| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Medium |
|
You are given a network of n nodes, labeled from 1 to n. You are also given times, a list of travel times as directed edges times[i] = (ui, vi, wi), where ui is the source node, vi is the target node, and wi is the time it takes for a signal to travel from source to target.
We will send a signal from a given node k. Return the minimum time it takes for all the n nodes to receive the signal. If it is impossible for all the n nodes to receive the signal, return -1.
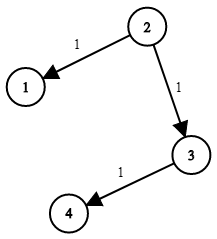
Example 1:
Input: times = [[2,1,1],[2,3,1],[3,4,1]], n = 4, k = 2 Output: 2
Example 2:
Input: times = [[1,2,1]], n = 2, k = 1 Output: 1
Example 3:
Input: times = [[1,2,1]], n = 2, k = 2 Output: -1
Constraints:
1 <= k <= n <= 1001 <= times.length <= 6000times[i].length == 31 <= ui, vi <= nui != vi0 <= wi <= 100- All the pairs
(ui, vi)are unique. (i.e., no multiple edges.)
We define
We maintain an array
Each time, we find the unvisited node
Finally, we return the maximum value in
The time complexity is
class Solution:
def networkDelayTime(self, times: List[List[int]], n: int, k: int) -> int:
g = [[inf] * n for _ in range(n)]
for u, v, w in times:
g[u - 1][v - 1] = w
dist = [inf] * n
dist[k - 1] = 0
vis = [False] * n
for _ in range(n):
t = -1
for j in range(n):
if not vis[j] and (t == -1 or dist[t] > dist[j]):
t = j
vis[t] = True
for j in range(n):
dist[j] = min(dist[j], dist[t] + g[t][j])
ans = max(dist)
return -1 if ans == inf else ansclass Solution {
public int networkDelayTime(int[][] times, int n, int k) {
int[][] g = new int[n][n];
int[] dist = new int[n];
final int inf = 1 << 29;
Arrays.fill(dist, inf);
for (var e : g) {
Arrays.fill(e, inf);
}
for (var e : times) {
g[e[0] - 1][e[1] - 1] = e[2];
}
dist[k - 1] = 0;
boolean[] vis = new boolean[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
int t = -1;
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (!vis[j] && (t == -1 || dist[t] > dist[j])) {
t = j;
}
}
vis[t] = true;
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
dist[j] = Math.min(dist[j], dist[t] + g[t][j]);
}
}
int ans = 0;
for (int x : dist) {
ans = Math.max(ans, x);
}
return ans == inf ? -1 : ans;
}
}class Solution {
public:
int networkDelayTime(vector<vector<int>>& times, int n, int k) {
const int inf = 1 << 29;
vector<vector<int>> g(n, vector<int>(n, inf));
for (const auto& e : times) {
g[e[0] - 1][e[1] - 1] = e[2];
}
vector<int> dist(n, inf);
dist[k - 1] = 0;
vector<bool> vis(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
int t = -1;
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (!vis[j] && (t == -1 || dist[t] > dist[j])) {
t = j;
}
}
vis[t] = true;
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
dist[j] = min(dist[j], dist[t] + g[t][j]);
}
}
int ans = ranges::max(dist);
return ans == inf ? -1 : ans;
}
};func networkDelayTime(times [][]int, n int, k int) int {
const inf = 1 << 29
g := make([][]int, n)
for i := range g {
g[i] = make([]int, n)
for j := range g[i] {
g[i][j] = inf
}
}
for _, e := range times {
g[e[0]-1][e[1]-1] = e[2]
}
dist := make([]int, n)
for i := range dist {
dist[i] = inf
}
dist[k-1] = 0
vis := make([]bool, n)
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
t := -1
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
if !vis[j] && (t == -1 || dist[t] > dist[j]) {
t = j
}
}
vis[t] = true
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
dist[j] = min(dist[j], dist[t]+g[t][j])
}
}
if ans := slices.Max(dist); ans != inf {
return ans
}
return -1
}function networkDelayTime(times: number[][], n: number, k: number): number {
const g: number[][] = Array.from({ length: n }, () => Array(n).fill(Infinity));
for (const [u, v, w] of times) {
g[u - 1][v - 1] = w;
}
const dist: number[] = Array(n).fill(Infinity);
dist[k - 1] = 0;
const vis: boolean[] = Array(n).fill(false);
for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
let t = -1;
for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (!vis[j] && (t === -1 || dist[j] < dist[t])) {
t = j;
}
}
vis[t] = true;
for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
dist[j] = Math.min(dist[j], dist[t] + g[t][j]);
}
}
const ans = Math.max(...dist);
return ans === Infinity ? -1 : ans;
}We can use a priority queue (heap) to optimize the naive Dijkstra algorithm.
