diff --git a/docs/Static-Analysis/10-Datalog-Based Program Analysis.md b/docs/Static-Analysis/10-Datalog-Based Program Analysis.md
index 5a36b46..cf3c15a 100644
--- a/docs/Static-Analysis/10-Datalog-Based Program Analysis.md
+++ b/docs/Static-Analysis/10-Datalog-Based Program Analysis.md
@@ -32,7 +32,7 @@ Datalog是一种声明式(Declarative)的编程语言。
- 没有函数
- 不是图灵完备的
-## Data
+## Facts
### Predicates
@@ -55,7 +55,7 @@ Atoms可以分成两类
- Arithmetic Atoms
- 如`age >= 18`
-## Logic
+## Rule
### Datalog Rules & Logic And
@@ -100,7 +100,7 @@ Datalog使用规则来进行推导(inference),其定义如下:
 -## Rule Satety
+## Rule Safety
讲到这里,停下来思考一下,这两条Rules看起来有什么问题吗?
@@ -133,8 +133,8 @@ Datalog使用规则来进行推导(inference),其定义如下:
Datalog的两大重要特性:
-- 单调性。因为事实(facts)不会被删除的。
-- 必然终止。
+- Monotonicity: 因为事实(facts)不会被删除的。
+- Termination:
- 事实的数量是**单调**的。
- 由Rule Safety,所能得到的IDB的大小也是**有限**的。
@@ -150,7 +150,7 @@ Datalog的两大重要特性:
和之前一样,我们把Call放到最后处理。
-## Datalog Model-EDB&IDB
+## Datalog Model-EDB & IDB
我们首先需要对前四条语句建模。输入的EDB代表了4个存储相应类型语句的table,输出为Variable和Field的指向关系。
@@ -252,14 +252,22 @@ e = d.f;
# Key Points
-- Pros
- - **Succinct** and **readable**
- - **Easy** to implement
- - **Benefit from off-the-shelf optimized Datalog engines**
-- Cons
- - **Restricted expressiveness**, i.e., it is impossible or inconvenient to express some logics
- - Cannot fully control **performance**
-- Overall Review
- - **Datalog** language
- - How to implement **pointer analysis via Datalog**
- - How to implement **taint analysis via Datalog**
\ No newline at end of file
+DataLog:
+
+- Pros
+
+ - **Succinct** and **readable**
+ - **Easy** to implement
+ - **Benefit from off-the-shelf optimized Datalog engines**
+
+- Cons
+ - **Restricted expressiveness**, i.e., it is impossible or inconvenient to express some logics
+ - Cannot fully control **performance**
+
+
+
+ Overall Review
+
+ - **Datalog** language
+ - How to implement **pointer analysis via Datalog**
+ - How to implement **taint analysis via Datalog**
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/Static-Analysis/11-CFL-Reachability and IFDS.md b/docs/Static-Analysis/11-CFL-Reachability and IFDS.md
index 9f1a949..7d3578a 100644
--- a/docs/Static-Analysis/11-CFL-Reachability and IFDS.md
+++ b/docs/Static-Analysis/11-CFL-Reachability and IFDS.md
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
# CFL-Reachability and IFDS
-前排提醒:如果你已经忘记了**数据流分析理论基础**部分的内容,请务必去复习一下再读本文。具体来说,你应该能够回忆起:
+前排提醒:如果你已经忘记了**数据流分析理论基础**部分的内容,请务必去复习一下再读本文具体来说,你应该能够回忆起:
- Meet/Join
- Transfer function
@@ -8,24 +8,14 @@
---
-标题看起来有点吓人,不过我们可以简单地描述一下即将要讲述的内容:
> IFDS是一种分析框架,在这种框架下,分析的数据流是满足CFL-Reachability这一性质的。
-本课主要内容如下:
-
-1. Feasible and Realizable Paths
-2. CFL-Reachability
-3. Overview of IFDS
-4. Supergraph and Flow Functions
-5. Exploded Supergraph and Tabulation Algorithm
-6. Understanding the Distributivity of IFDS
-
-# Feasible and Realizable Paths
+## Feasible and Realizable Paths
实际分析时,JDK中一个方法能产生的CFG是非常复杂的。不过,并非所有的路径都会被执行到,一个很自然的想法是,只分析可能被执行的路径。
-
-## Rule Satety
+## Rule Safety
讲到这里,停下来思考一下,这两条Rules看起来有什么问题吗?
@@ -133,8 +133,8 @@ Datalog使用规则来进行推导(inference),其定义如下:
Datalog的两大重要特性:
-- 单调性。因为事实(facts)不会被删除的。
-- 必然终止。
+- Monotonicity: 因为事实(facts)不会被删除的。
+- Termination:
- 事实的数量是**单调**的。
- 由Rule Safety,所能得到的IDB的大小也是**有限**的。
@@ -150,7 +150,7 @@ Datalog的两大重要特性:
和之前一样,我们把Call放到最后处理。
-## Datalog Model-EDB&IDB
+## Datalog Model-EDB & IDB
我们首先需要对前四条语句建模。输入的EDB代表了4个存储相应类型语句的table,输出为Variable和Field的指向关系。
@@ -252,14 +252,22 @@ e = d.f;
# Key Points
-- Pros
- - **Succinct** and **readable**
- - **Easy** to implement
- - **Benefit from off-the-shelf optimized Datalog engines**
-- Cons
- - **Restricted expressiveness**, i.e., it is impossible or inconvenient to express some logics
- - Cannot fully control **performance**
-- Overall Review
- - **Datalog** language
- - How to implement **pointer analysis via Datalog**
- - How to implement **taint analysis via Datalog**
\ No newline at end of file
+DataLog:
+
+- Pros
+
+ - **Succinct** and **readable**
+ - **Easy** to implement
+ - **Benefit from off-the-shelf optimized Datalog engines**
+
+- Cons
+ - **Restricted expressiveness**, i.e., it is impossible or inconvenient to express some logics
+ - Cannot fully control **performance**
+
+
+
+ Overall Review
+
+ - **Datalog** language
+ - How to implement **pointer analysis via Datalog**
+ - How to implement **taint analysis via Datalog**
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/Static-Analysis/11-CFL-Reachability and IFDS.md b/docs/Static-Analysis/11-CFL-Reachability and IFDS.md
index 9f1a949..7d3578a 100644
--- a/docs/Static-Analysis/11-CFL-Reachability and IFDS.md
+++ b/docs/Static-Analysis/11-CFL-Reachability and IFDS.md
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
# CFL-Reachability and IFDS
-前排提醒:如果你已经忘记了**数据流分析理论基础**部分的内容,请务必去复习一下再读本文。具体来说,你应该能够回忆起:
+前排提醒:如果你已经忘记了**数据流分析理论基础**部分的内容,请务必去复习一下再读本文具体来说,你应该能够回忆起:
- Meet/Join
- Transfer function
@@ -8,24 +8,14 @@
---
-标题看起来有点吓人,不过我们可以简单地描述一下即将要讲述的内容:
> IFDS是一种分析框架,在这种框架下,分析的数据流是满足CFL-Reachability这一性质的。
-本课主要内容如下:
-
-1. Feasible and Realizable Paths
-2. CFL-Reachability
-3. Overview of IFDS
-4. Supergraph and Flow Functions
-5. Exploded Supergraph and Tabulation Algorithm
-6. Understanding the Distributivity of IFDS
-
-# Feasible and Realizable Paths
+## Feasible and Realizable Paths
实际分析时,JDK中一个方法能产生的CFG是非常复杂的。不过,并非所有的路径都会被执行到,一个很自然的想法是,只分析可能被执行的路径。
- +
虽然并非所有的路径都会被执行到。**可是`判断一条路径是否feasible`本身是不可判定(undecidable)的。**
@@ -47,8 +37,7 @@
> The paths in which “returns” are matched with corresponding “calls”.
-- Realizable paths may not be executable, but unrealizable paths
- must not be executable.
+- Realizable paths may not be executable, but unrealizable paths must not be executable.
- 可以把executable/feasible path看作realizable path的真子集
- Our goal is to **recognize realizable paths** so that we could avoid polluting analysis results along unrealizable paths.
- 这个问题和括号匹配问题本质上是一样的。
@@ -57,11 +46,11 @@
+
虽然并非所有的路径都会被执行到。**可是`判断一条路径是否feasible`本身是不可判定(undecidable)的。**
@@ -47,8 +37,7 @@
> The paths in which “returns” are matched with corresponding “calls”.
-- Realizable paths may not be executable, but unrealizable paths
- must not be executable.
+- Realizable paths may not be executable, but unrealizable paths must not be executable.
- 可以把executable/feasible path看作realizable path的真子集
- Our goal is to **recognize realizable paths** so that we could avoid polluting analysis results along unrealizable paths.
- 这个问题和括号匹配问题本质上是一样的。
@@ -57,11 +46,11 @@
 -# CFL-Reachability
+## CFL-Reachability
> A path is considered to connect two nodes A and B, or **B is reachable from A**, only if **the concatenation of the labels on the edges of the path is a word in a specified context-free language.**
-这里默认读者学习过上下文无关语言(context-free language)相关的知识(编译原理和计算理论几乎是每个学校计算机系的必修课)。具体来说,你应该知道:
+这里默认读者学习过上下文无关语言(context-free language)相关的知识。具体来说,你应该知道:
- 终结符(nonterminal)
- 非终结符(terminal)
@@ -69,7 +58,7 @@
- (最左/最右)推导
- 正则文法/上下文无关文法和图灵机之间计算表达能力的差异
-我们进一步定义一个语言`L(realizable)`,右侧黄色框中的4个字符串都是语言L的一部分。
+我们进一步定义一个语言`L(realizable)`,右侧黄色框中的4个字符串都是语言L的一部分
-# CFL-Reachability
+## CFL-Reachability
> A path is considered to connect two nodes A and B, or **B is reachable from A**, only if **the concatenation of the labels on the edges of the path is a word in a specified context-free language.**
-这里默认读者学习过上下文无关语言(context-free language)相关的知识(编译原理和计算理论几乎是每个学校计算机系的必修课)。具体来说,你应该知道:
+这里默认读者学习过上下文无关语言(context-free language)相关的知识。具体来说,你应该知道:
- 终结符(nonterminal)
- 非终结符(terminal)
@@ -69,7 +58,7 @@
- (最左/最右)推导
- 正则文法/上下文无关文法和图灵机之间计算表达能力的差异
-我们进一步定义一个语言`L(realizable)`,右侧黄色框中的4个字符串都是语言L的一部分。
+我们进一步定义一个语言`L(realizable)`,右侧黄色框中的4个字符串都是语言L的一部分
 @@ -83,13 +72,16 @@
@@ -83,13 +72,16 @@
 -# Overview of IFDS
+## Overview of IFDS
> “Precise Interprocedural Dataflow Analysis via Graph Reachability”
>
-> --Thomas Reps, Susan Horwitz, and Mooly Sagiv, POPL’95
+> --Thomas Reps, Susan Horwitz, and Mooly Sagiv, POPL’95
+
+IFDS is for interprocedural data flow analysis with **distributive** flow functions over **finite** domains.
