상화된 패턴/설계가 전혀 없고 객체만 존재, 객체는 자신의 동작을 스스로 정의
- 클래스 지향 언어 => 한 클래스를 다중 복사(인스턴스화). 클래스 작동 계획을 실제 객체로 복사
- 프로토타입 기반 언어 => 복사 과정이 없음. 객체 생성 후 프로토타입 객체와
[[Prototype]] 프로퍼티를 통해 연결될 뿐
- => 객체 생성 시 프로퍼티를 복사하지 않음. 대신, 두 객체의 링크를 걸고 다른 쪽의 프로퍼티/함수에 접근 가능하게 위임
const Car = function (model, year, miles) {
this.model = model;
this.year = year;
this.miles = miles;
this.wheelCount = 4;
};
Car.prototype.go = function () {
console.log('vroom');
};
Car.prototype.break = function () {
console.log('screech');
};
// 1. 생성자를 이용해 객체 생성하기
const myCar = new Car('ford', 2014, 50000);
console.log(myCar.wheelCount) // 4
myCar.go(); // vroom
// 2. Object.create를 이용해 객체 생성하기
const clonedCar = Object.create(myCar);