| comments | difficulty | edit_url | rating | source | tags | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
中等 |
1837 |
第 33 场双周赛 Q4 |
|
给你一个二维字符网格数组 grid ,大小为 m x n ,你需要检查 grid 中是否存在 相同值 形成的环。
一个环是一条开始和结束于同一个格子的长度 大于等于 4 的路径。对于一个给定的格子,你可以移动到它上、下、左、右四个方向相邻的格子之一,可以移动的前提是这两个格子有 相同的值 。
同时,你也不能回到上一次移动时所在的格子。比方说,环 (1, 1) -> (1, 2) -> (1, 1) 是不合法的,因为从 (1, 2) 移动到 (1, 1) 回到了上一次移动时的格子。
如果 grid 中有相同值形成的环,请你返回 true ,否则返回 false 。
示例 1:
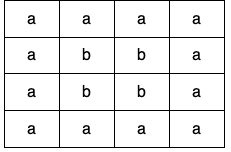
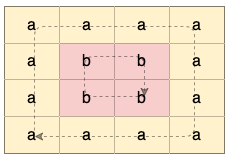
输入:grid = [["a","a","a","a"],["a","b","b","a"],["a","b","b","a"],["a","a","a","a"]] 输出:true 解释:如下图所示,有 2 个用不同颜色标出来的环:
示例 2:
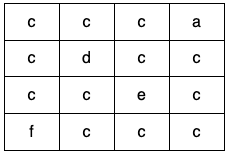
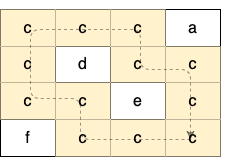
输入:grid = [["c","c","c","a"],["c","d","c","c"],["c","c","e","c"],["f","c","c","c"]] 输出:true 解释:如下图所示,只有高亮所示的一个合法环: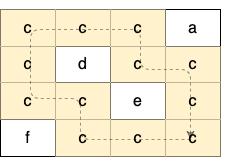
示例 3:
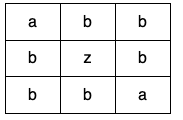
输入:grid = [["a","b","b"],["b","z","b"],["b","b","a"]] 输出:false
提示:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m <= 5001 <= n <= 500grid只包含小写英文字母。
我们可以遍历二维网格中的每一个格子,对于每一个格子,如果格子
时间复杂度
class Solution:
def containsCycle(self, grid: List[List[str]]) -> bool:
m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])
vis = [[False] * n for _ in range(m)]
dirs = (-1, 0, 1, 0, -1)
for i, row in enumerate(grid):
for j, x in enumerate(row):
if vis[i][j]:
continue
vis[i][j] = True
q = [(i, j, -1, -1)]
while q:
x, y, px, py = q.pop()
for dx, dy in pairwise(dirs):
nx, ny = x + dx, y + dy
if 0 <= nx < m and 0 <= ny < n:
if grid[nx][ny] != grid[i][j] or (nx == px and ny == py):
continue
if vis[nx][ny]:
return True
vis[nx][ny] = True
q.append((nx, ny, x, y))
return Falseclass Solution {
public boolean containsCycle(char[][] grid) {
int m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length;
boolean[][] vis = new boolean[m][n];
final int[] dirs = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (!vis[i][j]) {
Deque<int[]> q = new ArrayDeque<>();
q.offer(new int[] {i, j, -1, -1});
vis[i][j] = true;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int[] p = q.poll();
int x = p[0], y = p[1], px = p[2], py = p[3];
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
int nx = x + dirs[k], ny = y + dirs[k + 1];
if (nx >= 0 && nx < m && ny >= 0 && ny < n) {
if (grid[nx][ny] != grid[x][y] || (nx == px && ny == py)) {
continue;
}
if (vis[nx][ny]) {
return true;
}
q.offer(new int[] {nx, ny, x, y});
vis[nx][ny] = true;
}
}
}
}
}
}
return false;
}
}class Solution {
public:
bool containsCycle(vector<vector<char>>& grid) {
int m = grid.size(), n = grid[0].size();
vector<vector<bool>> vis(m, vector<bool>(n));
const vector<int> dirs = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (!vis[i][j]) {
queue<array<int, 4>> q;
q.push({i, j, -1, -1});
vis[i][j] = true;
while (!q.empty()) {
auto p = q.front();
q.pop();
int x = p[0], y = p[1], px = p[2], py = p[3];
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
int nx = x + dirs[k], ny = y + dirs[k + 1];
if (nx >= 0 && nx < m && ny >= 0 && ny < n) {
if (grid[nx][ny] != grid[x][y] || (nx == px && ny == py)) {
continue;
}
if (vis[nx][ny]) {
return true;
}
q.push({nx, ny, x, y});
vis[nx][ny] = true;
}
}
}
}
}
}
return false;
}
};func containsCycle(grid [][]byte) bool {
m, n := len(grid), len(grid[0])
vis := make([][]bool, m)
for i := range vis {
vis[i] = make([]bool, n)
}
dirs := []int{-1, 0, 1, 0, -1}
for i := 0; i < m; i++ {
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
if !vis[i][j] {
q := [][]int{{i, j, -1, -1}}