-所谓IFDS,其实是四个单词(Interprocedural, Finite, Distributive, Subset)的缩写。如果一个问题满足这四个性质,则可以用相应的框架来解决问题。
+所谓IFDS,其实是四个单词(Interprocedural, Finite, Distributive, Subset)的缩写。
+如果一个问题满足这四个性质,则可以用相应的框架来解决问题。
复习两个旧概念,介绍一个新概念:
@@ -99,7 +91,7 @@
- 可以理解按照顺序,先后应用一条path上edge/node的transfer function:
- -
-# Overview of IFDS
+## Overview of IFDS
> “Precise Interprocedural Dataflow Analysis via Graph Reachability”
>
-> --Thomas Reps, Susan Horwitz, and Mooly Sagiv, POPL’95
+> --Thomas Reps, Susan Horwitz, and Mooly Sagiv, POPL’95
+
+IFDS is for interprocedural data flow analysis with **distributive** flow functions over **finite** domains.
-所谓IFDS,其实是四个单词(Interprocedural, Finite, Distributive, Subset)的缩写。如果一个问题满足这四个性质,则可以用相应的框架来解决问题。
+所谓IFDS,其实是四个单词(Interprocedural, Finite, Distributive, Subset)的缩写。
+如果一个问题满足这四个性质,则可以用相应的框架来解决问题。
复习两个旧概念,介绍一个新概念:
@@ -99,7 +91,7 @@
- 可以理解按照顺序,先后应用一条path上edge/node的transfer function:
- -  +
+  - `Meet-Over-All-Paths(MOP)`
@@ -119,19 +111,20 @@
---
-接下来要讲一些比较难懂的内容~~战术喝水~~。
-
- `Meet-Over-All-Paths(MOP)`
@@ -119,19 +111,20 @@
---
-接下来要讲一些比较难懂的内容~~战术喝水~~。
-
 -# Supergraph and Flow Functions
+## Supergraph and Flow Functions
+
+### Supergraph
-## Supergraph
+In IFDS, a program is represented by $G^* = (N^*,E^*)$ called a supergraph
-可以理解成IFDS分析体系下的ICFG(Interprocedural Control Flow Graph,即过程间控制流图)。这里只需要了解一下其中的三种edge(图中的G*即指supergraph):
+可以理解成IFDS分析体系下的ICFG(Interprocedural Control Flow Graph,即过程间控制流图)。
+这里只需要了解一下其中的三种edge(图中的G*即指supergraph):
-# Supergraph and Flow Functions
+## Supergraph and Flow Functions
+
+### Supergraph
-## Supergraph
+In IFDS, a program is represented by $G^* = (N^*,E^*)$ called a supergraph
-可以理解成IFDS分析体系下的ICFG(Interprocedural Control Flow Graph,即过程间控制流图)。这里只需要了解一下其中的三种edge(图中的G*即指supergraph):
+可以理解成IFDS分析体系下的ICFG(Interprocedural Control Flow Graph,即过程间控制流图)。
+这里只需要了解一下其中的三种edge(图中的G*即指supergraph):
 -## Design Flow Functions
+### Design Flow Functions
定义`Possibly-uninitialized variables`:
@@ -139,7 +132,7 @@
我们接下来的例子求的就是这样的变量。
-### lambda expression
+#### lambda expression
为了后续叙述方便,这里简单地介绍一下lambda表达式。
@@ -151,7 +144,7 @@
-## Design Flow Functions
+### Design Flow Functions
定义`Possibly-uninitialized variables`:
@@ -139,7 +132,7 @@
我们接下来的例子求的就是这样的变量。
-### lambda expression
+#### lambda expression
为了后续叙述方便,这里简单地介绍一下lambda表达式。
@@ -151,7 +144,7 @@
 -### Example of Flow Functions
+#### Example of Flow Functions
在进入main后,全局变量g和局部变量x一定是没有初始化的。
@@ -177,11 +170,11 @@
-### Example of Flow Functions
+#### Example of Flow Functions
在进入main后,全局变量g和局部变量x一定是没有初始化的。
@@ -177,11 +170,11 @@
 -# Exploded Supergraph and Tabulation Algorithm
+## Exploded Supergraph and Tabulation Algorithm
-## Build Exploded Supergraph
+### Build Exploded Supergraph
-Flow Function对应着二元关系。
+Flow Function对应着二元关系
-# Exploded Supergraph and Tabulation Algorithm
+## Exploded Supergraph and Tabulation Algorithm
-## Build Exploded Supergraph
+### Build Exploded Supergraph
-Flow Function对应着二元关系。
+Flow Function对应着二元关系
 @@ -194,37 +187,35 @@ Flow Function对应着二元关系。
你是否也觉得上面例子中0->0这条边挺奇怪的?它的存在是被刻意设计的。因为IFDS主要依赖于可达性(reachability)做分析。如果没有这样的边,在IFDS中没有办法判断在n4这个点处,a是否满足某种性质。
-
@@ -194,37 +187,35 @@ Flow Function对应着二元关系。
你是否也觉得上面例子中0->0这条边挺奇怪的?它的存在是被刻意设计的。因为IFDS主要依赖于可达性(reachability)做分析。如果没有这样的边,在IFDS中没有办法判断在n4这个点处,a是否满足某种性质。
- +
+ 而加上这条总是存在的Glue Edge之后,就可以满足IFDS分析的要求。
-
而加上这条总是存在的Glue Edge之后,就可以满足IFDS分析的要求。
- +
+ -回到我们之前的例子,用新的二元关系的视角去**手动分析**,将会是这样(视频之后会做的会做的~~吧~~,咕!):
+回到我们之前的例子,用新的二元关系的视角去**手动分析**,将会是这样:
标黄部分比较重要,它的意思是:如果a或g一开始没有被初始化,则a都没有被初始化。
-
-回到我们之前的例子,用新的二元关系的视角去**手动分析**,将会是这样(视频之后会做的会做的~~吧~~,咕!):
+回到我们之前的例子,用新的二元关系的视角去**手动分析**,将会是这样:
标黄部分比较重要,它的意思是:如果a或g一开始没有被初始化,则a都没有被初始化。
- +
+ 最后构造出来的Exploded Supergraph是这样的:
-
最后构造出来的Exploded Supergraph是这样的:
- +
+ 怎样使用这样的分析结果呢?我们来考虑一个问题,全局变量g在程序片段运行结束时,是否可能没有被初始化?
-
怎样使用这样的分析结果呢?我们来考虑一个问题,全局变量g在程序片段运行结束时,是否可能没有被初始化?
- +
+ 结果是,g在这里可能没有被初始化。
-
结果是,g在这里可能没有被初始化。
- +
+ 而之前提到的realizable path在这里也能提供更高的精度。
-
而之前提到的realizable path在这里也能提供更高的精度。
- -
-
-
- +
+
 -## Tabulation Algorithm
+### Tabulation Algorithm
刚才我们是手动分析的,而用Tabulation算法,可以在$$ O(ED^3)$$复杂度(E为Edge的数量,D为Data facts的数量,如在下面的例子中,D为3)下得到MRP的结果:
@@ -234,7 +225,7 @@ Flow Function对应着二元关系。
-## Tabulation Algorithm
+### Tabulation Algorithm
刚才我们是手动分析的,而用Tabulation算法,可以在$$ O(ED^3)$$复杂度(E为Edge的数量,D为Data facts的数量,如在下面的例子中,D为3)下得到MRP的结果:
@@ -234,7 +225,7 @@ Flow Function对应着二元关系。
 -# Understanding the Distributivity of IFDS
+## Understanding the Distributivity of IFDS
这里的Distributivity是指Flow Function的性质,即满足:
diff --git a/docs/Static-Analysis/12-Soundness and Soundiness.md b/docs/Static-Analysis/12-Soundness and Soundiness.md
index 9f29ed3..504837d 100644
--- a/docs/Static-Analysis/12-Soundness and Soundiness.md
+++ b/docs/Static-Analysis/12-Soundness and Soundiness.md
@@ -1,264 +1,151 @@
-# CFL-Reachability and IFDS
+# Soundiness
-前排提醒:如果你已经忘记了**数据流分析理论基础**部分的内容,请务必去复习一下再读本文。具体来说,你应该能够回忆起:
+在时间中很难实现sound的算法,所以专家们提出一个与Soundness不同的概念Soundiness。(关于Soundness,可以回顾B站上的前两节课)。
-- Meet/Join
-- Transfer function
-- Bottom/Top
+本文主要内容如下:
----
+1. Soundness and Soundiness
+2. Hard Language Feature: Java Reflection
+3. Hard Language Feature: Native Code
-标题看起来有点吓人,不过我们可以简单地描述一下即将要讲述的内容:
+# Soundness and Soundiness
-> IFDS是一种分析框架,在这种框架下,分析的数据流是满足CFL-Reachability这一性质的。
+回顾Soundness的定义(没有漏报bug就是sound):
-本课主要内容如下:
+> **Conservative** approximation: the analysis **captures all program behaviors**, or the analysis result **models all possible executions** of the program.
-1. Feasible and Realizable Paths
-2. CFL-Reachability
-3. Overview of IFDS
-4. Supergraph and Flow Functions
-5. Exploded Supergraph and Tabulation Algorithm
-6. Understanding the Distributivity of IFDS
+无论是学术界还是工业界的算法,都是不完全sound的。
-# Feasible and Realizable Paths
+这是由于很多语言拥有的部分高级特性对于静态分析来说是难以分析的:
-实际分析时,JDK中一个方法能产生的CFG是非常复杂的。不过,并非所有的路径都会被执行到,一个很自然的想法是,只分析可能被执行的路径。
+- Java
+ - Reflection, native code, dynamic class loading, etc.
