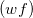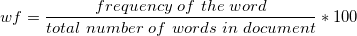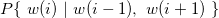Usually this would involve the following steps:
- Removal of special characters
- Change case for all words to lowercase
- Do stemming and remove the words that don't matter
- Do tokenization by using the following procedure
This is the most basic model for Natural Language Processing. It works as follows:
- Select all distinct words and set them as columns of a matrix
- Create as many rows as the number of observations
- Each cell should now contain for each observation, the number of times the word appeared in it
- Filter out other non-relevant words by setting a minimum frequency that a word must have across all observations in order for it to stay,
- Train this matrix for the classes available in a similar fashion to classification.
- The matrix created in Step 3 in the example above is called the Term Document Matrix
- The commonly used models for classification on NLP based problems are Naive Bayes, Decision Tree Learning & Random Forest classification but others maybe used as well if they fit the data well.
-
Word Frequency Proportions
: The proportions of each word with respect to all the words in the document. It is usually given by the equation:
-
Raw Word count: The raw word count for every word is taken as such.
-
Binary: if a word appears then 1, else 0
-
TF-IDF: Term Frequency - Inverse Document Frequency (takes into account the words that appear.
This is the segment of NLP that deals with tagging various elements of a sentence with the parts of speech group that they belong to.
In the sentence Albert Einstein is a genius, the ability of an algorithm to decipher that Abert Einstein is a person, is called NER, and is another application of NLP. The results are provided in form parse tree.
There are often more advanced problems that researchers of NLP face, like synonymy(multiple words having the same meaning) and polysemy(one word having multiple meanings). A common technique used for this is the creation of Latent Variables.
This is the art of changing certain aspects of a particular article that it appears to be a different one and avoids plagiarism. This algorithm works on the principal of Bayesian ML. A popular technique that we use for this is called Trigram Model. It models each word in the document as
Then, we replace each word in the document with a certain probability, P. If we change literally every word then there will be high chance for the document to make no sense at all. Therefore it's essential that we only change some words and let others be.
Both LSA and Trigram Models are unsupervised algorithms(have no class labels) and tend to learn the structure of our data.
Taking into account the words that appear most frequently in many documents and therefore neglecting words like is, an, the etcetera.
Split all the different sentences into different words, each word gets a column which would contain the frequency of appearance of that word. This would be a sparse matrix that we would then operate upon it at will.
The process of collecting only the roots of words so that even if the same words appear in different forms, we always have a steady output and our machine learning models learn to recognize them properly and as the same words. While stemming is the more basic/crude version of the above, Lemmatization is more sophisticated than that. While a stemmer might give you the word theiv after stemming the word theives, the lemmatizer will give you theif as the answer.
The idea to combine words that often appear together using a probabilistic distribution over the terms. After this, these pairs of variables with very correlation will then be used to revamp the data accordingly, and hopefully the dimensions of this new data will be much lesser than the original one. Although, this would almost certainly help solve the Synonymy problem but it's not quite proven whether or not it helps solve the polysemy problem adn I think, ideally, it shouldn't.
A corpus is a collection of texts of the same type.
The property that a matrix holding a lot of zeroes and very few values, is called sparsity. This is usually not a good thing and can be reduced, either by removing the least frequent words by using the max_features parameter of CountVectorizer method (in Python) or using Dimensionality Reduction techniques.
[1] CountVectorizer: It can be used to all the text cleaning necessary for the Bag of Words model, instead of having do to it manually. Read documentation for more.