vis[i][j] = true
for len(q) > 0 {
p := q[0]
q = q[1:]
x, y, px, py := p[0], p[1], p[2], p[3]
for k := 0; k < 4; k++ {
nx, ny := x+dirs[k], y+dirs[k+1]
if nx >= 0 && nx < m && ny >= 0 && ny < n {
if grid[nx][ny] != grid[x][y] || (nx == px && ny == py) {
continue
}
if vis[nx][ny] {
return true
}
q = append(q, []int{nx, ny, x, y})
vis[nx][ny] = true
}
}
}
}
}
}
return false
}function containsCycle(grid: string[][]): boolean {
const [m, n] = [grid.length, grid[0].length];
const vis: boolean[][] = Array.from({ length: m }, () => Array(n).fill(false));
const dirs = [-1, 0, 1, 0, -1];
for (let i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (!vis[i][j]) {
const q: [number, number, number, number][] = [[i, j, -1, -1]];
vis[i][j] = true;
for (const [x, y, px, py] of q) {
for (let k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
const [nx, ny] = [x + dirs[k], y + dirs[k + 1]];
if (nx >= 0 && nx < m && ny >= 0 && ny < n) {
if (grid[nx][ny] !== grid[x][y] || (nx === px && ny === py)) {
continue;
}
if (vis[nx][ny]) {
return true;
}
q.push([nx, ny, x, y]);
vis[nx][ny] = true;
}
}
}
}
}
}
return false;
}impl Solution {
pub fn contains_cycle(grid: Vec<Vec<char>>) -> bool {
let m = grid.len();
let n = grid[0].len();
let mut vis = vec![vec![false; n]; m];
let dirs = vec![-1, 0, 1, 0, -1];
for i in 0..m {
for j in 0..n {
if !vis[i][j] {
let mut q = vec![(i as isize, j as isize, -1, -1)];
vis[i][j] = true;
while !q.is_empty() {
let (x, y, px, py) = q.pop().unwrap();
for k in 0..4 {
let nx = x + dirs[k];
let ny = y + dirs[k + 1];
if nx >= 0 && nx < m as isize && ny >= 0 && ny < n as isize {
let nx = nx as usize;
let ny = ny as usize;
if grid[nx][ny] != grid[x as usize][y as usize]
|| (nx == px as usize && ny == py as usize)
{
continue;
}
if vis[nx][ny] {
return true;
}
q.push((nx as isize, ny as isize, x, y));
vis[nx][ny] = true;
}
}
}
}
}
}
false
}
}/**
* @param {character[][]} grid
* @return {boolean}
*/
var containsCycle = function (grid) {
const [m, n] = [grid.length, grid[0].length];
const vis = Array.from({ length: m }, () => Array(n).fill(false));
const dirs = [-1, 0, 1, 0, -1];
for (let i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (!vis[i][j]) {
const q = [[i, j, -1, -1]];
vis[i][j] = true;
for (const [x, y, px, py] of q) {
for (let k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
const [nx, ny] = [x + dirs[k], y + dirs[k + 1]];
if (nx >= 0 && nx < m && ny >= 0 && ny < n) {
if (grid[nx][ny] !== grid[x][y] || (nx === px && ny === py)) {
continue;
}
if (vis[nx][ny]) {
return true;
}
q.push([nx, ny, x, y]);
vis[nx][ny] = true;
}
}
}
}
}
}
return false;
};我们可以遍历二维网格中的每一个格子,对于每一个格子,如果格子
时间复杂度
class Solution:
def containsCycle(self, grid: List[List[str]]) -> bool:
def dfs(x: int, y: int, px: int, py: int) -> bool:
vis[x][y] = True
for dx, dy in pairwise(dirs):
nx, ny = x + dx, y + dy
if 0 <= nx < m and 0 <= ny < n:
if grid[nx][ny] != grid[x][y] or (nx == px and ny == py):
continue
if vis[nx][ny] or dfs(nx, ny, x, y):
return True
return False
m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])
vis = [[False] * n for _ in range(m)]
dirs = (-1, 0, 1, 0, -1)
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
if vis[i][j]:
continue
if dfs(i, j, -1, -1):
return True
return Falseclass Solution {
private char[][] grid;
private boolean[][] vis;
private final int[] dirs = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
private int m;
private int n;
public boolean containsCycle(char[][] grid) {
this.grid = grid;
m = grid.length;
n = grid[0].length;