+- JavaScript
+ - eval, document object model (DOM), etc.
+- C/C++
+ - Pointer arithmetic, function pointers, etc.
-
-# Understanding the Distributivity of IFDS
+## Understanding the Distributivity of IFDS
这里的Distributivity是指Flow Function的性质,即满足:
diff --git a/docs/Static-Analysis/12-Soundness and Soundiness.md b/docs/Static-Analysis/12-Soundness and Soundiness.md
index 9f29ed3..504837d 100644
--- a/docs/Static-Analysis/12-Soundness and Soundiness.md
+++ b/docs/Static-Analysis/12-Soundness and Soundiness.md
@@ -1,264 +1,151 @@
-# CFL-Reachability and IFDS
+# Soundiness
-前排提醒:如果你已经忘记了**数据流分析理论基础**部分的内容,请务必去复习一下再读本文。具体来说,你应该能够回忆起:
+在时间中很难实现sound的算法,所以专家们提出一个与Soundness不同的概念Soundiness。(关于Soundness,可以回顾B站上的前两节课)。
-- Meet/Join
-- Transfer function
-- Bottom/Top
+本文主要内容如下:
----
+1. Soundness and Soundiness
+2. Hard Language Feature: Java Reflection
+3. Hard Language Feature: Native Code
-标题看起来有点吓人,不过我们可以简单地描述一下即将要讲述的内容:
+# Soundness and Soundiness
-> IFDS是一种分析框架,在这种框架下,分析的数据流是满足CFL-Reachability这一性质的。
+回顾Soundness的定义(没有漏报bug就是sound):
-本课主要内容如下:
+> **Conservative** approximation: the analysis **captures all program behaviors**, or the analysis result **models all possible executions** of the program.
-1. Feasible and Realizable Paths
-2. CFL-Reachability
-3. Overview of IFDS
-4. Supergraph and Flow Functions
-5. Exploded Supergraph and Tabulation Algorithm
-6. Understanding the Distributivity of IFDS
+无论是学术界还是工业界的算法,都是不完全sound的。
-# Feasible and Realizable Paths
+这是由于很多语言拥有的部分高级特性对于静态分析来说是难以分析的:
-实际分析时,JDK中一个方法能产生的CFG是非常复杂的。不过,并非所有的路径都会被执行到,一个很自然的想法是,只分析可能被执行的路径。
+- Java
+ - Reflection, native code, dynamic class loading, etc.
+- JavaScript
+ - eval, document object model (DOM), etc.
+- C/C++
+ - Pointer arithmetic, function pointers, etc.
- +例如对C/C++中的一个指针p,加上某个经过运算的偏移量x,为了分析的安全,只能假设p+x可以指向内存中的任何一个地方。
-虽然并非所有的路径都会被执行到。**可是`判断一条路径是否feasible`本身是不可判定(undecidable)的。**
+为了解决这一问题,专家们提出一个新的概念Soundiness,对应的形容词是Soundy。
-这并不代表我们束手无策了,我们来看一个例子:
+> A **soundy** analysis typically means that the analysis is mostly sound, with **well-identified** unsound treatments to hard/specific language features.
-
+把新旧词汇放到一起做个比较:
-动态执行时x和y都有确定的值,而上下文不敏感的分析中,x和y的取值都会是NAC,更具体的说,就是`{18,30,-1}`。
+- A **sound** analysis requires to **capture all** dynamic behaviors
+ - 完全理想情况
+- A **soundy** analysis aims to **capture all** dynamic behaviors **with certain hard language features unsoundly handled within reason**
+ - 现实情况
+- An **unsound** analysis **deliberately ignores certain behaviors in its design for better efficiency, precision or accessibility**
+ - 过于现实的情况
-仔细地观察x的两个不精确的分析结果,可以发现-1这个结果在当前框架下是不可避免的:
+# Hard Language Feature: Java Reflection
-
+例如对C/C++中的一个指针p,加上某个经过运算的偏移量x,为了分析的安全,只能假设p+x可以指向内存中的任何一个地方。
-虽然并非所有的路径都会被执行到。**可是`判断一条路径是否feasible`本身是不可判定(undecidable)的。**
+为了解决这一问题,专家们提出一个新的概念Soundiness,对应的形容词是Soundy。
-这并不代表我们束手无策了,我们来看一个例子:
+> A **soundy** analysis typically means that the analysis is mostly sound, with **well-identified** unsound treatments to hard/specific language features.
-
+把新旧词汇放到一起做个比较:
-动态执行时x和y都有确定的值,而上下文不敏感的分析中,x和y的取值都会是NAC,更具体的说,就是`{18,30,-1}`。
+- A **sound** analysis requires to **capture all** dynamic behaviors
+ - 完全理想情况
+- A **soundy** analysis aims to **capture all** dynamic behaviors **with certain hard language features unsoundly handled within reason**
+ - 现实情况
+- An **unsound** analysis **deliberately ignores certain behaviors in its design for better efficiency, precision or accessibility**
+ - 过于现实的情况
-仔细地观察x的两个不精确的分析结果,可以发现-1这个结果在当前框架下是不可避免的:
+# Hard Language Feature: Java Reflection
- +说了这么多抽象的概念,接下来具体说说在Java里给静态分析添乱的特性。
-而30这个不精确的结果则是可以避免的(比如使用我们之前介绍过的上下文敏感指针分析):
+
+说了这么多抽象的概念,接下来具体说说在Java里给静态分析添乱的特性。
-而30这个不精确的结果则是可以避免的(比如使用我们之前介绍过的上下文敏感指针分析):
+ -
- +## Java Reflection
-定义一个新概念`Realizable Paths`:
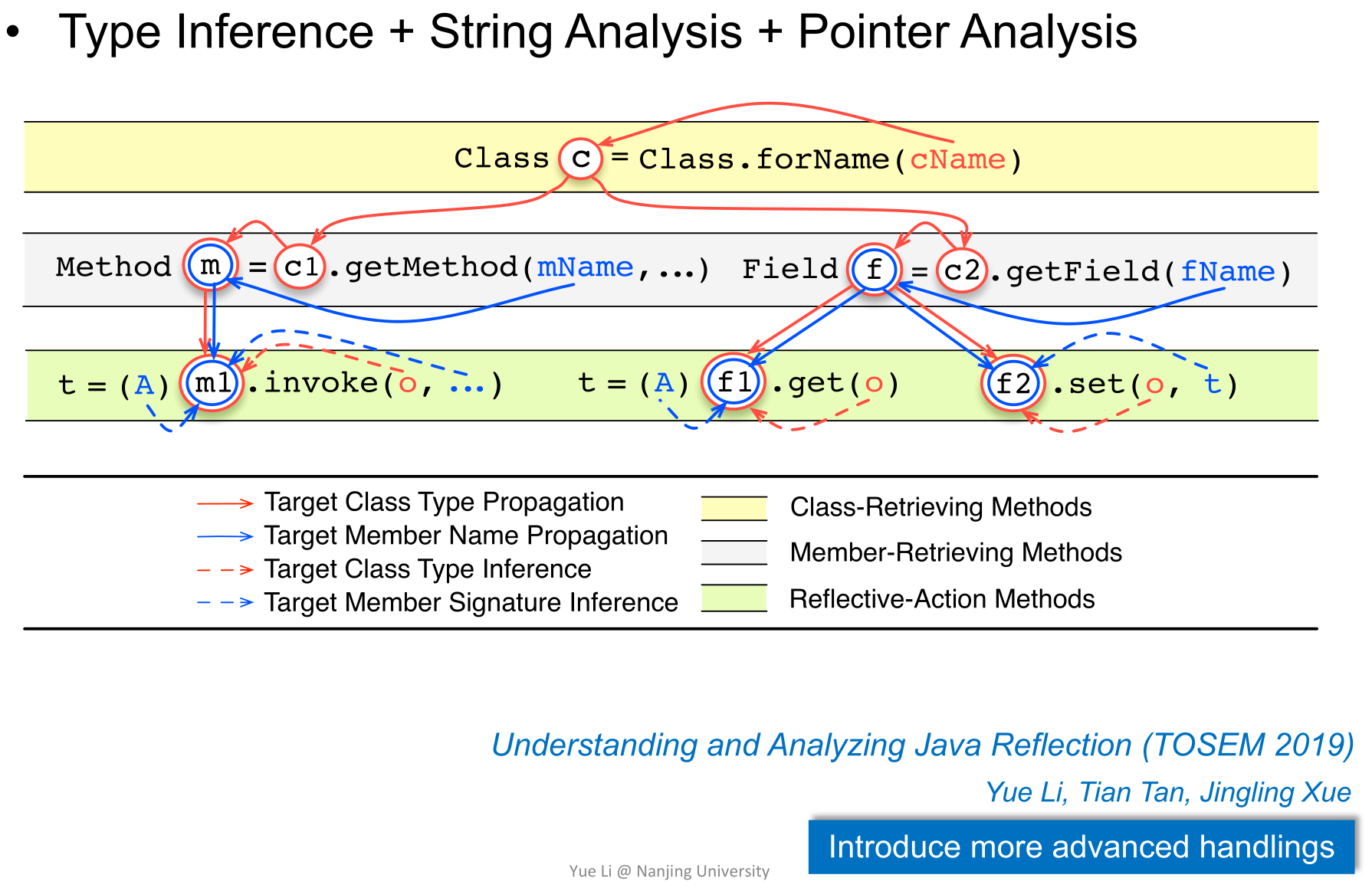
+首先,右上角Run-time代码块中的前三行的Class、Method和Field都是Metaobject。然后就能够以Metaobject执行一系列操作,如`c.newInstance()`就相当于左下角的`new Person()`。
-> The paths in which “returns” are matched with corresponding “calls”.
+使用Reflection时,无法在编译时确定其行为,只能在运行时确定。
-- Realizable paths may not be executable, but unrealizable paths
- must not be executable.
- - 可以把executable/feasible path看作realizable path的真子集
-- Our goal is to **recognize realizable paths** so that we could avoid polluting analysis results along unrealizable paths.