We define
We define a priority queue
Finally, we return the maximum value in
The time complexity is
class Solution:
def networkDelayTime(self, times: List[List[int]], n: int, k: int) -> int:
g = [[] for _ in range(n)]
for u, v, w in times:
g[u - 1].append((v - 1, w))
dist = [inf] * n
dist[k - 1] = 0
pq = [(0, k - 1)]
while pq:
d, u = heappop(pq)
if d > dist[u]:
continue
for v, w in g[u]:
if (nd := d + w) < dist[v]:
dist[v] = nd
heappush(pq, (nd, v))
ans = max(dist)
return -1 if ans == inf else ansclass Solution {
public int networkDelayTime(int[][] times, int n, int k) {
final int inf = 1 << 29;
List<int[]>[] g = new List[n];
Arrays.setAll(g, i -> new ArrayList<>());
for (var e : times) {
g[e[0] - 1].add(new int[] {e[1] - 1, e[2]});
}
int[] dist = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(dist, inf);
dist[k - 1] = 0;
PriorityQueue<int[]> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparingInt(a -> a[0]));
pq.offer(new int[] {0, k - 1});
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
var p = pq.poll();
int d = p[0], u = p[1];
if (d > dist[u]) {
continue;
}
for (var e : g[u]) {
int v = e[0], w = e[1];
if (dist[v] > dist[u] + w) {
dist[v] = dist[u] + w;
pq.offer(new int[] {dist[v], v});
}
}
}
int ans = Arrays.stream(dist).max().getAsInt();
return ans == inf ? -1 : ans;
}
}class Solution {
public:
int networkDelayTime(vector<vector<int>>& times, int n, int k) {
const int inf = 1 << 29;
using pii = pair<int, int>;
vector<vector<pii>> g(n);
for (auto& edge : times) {
g[edge[0] - 1].emplace_back(edge[1] - 1, edge[2]);
}
vector<int> dist(n, inf);
dist[k - 1] = 0;
priority_queue<pii, vector<pii>, greater<>> pq;
pq.emplace(0, k - 1);
while (!pq.empty()) {
auto [d, u] = pq.top();
pq.pop();
if (d > dist[u]) {
continue;
}
for (auto& [v, w] : g[u]) {
if (dist[v] > dist[u] + w) {
dist[v] = dist[u] + w;
pq.emplace(dist[v], v);
}
}
}
int ans = ranges::max(dist);
return ans == inf ? -1 : ans;
}
};func networkDelayTime(times [][]int, n int, k int) int {
g := make([][][2]int, n)
for _, e := range times {
u, v, w := e[0]-1, e[1]-1, e[2]
g[u] = append(g[u], [2]int{v, w})
}
dist := make([]int, n)
const inf int = 1 << 29
for i := range dist {
dist[i] = inf
}
dist[k-1] = 0
pq := hp{{0, k - 1}}
for len(pq) > 0 {
p := heap.Pop(&pq).(pair)
d, u := p.x, p.i
if d > dist[u] {
continue
}
for _, e := range g[u] {
v, w := e[0], e[1]
if nd := d + w; nd < dist[v] {
dist[v] = nd
heap.Push(&pq, pair{nd, v})
}
}
}
if ans := slices.Max(dist); ans < inf {
return ans
}
return -1
}
type pair struct{ x, i int }
type hp []pair
func (h hp) Len() int { return len(h) }
func (h hp) Less(i, j int) bool { return h[i].x < h[j].x }
func (h hp) Swap(i, j int) { h[i], h[j] = h[j], h[i] }
func (h *hp) Push(x any) { *h = append(*h, x.(pair)) }
func (h *hp) Pop() (x any) { a := *h; x = a[len(a)-1]; *h = a[:len(a)-1]; return }function networkDelayTime(times: number[][], n: number, k: number): number {
const g: [number, number][][] = Array.from({ length: n }, () => []);
for (const [u, v, w] of times) {
g[u - 1].push([v - 1, w]);
}
const dist: number[] = Array(n).fill(Infinity);
dist[k - 1] = 0;
const pq = new MinPriorityQueue({ priority: v => v[0] });
pq.enqueue([0, k - 1]);
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
const [d, u] = pq.dequeue().element;
if (d > dist[u]) {
continue;
}
for (const [v, w] of g[u]) {
if (dist[v] > dist[u] + w) {
dist[v] = dist[u] + w;
pq.enqueue([dist[v], v]);
}
}
}
const ans = Math.max(...dist);
return ans === Infinity ? -1 : ans;
}