vis = new boolean[m][n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (!vis[i][j] && dfs(i, j, -1, -1)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
private boolean dfs(int x, int y, int px, int py) {
vis[x][y] = true;
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
int nx = x + dirs[k], ny = y + dirs[k + 1];
if (nx >= 0 && nx < m && ny >= 0 && ny < n) {
if (grid[nx][ny] != grid[x][y] || (nx == px && ny == py)) {
continue;
}
if (vis[nx][ny] || dfs(nx, ny, x, y)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
}class Solution {
public:
bool containsCycle(vector<vector<char>>& grid) {
int m = grid.size(), n = grid[0].size();
vector<vector<bool>> vis(m, vector<bool>(n));
const vector<int> dirs = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
auto dfs = [&](this auto&& dfs, int x, int y, int px, int py) -> bool {
vis[x][y] = true;
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
int nx = x + dirs[k], ny = y + dirs[k + 1];
if (nx >= 0 && nx < m && ny >= 0 && ny < n) {
if (grid[nx][ny] != grid[x][y] || (nx == px && ny == py)) {
continue;
}
if (vis[nx][ny] || dfs(nx, ny, x, y)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
};
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (!vis[i][j] && dfs(i, j, -1, -1)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
};func containsCycle(grid [][]byte) bool {
m, n := len(grid), len(grid[0])
vis := make([][]bool, m)
for i := range vis {
vis[i] = make([]bool, n)
}
dirs := []int{-1, 0, 1, 0, -1}
var dfs func(x, y, px, py int) bool
dfs = func(x, y, px, py int) bool {
vis[x][y] = true
for k := 0; k < 4; k++ {
nx, ny := x+dirs[k], y+dirs[k+1]
if nx >= 0 && nx < m && ny >= 0 && ny < n {
if grid[nx][ny] != grid[x][y] || (nx == px && ny == py) {
continue
}
if vis[nx][ny] || dfs(nx, ny, x, y) {
return true
}
}
}
return false
}
for i := 0; i < m; i++ {
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
if !vis[i][j] && dfs(i, j, -1, -1) {
return true
}
}
}
return false
}function containsCycle(grid: string[][]): boolean {
const [m, n] = [grid.length, grid[0].length];
const vis: boolean[][] = Array.from({ length: m }, () => Array(n).fill(false));
const dfs = (x: number, y: number, px: number, py: number): boolean => {
vis[x][y] = true;
const dirs = [-1, 0, 1, 0, -1];
for (let k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
const [nx, ny] = [x + dirs[k], y + dirs[k + 1]];
if (nx >= 0 && nx < m && ny >= 0 && ny < n) {
if (grid[nx][ny] !== grid[x][y] || (nx === px && ny === py)) {
continue;
}
if (vis[nx][ny] || dfs(nx, ny, x, y)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
};
for (let i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (!vis[i][j] && dfs(i, j, -1, -1)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}impl Solution {
pub fn contains_cycle(grid: Vec<Vec<char>>) -> bool {
let m = grid.len();
let n = grid[0].len();
let mut vis = vec![vec![false; n]; m];
let dirs = vec![-1, 0, 1, 0, -1];
fn dfs(
x: usize,
y: usize,
px: isize,
py: isize,
grid: &Vec<Vec<char>>,
vis: &mut Vec<Vec<bool>>,
dirs: &Vec<isize>,
) -> bool {
vis[x][y] = true;
for k in 0..4 {
let nx = (x as isize + dirs[k]) as usize;
let ny = (y as isize + dirs[k + 1]) as usize;
if nx < grid.len() && ny < grid[0].len() {
if grid[nx][ny] != grid[x][y] || (nx as isize == px && ny as isize == py) {
continue;
}
if vis[nx][ny] || dfs(nx, ny, x as isize, y as isize, grid, vis, dirs) {
return true;
}
}
}
false
}
for i in 0..m {
for j in 0..n {
if !vis[i][j] && dfs(i, j, -1, -1, &grid, &mut vis, &dirs) {
return true;
}
}
}
false
}
}