- - 这个问题和括号匹配问题本质上是一样的。
- - 如果你是计算机系大一的学生,或许会想到用stack来做括号匹配问题。
- - 而如果你刚刚修过计算理论课程,你应该能够想起来使用上下文无关文法能够很好地识别一个匹配的括号串(Balanced-Parenthesis Problem)。
+
+## Java Reflection
-定义一个新概念`Realizable Paths`:
+首先,右上角Run-time代码块中的前三行的Class、Method和Field都是Metaobject。然后就能够以Metaobject执行一系列操作,如`c.newInstance()`就相当于左下角的`new Person()`。
-> The paths in which “returns” are matched with corresponding “calls”.
+使用Reflection时,无法在编译时确定其行为,只能在运行时确定。
-- Realizable paths may not be executable, but unrealizable paths
- must not be executable.
- - 可以把executable/feasible path看作realizable path的真子集
-- Our goal is to **recognize realizable paths** so that we could avoid polluting analysis results along unrealizable paths.
- - 这个问题和括号匹配问题本质上是一样的。
- - 如果你是计算机系大一的学生,或许会想到用stack来做括号匹配问题。
- - 而如果你刚刚修过计算理论课程,你应该能够想起来使用上下文无关文法能够很好地识别一个匹配的括号串(Balanced-Parenthesis Problem)。
+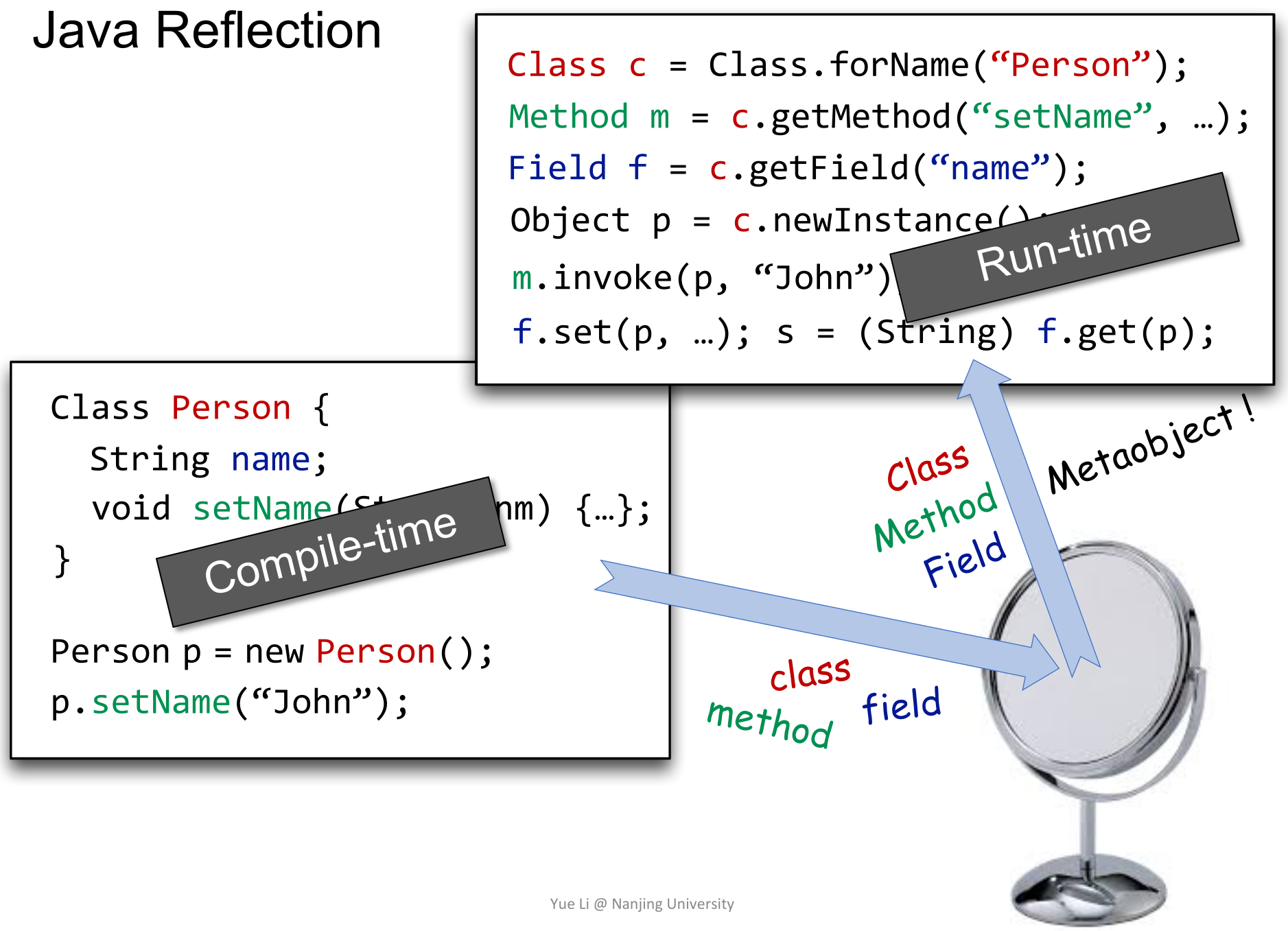 -
- +## Why Analyze It
-# CFL-Reachability
+可能会**错失检测出某些bug的机会**(忽略`m.invoke`所引入的调用时发生),也可能**导致分析的结果不安全**(忽略`f.set(a,a)`的作用时发生,将会错误地认为箭头指向处的cast可以优化掉)。
-> A path is considered to connect two nodes A and B, or **B is reachable from A**, only if **the concatenation of the labels on the edges of the path is a word in a specified context-free language.**
+
+## Why Analyze It
-# CFL-Reachability
+可能会**错失检测出某些bug的机会**(忽略`m.invoke`所引入的调用时发生),也可能**导致分析的结果不安全**(忽略`f.set(a,a)`的作用时发生,将会错误地认为箭头指向处的cast可以优化掉)。
-> A path is considered to connect two nodes A and B, or **B is reachable from A**, only if **the concatenation of the labels on the edges of the path is a word in a specified context-free language.**
+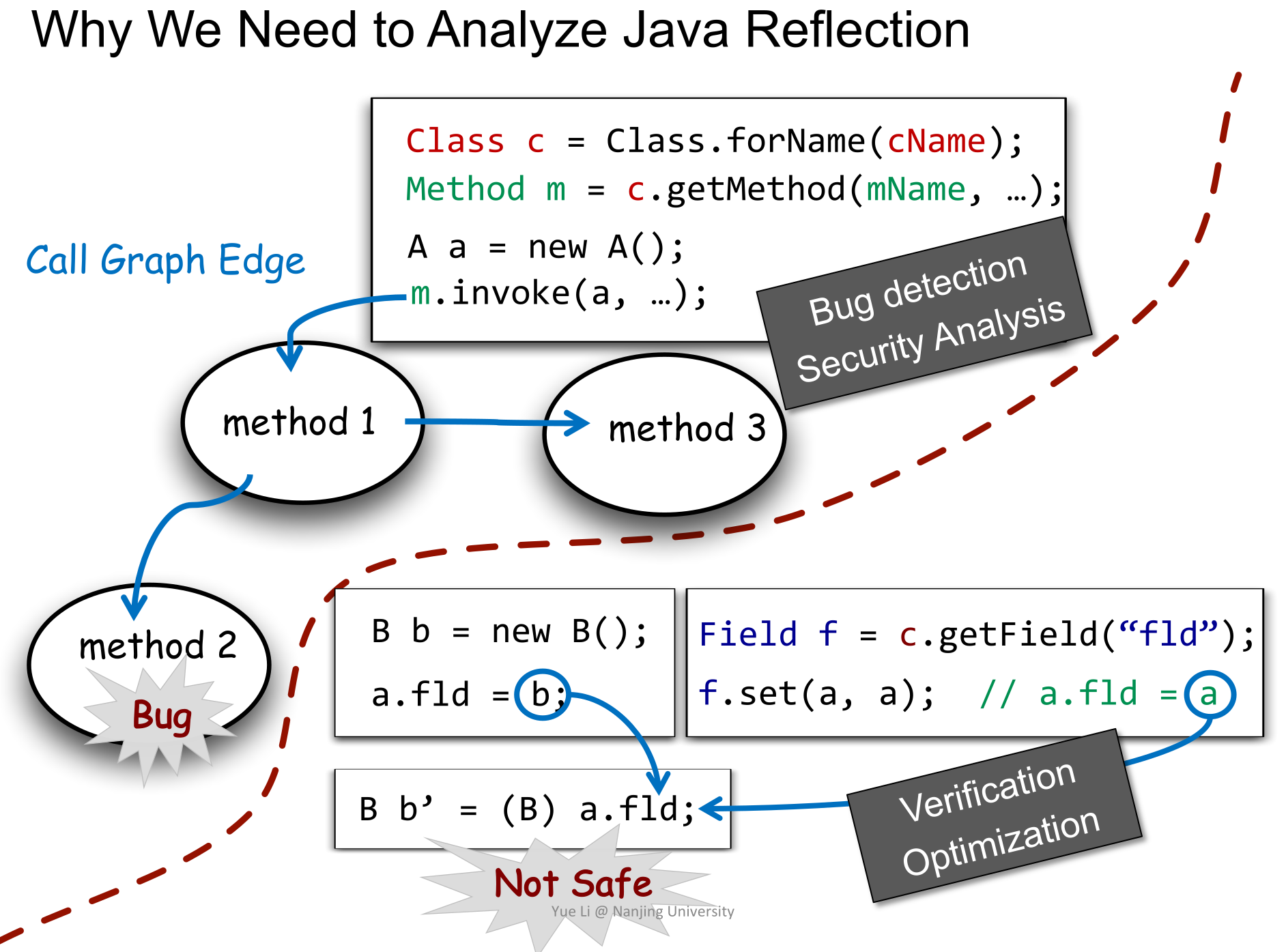 -这里默认读者学习过上下文无关语言(context-free language)相关的知识(编译原理和计算理论几乎是每个学校计算机系的必修课)。具体来说,你应该知道:
+## How to Analyze It
-- 终结符(nonterminal)
-- 非终结符(terminal)
-- 空串符号$$ \epsilon$$
-- (最左/最右)推导
-- 正则文法/上下文无关文法和图灵机之间计算表达能力的差异
+一种方法是模拟动态运行过程,只要知道关键调用时的字符串,就能分析出结果:
-我们进一步定义一个语言`L(realizable)`,右侧黄色框中的4个字符串都是语言L的一部分。
+
-这里默认读者学习过上下文无关语言(context-free language)相关的知识(编译原理和计算理论几乎是每个学校计算机系的必修课)。具体来说,你应该知道:
+## How to Analyze It
-- 终结符(nonterminal)
-- 非终结符(terminal)
-- 空串符号$$ \epsilon$$
-- (最左/最右)推导
-- 正则文法/上下文无关文法和图灵机之间计算表达能力的差异
+一种方法是模拟动态运行过程,只要知道关键调用时的字符串,就能分析出结果:
-我们进一步定义一个语言`L(realizable)`,右侧黄色框中的4个字符串都是语言L的一部分。
+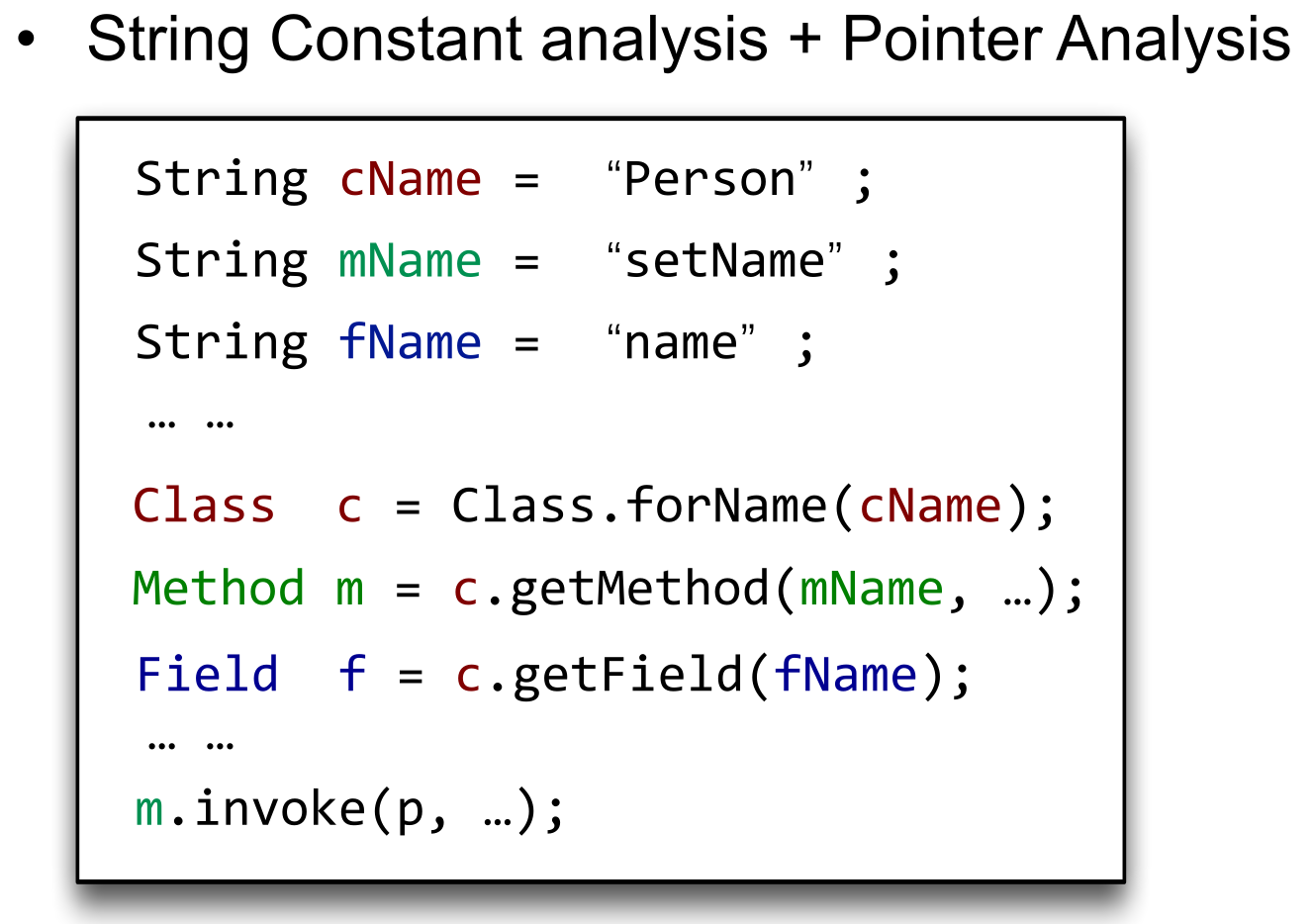 -
- +**吗?**
-还是太抽象了!我们拿两个例子来看看:
+
+**吗?**
-还是太抽象了!我们拿两个例子来看看:
+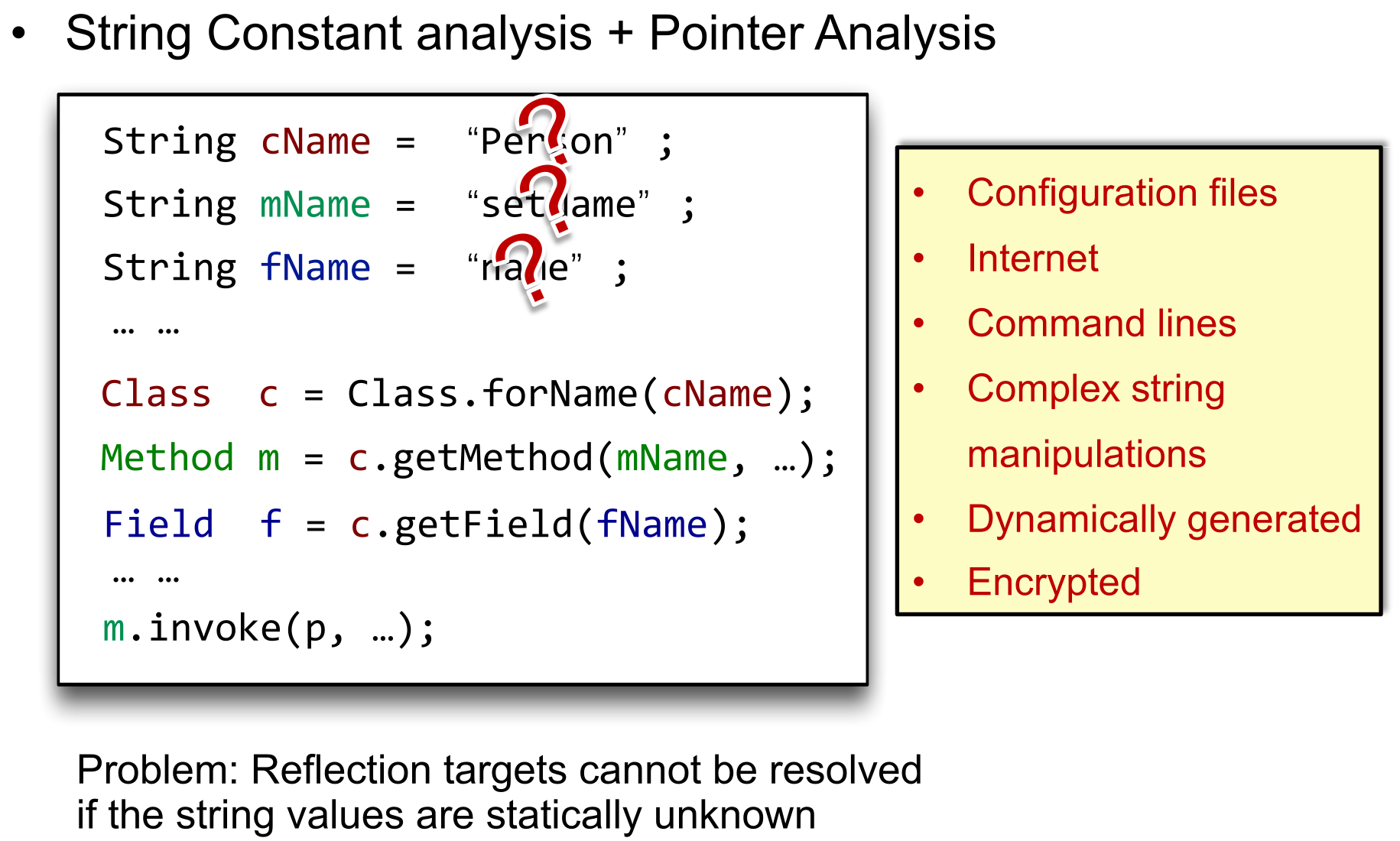 -
- +因为有太多的因素(见右边黄框内容)可能会影响到字符串的值,而其中很多是无法静态确定的。基于字符串常量的分析此时并不奏效……
-图中绿色标记的Call Edge和Return Edge分别是字符串中的$$ (_1$$和$$ )_1$$,而其他的边则是字符串中的e。
+## Real research paper
-看完一个属于L的例子,再来一个不属于L的例子:
+
+因为有太多的因素(见右边黄框内容)可能会影响到字符串的值,而其中很多是无法静态确定的。基于字符串常量的分析此时并不奏效……
-图中绿色标记的Call Edge和Return Edge分别是字符串中的$$ (_1$$和$$ )_1$$,而其他的边则是字符串中的e。
+## Real research paper
-看完一个属于L的例子,再来一个不属于L的例子:
+ -
- +这来源于一个巧妙的观察:
-# Overview of IFDS
+> When string arguments cannot be resolved statically, **infer the reflective targets at their usage points**!
-> “Precise Interprocedural Dataflow Analysis via Graph Reachability”
->
-> --Thomas Reps, Susan Horwitz, and Mooly Sagiv, POPL’95
+getClass获得Class的Metaobject。
-所谓IFDS,其实是四个单词(Interprocedural, Finite, Distributive, Subset)的缩写。如果一个问题满足这四个性质,则可以用相应的框架来解决问题。
+这里的cmd是动态的命令,静态时无法分析……
-复习两个旧概念,介绍一个新概念:
+
+这来源于一个巧妙的观察:
-# Overview of IFDS
+> When string arguments cannot be resolved statically, **infer the reflective targets at their usage points**!
-> “Precise Interprocedural Dataflow Analysis via Graph Reachability”
->
-> --Thomas Reps, Susan Horwitz, and Mooly Sagiv, POPL’95
+getClass获得Class的Metaobject。
-所谓IFDS,其实是四个单词(Interprocedural, Finite, Distributive, Subset)的缩写。如果一个问题满足这四个性质,则可以用相应的框架来解决问题。
+这里的cmd是动态的命令,静态时无法分析……
-复习两个旧概念,介绍一个新概念:
+ -- `Path Function`
+但是!在篮圈处的调用中,由于只传入parameter这一个参数,而在155行我们已经知道其类型就是``FrameworkCommandInterpreter`(或其子类/父类)。
- - > Path function for path p, denoted as $$ pf_p$$, is a composition of flow functions for all edges (sometimes nodes) on p
+
-- `Path Function`
+但是!在篮圈处的调用中,由于只传入parameter这一个参数,而在155行我们已经知道其类型就是``FrameworkCommandInterpreter`(或其子类/父类)。
- - > Path function for path p, denoted as $$ pf_p$$, is a composition of flow functions for all edges (sometimes nodes) on p
+ - - 可以理解按照顺序,先后应用一条path上edge/node的transfer function:
+
- - 可以理解按照顺序,先后应用一条path上edge/node的transfer function:
+ - -
- -  +此外也有和动态分析结合的方法:
-- `Meet-Over-All-Paths(MOP)`
+
+此外也有和动态分析结合的方法:
-- `Meet-Over-All-Paths(MOP)`
+ - - > For each node n, MOP n provides a “meet-over-all-paths” solution where Paths(start, n) denotes the set of paths in CFG from the start node to n.
+# Hard Language Feature: Native Code
- - 即对所有的开始点start,都以bottom作为path function的输入,并在终点n处对所有的结果做meet操作。
+## Native Code
- -
- - > For each node n, MOP n provides a “meet-over-all-paths” solution where Paths(start, n) denotes the set of paths in CFG from the start node to n.
+# Hard Language Feature: Native Code
- - 即对所有的开始点start,都以bottom作为path function的输入,并在终点n处对所有的结果做meet操作。
+## Native Code
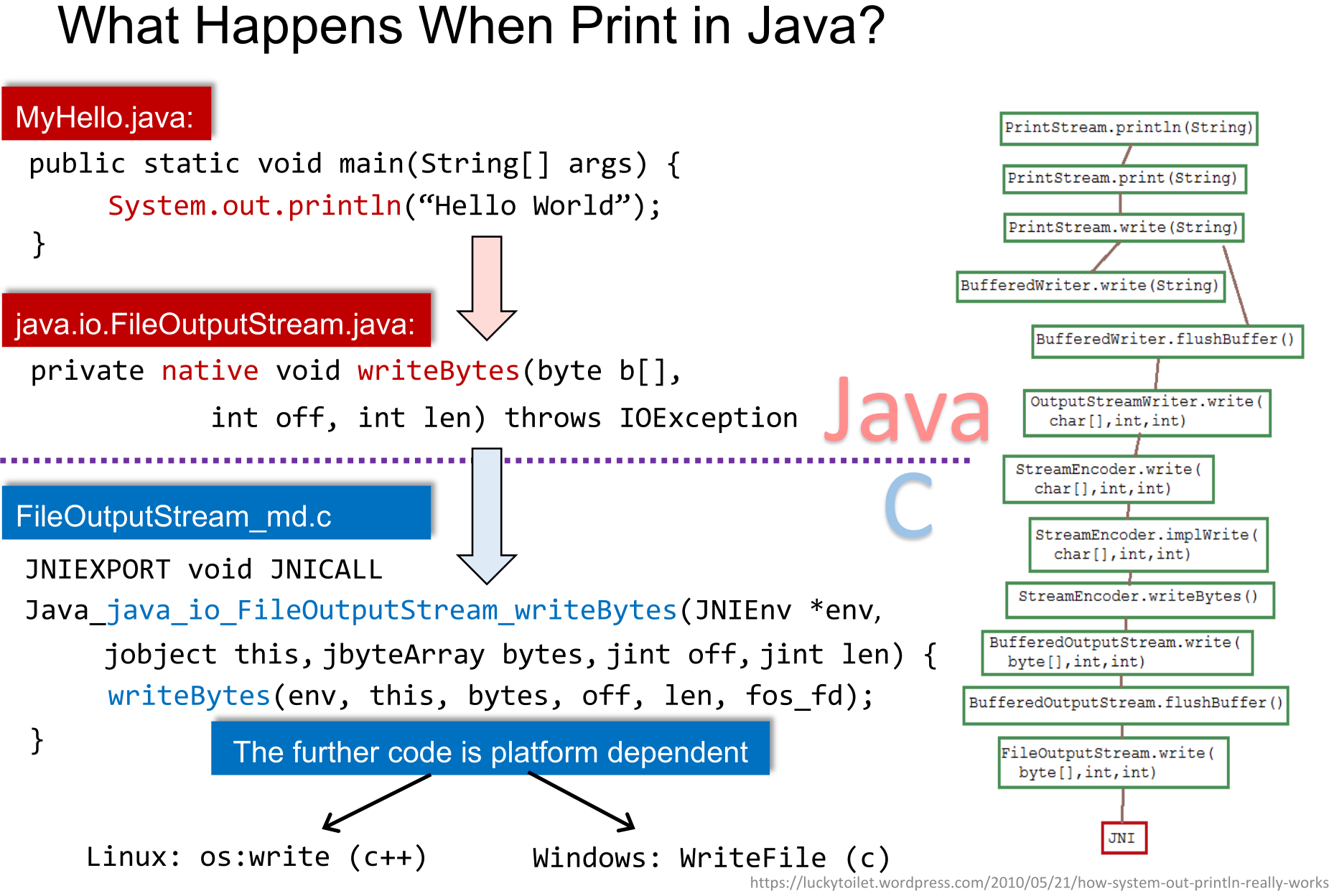
- -  +在Java中,一句简单的`println`最后会调用**与底层平台相关的C或C++代码**,这些代码就称为Native Code。Java也借此实现了 `Run anywhere`的目标。
-- `Meet-Over-All-Realizable-Paths(MRP)`
+
+在Java中,一句简单的`println`最后会调用**与底层平台相关的C或C++代码**,这些代码就称为Native Code。Java也借此实现了 `Run anywhere`的目标。
-- `Meet-Over-All-Realizable-Paths(MRP)`
+ - - > For each node n, MRP n provides a “meet-over-all-realizable-paths” solution where RPaths(start, n) denotes the set of realizable paths (the path’s word is in the language L(realizable)) from the start node to n.
+### Java Native Interface(JNI)
- - 在前者概念的基础上限制Meet的对象为Realizable-Path
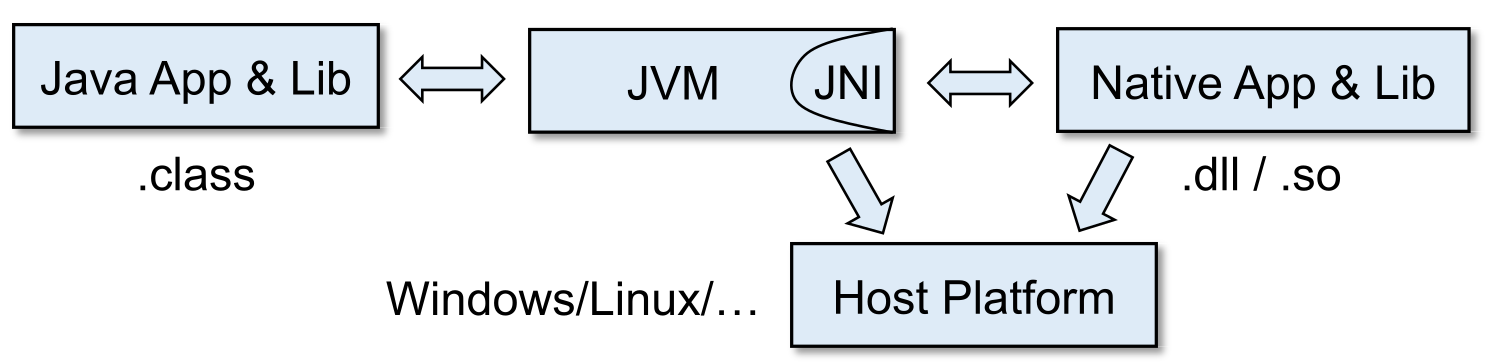
+JNI允许JVM与Native Code写出的Native Lib交互。进而提供与OS交互、提高性能和代码复用(指在Java中使用别的C/C++编写的libraries)的功能。
- -
- - > For each node n, MRP n provides a “meet-over-all-realizable-paths” solution where RPaths(start, n) denotes the set of realizable paths (the path’s word is in the language L(realizable)) from the start node to n.
+### Java Native Interface(JNI)
- - 在前者概念的基础上限制Meet的对象为Realizable-Path
+JNI允许JVM与Native Code写出的Native Lib交互。进而提供与OS交互、提高性能和代码复用(指在Java中使用别的C/C++编写的libraries)的功能。
- -  +
+ ----
+## Why Native Code is Hard
-接下来要讲一些比较难懂的内容~~战术喝水~~。
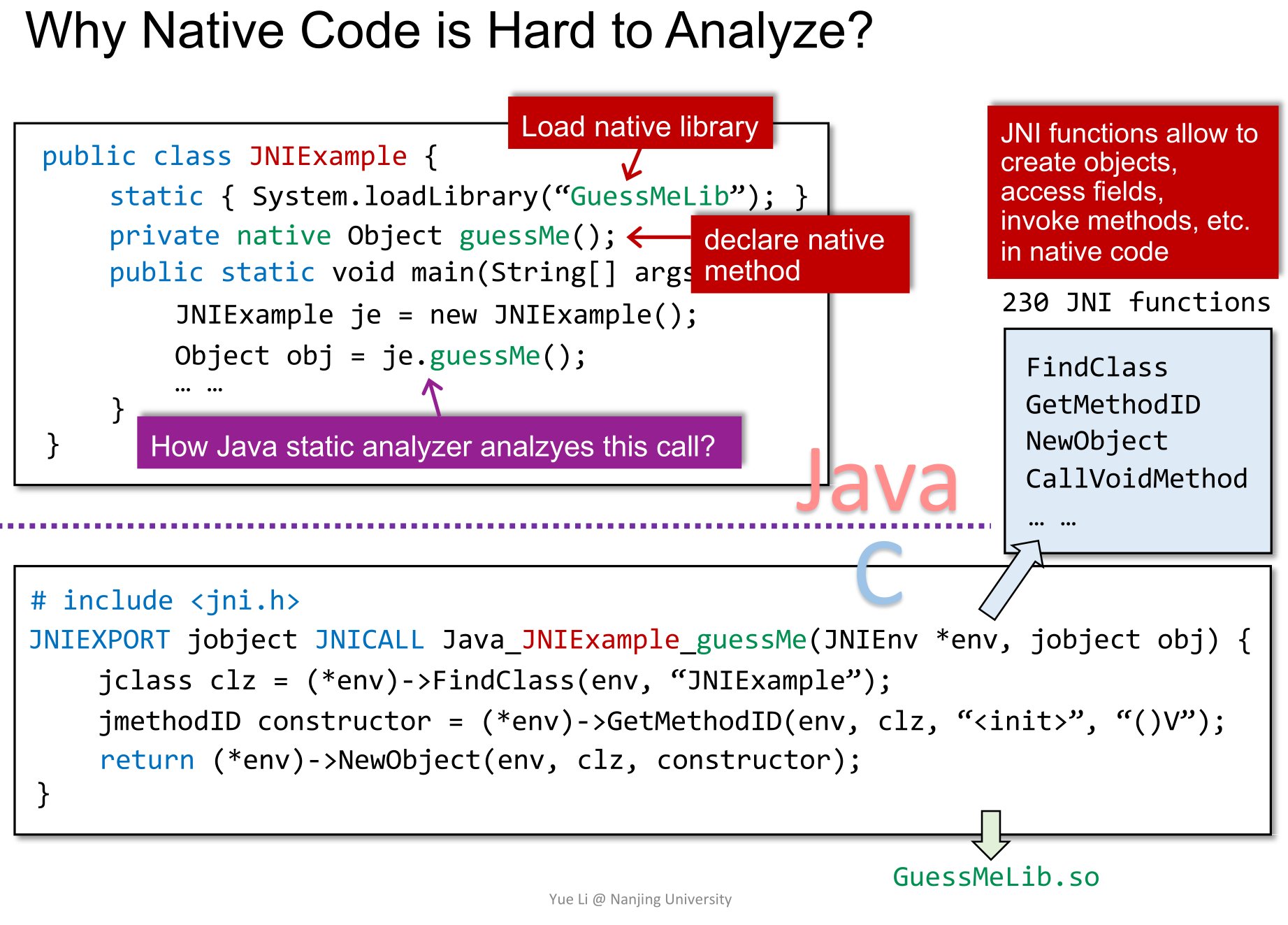
+为了使用Native Library中的一个Method,需要经过这些步骤:
-
----
+## Why Native Code is Hard
-接下来要讲一些比较难懂的内容~~战术喝水~~。
+为了使用Native Library中的一个Method,需要经过这些步骤:
- +1. 用C/C++按照标准写一个库并编译生成`*.so`文件
+2. 在Java中加载Native Library
+3. 在Java中声明Native Method
+4. 调用Native Method
-# Supergraph and Flow Functions
+然而:
-## Supergraph
+1. 类似的JNI可提供的操作有230种(在2020年如此)
+2. 由此引出紫框中的问题:`如何分析Native Call?`
-可以理解成IFDS分析体系下的ICFG(Interprocedural Control Flow Graph,即过程间控制流图)。这里只需要了解一下其中的三种edge(图中的G*即指supergraph):
+
+1. 用C/C++按照标准写一个库并编译生成`*.so`文件
+2. 在Java中加载Native Library
+3. 在Java中声明Native Method
+4. 调用Native Method
-# Supergraph and Flow Functions
+然而:
-## Supergraph
+1. 类似的JNI可提供的操作有230种(在2020年如此)
+2. 由此引出紫框中的问题:`如何分析Native Call?`
-可以理解成IFDS分析体系下的ICFG(Interprocedural Control Flow Graph,即过程间控制流图)。这里只需要了解一下其中的三种edge(图中的G*即指supergraph):
+ -
- +### Current Practice & More
-## Design Flow Functions
+接下来介绍一个现有的解决方法,然后给新的拓展阅读方向。~~对,本次讲的都是前沿内容。~~
-定义`Possibly-uninitialized variables`:
+
+### Current Practice & More
-## Design Flow Functions
+接下来介绍一个现有的解决方法,然后给新的拓展阅读方向。~~对,本次讲的都是前沿内容。~~
-定义`Possibly-uninitialized variables`:
+ -> **For each node n** ∈ N*, determine **the set of variables that may be uninitialized** before execution reaches n.
+arraycopy(src,3,dest,4,5)就是从src的第三个元素起,拷贝起始位置是dest的第四个元素,总共拷贝5个元素。
-我们接下来的例子求的就是这样的变量。
+如果不分析Native Code,我们就会失去很多信息。而Modeling的分析方法是:
-### lambda expression
+- 先将其副作用用Java代码表示出来(图中第一个方框)
+- 然后用指针分析的方法进一步抽象其副作用(图中第二个方框)
-为了后续叙述方便,这里简单地介绍一下lambda表达式。
+
-> **For each node n** ∈ N*, determine **the set of variables that may be uninitialized** before execution reaches n.
+arraycopy(src,3,dest,4,5)就是从src的第三个元素起,拷贝起始位置是dest的第四个元素,总共拷贝5个元素。
-我们接下来的例子求的就是这样的变量。
+如果不分析Native Code,我们就会失去很多信息。而Modeling的分析方法是:
-### lambda expression
+- 先将其副作用用Java代码表示出来(图中第一个方框)
+- 然后用指针分析的方法进一步抽象其副作用(图中第二个方框)
-为了后续叙述方便,这里简单地介绍一下lambda表达式。
+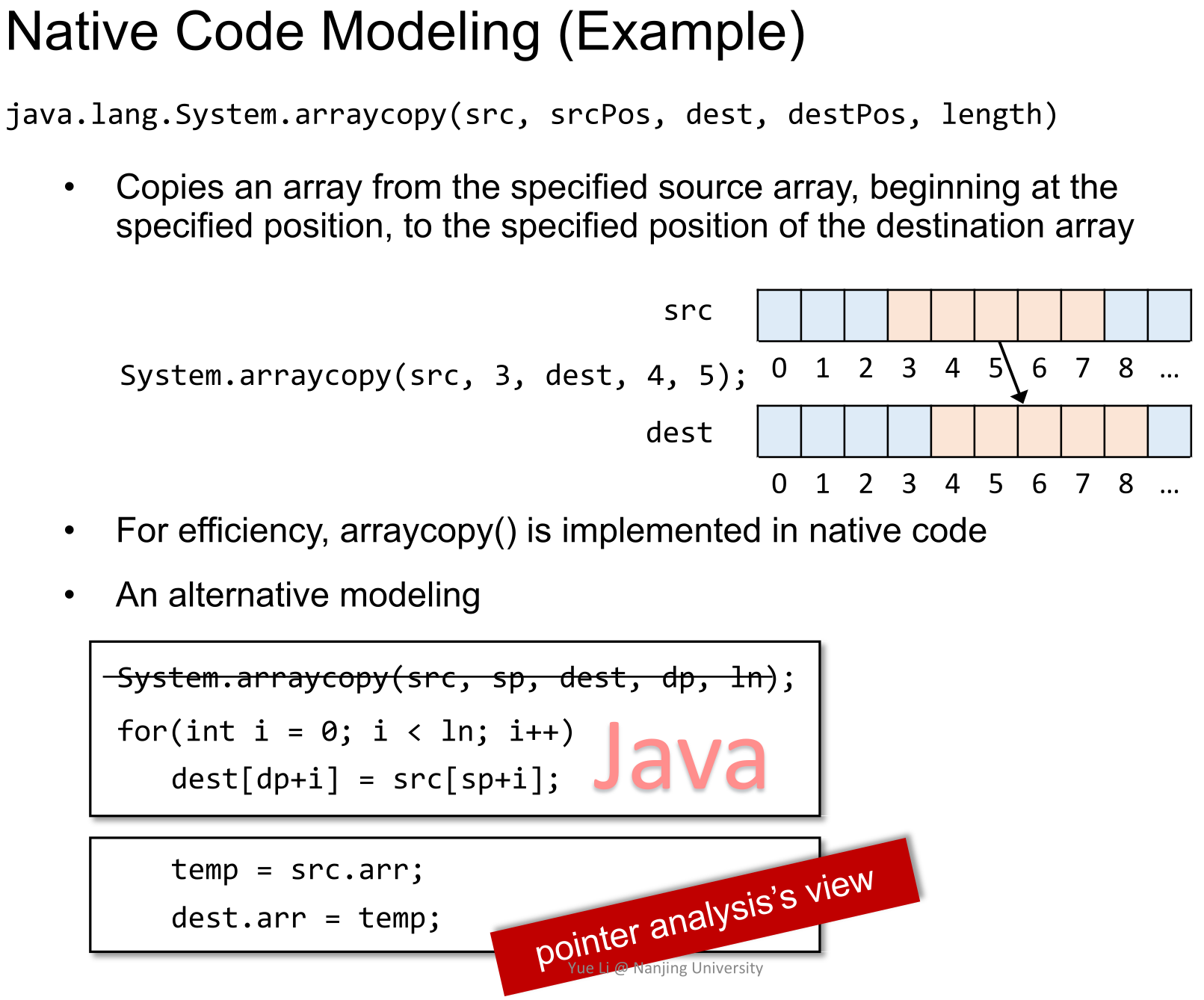 -以$$ \lambda$$标识一个lambda表达式,从开头到中间点间的符号代表**参数列表**,从中间点到最后的符号代表**函数体**。如下例子,就代表这样一个函数调用:
+如果对Soundiness感兴趣,推荐网站http://soundiness.org
-- 函数以x作为输入参数
-- 函数返回值为x+1
-- 调用函数时传入的参数为3
+
-以$$ \lambda$$标识一个lambda表达式,从开头到中间点间的符号代表**参数列表**,从中间点到最后的符号代表**函数体**。如下例子,就代表这样一个函数调用:
+如果对Soundiness感兴趣,推荐网站http://soundiness.org
-- 函数以x作为输入参数
-- 函数返回值为x+1
-- 调用函数时传入的参数为3
+ -
- +# Key Points
-### Example of Flow Functions
-
-在进入main后,全局变量g和局部变量x一定是没有初始化的。
-
-
+# Key Points
-### Example of Flow Functions
-
-在进入main后,全局变量g和局部变量x一定是没有初始化的。
-
- -
-随后x被初始化:
-
-
-
-随后x被初始化:
-
- -
-以x来初始化a,a是否被初始化与x一致。
-
-
-
-以x来初始化a,a是否被初始化与x一致。
-
- -
-这个函数比较奇妙,它表达的意思是:如果a和g都被初始化了,则a是被初始化的,否则认为a没有被初始化。
-
-
-
-这个函数比较奇妙,它表达的意思是:如果a和g都被初始化了,则a是被初始化的,否则认为a没有被初始化。
-
- -
-注意左侧以红色标记的函数,这样写能够使得在$$ Ret_p$$处g是否已经被赋值/初始化取决于是否在被调用函数中被赋值。
-
-
-
-注意左侧以红色标记的函数,这样写能够使得在$$ Ret_p$$处g是否已经被赋值/初始化取决于是否在被调用函数中被赋值。
-
- 
-
-这里涉及一个特殊的情况,由于离开了函数,所以要去除函数内部变量a。
-
-

-
-这里涉及一个特殊的情况,由于离开了函数,所以要去除函数内部变量a。
-
- -
-# Exploded Supergraph and Tabulation Algorithm
-
-## Build Exploded Supergraph
-
-Flow Function对应着二元关系。
-
-
-
-# Exploded Supergraph and Tabulation Algorithm
-
-## Build Exploded Supergraph
-
-Flow Function对应着二元关系。
-
- -
-直接从左到右解释例子:
-
-1. 输出和输入完全一致
-2. 无论输入为什么,输出都包含a
-3. 输出一定不包含a,且一定包含b,其他变量(这里是c)则保持不变
-4. 如果输入包含a,则输出一定包含b;否则一定不包含b
-
-你是否也觉得上面例子中0->0这条边挺奇怪的?它的存在是被刻意设计的。因为IFDS主要依赖于可达性(reachability)做分析。如果没有这样的边,在IFDS中没有办法判断在n4这个点处,a是否满足某种性质。
-
-
-
-直接从左到右解释例子:
-
-1. 输出和输入完全一致
-2. 无论输入为什么,输出都包含a
-3. 输出一定不包含a,且一定包含b,其他变量(这里是c)则保持不变
-4. 如果输入包含a,则输出一定包含b;否则一定不包含b
-
-你是否也觉得上面例子中0->0这条边挺奇怪的?它的存在是被刻意设计的。因为IFDS主要依赖于可达性(reachability)做分析。如果没有这样的边,在IFDS中没有办法判断在n4这个点处,a是否满足某种性质。
-
- -
-而加上这条总是存在的Glue Edge之后,就可以满足IFDS分析的要求。
-
-
-
-而加上这条总是存在的Glue Edge之后,就可以满足IFDS分析的要求。
-
- -
-回到我们之前的例子,用新的二元关系的视角去**手动分析**,将会是这样(视频之后会做的会做的~~吧~~,咕!):
-
-标黄部分比较重要,它的意思是:如果a或g一开始没有被初始化,则a都没有被初始化。
-
-
-
-回到我们之前的例子,用新的二元关系的视角去**手动分析**,将会是这样(视频之后会做的会做的~~吧~~,咕!):
-
-标黄部分比较重要,它的意思是:如果a或g一开始没有被初始化,则a都没有被初始化。
-
- -
-最后构造出来的Exploded Supergraph是这样的:
-
-
-
-最后构造出来的Exploded Supergraph是这样的:
-
- -
-怎样使用这样的分析结果呢?我们来考虑一个问题,全局变量g在程序片段运行结束时,是否可能没有被初始化?
-
-
-
-怎样使用这样的分析结果呢?我们来考虑一个问题,全局变量g在程序片段运行结束时,是否可能没有被初始化?
-
- -
-结果是,g在这里可能没有被初始化。
-
-
-
-结果是,g在这里可能没有被初始化。
-
- -
-而之前提到的realizable path在这里也能提供更高的精度。
-
-
-
-而之前提到的realizable path在这里也能提供更高的精度。
-
- -
-
-
- -
-## Tabulation Algorithm
-
-刚才我们是手动分析的,而用Tabulation算法,可以在$$ O(ED^3)$$复杂度(E为Edge的数量,D为Data facts的数量,如在下面的例子中,D为3)下得到MRP的结果:
-
-
-
-## Tabulation Algorithm
-
-刚才我们是手动分析的,而用Tabulation算法,可以在$$ O(ED^3)$$复杂度(E为Edge的数量,D为Data facts的数量,如在下面的例子中,D为3)下得到MRP的结果:
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-# Understanding the Distributivity of IFDS
-
-这里的Distributivity是指Flow Function的性质,即满足:
-
-$$ \forall(x,y). f(x\cdot y)=f(x)\cdot f(y)$$
-
-- 这样的要求使得我们**无法用IFDS来做常量传播(constant propagation)和指针分析(pointer analysis)**
-- 换句话说,在IFDS中,我们**可以表达逻辑或,但无法表达逻辑与**
-- 更广泛地说,**如果我们需要考虑多个输入来决定输出**,那么由于Distributivity性质没有被满足,**无法用IFDS来解决**。
-
-
-
-# Understanding the Distributivity of IFDS
-
-这里的Distributivity是指Flow Function的性质,即满足:
-
-$$ \forall(x,y). f(x\cdot y)=f(x)\cdot f(y)$$
-
-- 这样的要求使得我们**无法用IFDS来做常量传播(constant propagation)和指针分析(pointer analysis)**
-- 换句话说,在IFDS中,我们**可以表达逻辑或,但无法表达逻辑与**
-- 更广泛地说,**如果我们需要考虑多个输入来决定输出**,那么由于Distributivity性质没有被满足,**无法用IFDS来解决**。
-
- -
-上图最后的问题答案是**可以使用IFDS,因为只需要考虑单一的输入即可决定输出**。
-
-再来看看指针分析的例子:
-
-
-
-上图最后的问题答案是**可以使用IFDS,因为只需要考虑单一的输入即可决定输出**。
-
-再来看看指针分析的例子:
-
- -
-注意图中的虚线部分,由于没有别名(alias)信息,这个边是无法被IFDS框架分析出来的。而IFDS是无法处理别名信息的,因为别名信息的另一种意义是“x和y**都**指向同一个对象”——这需要我们同时考虑x和y来决定他们是否指向同一个对象。
-
-> Note: If we want to obtain alias information in IFDS, say alias(x,y), to produce correct outputs, we need to consider multiple input data facts, x and y, which cannot be done in standard IFDS as **flow functions handle input facts independently (one fact per time). Thus pointer analysis is non-distributive.**
-
-## Key Points
-
-- Understand **CFL-Reachability**
-- Understand **the basic idea** of IFDS
- - 大概知道有几个阶段即可
-- Understand **what problems can be solved** by IFDS
\ No newline at end of file
+- Understand **soundiness: its motivation and concept**
+- Understand why **Java reflection and native** code are hard to analyze
\ No newline at end of file
-
-注意图中的虚线部分,由于没有别名(alias)信息,这个边是无法被IFDS框架分析出来的。而IFDS是无法处理别名信息的,因为别名信息的另一种意义是“x和y**都**指向同一个对象”——这需要我们同时考虑x和y来决定他们是否指向同一个对象。
-
-> Note: If we want to obtain alias information in IFDS, say alias(x,y), to produce correct outputs, we need to consider multiple input data facts, x and y, which cannot be done in standard IFDS as **flow functions handle input facts independently (one fact per time). Thus pointer analysis is non-distributive.**
-
-## Key Points
-
-- Understand **CFL-Reachability**
-- Understand **the basic idea** of IFDS
- - 大概知道有几个阶段即可
-- Understand **what problems can be solved** by IFDS
\ No newline at end of file
+- Understand **soundiness: its motivation and concept**
+- Understand why **Java reflection and native** code are hard to analyze
\ No newline at end of file
 -## Rule Satety
+## Rule Safety
讲到这里,停下来思考一下,这两条Rules看起来有什么问题吗?
@@ -133,8 +133,8 @@ Datalog使用规则来进行推导(inference),其定义如下:
Datalog的两大重要特性:
-- 单调性。因为事实(facts)不会被删除的。
-- 必然终止。
+- Monotonicity: 因为事实(facts)不会被删除的。
+- Termination:
- 事实的数量是**单调**的。
- 由Rule Safety,所能得到的IDB的大小也是**有限**的。
@@ -150,7 +150,7 @@ Datalog的两大重要特性:
和之前一样,我们把Call放到最后处理。
-## Datalog Model-EDB&IDB
+## Datalog Model-EDB & IDB
我们首先需要对前四条语句建模。输入的EDB代表了4个存储相应类型语句的table,输出为Variable和Field的指向关系。
@@ -252,14 +252,22 @@ e = d.f;
# Key Points
-- Pros
- - **Succinct** and **readable**
- - **Easy** to implement
- - **Benefit from off-the-shelf optimized Datalog engines**
-- Cons
- - **Restricted expressiveness**, i.e., it is impossible or inconvenient to express some logics
- - Cannot fully control **performance**
-- Overall Review
- - **Datalog** language
- - How to implement **pointer analysis via Datalog**
- - How to implement **taint analysis via Datalog**
\ No newline at end of file
+DataLog:
+
+- Pros
+
+ - **Succinct** and **readable**
+ - **Easy** to implement
+ - **Benefit from off-the-shelf optimized Datalog engines**
+
+- Cons
+ - **Restricted expressiveness**, i.e., it is impossible or inconvenient to express some logics
+ - Cannot fully control **performance**
+
+
+
+ Overall Review
+
+ - **Datalog** language
+ - How to implement **pointer analysis via Datalog**
+ - How to implement **taint analysis via Datalog**
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/Static-Analysis/11-CFL-Reachability and IFDS.md b/docs/Static-Analysis/11-CFL-Reachability and IFDS.md
index 9f1a949..7d3578a 100644
--- a/docs/Static-Analysis/11-CFL-Reachability and IFDS.md
+++ b/docs/Static-Analysis/11-CFL-Reachability and IFDS.md
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
# CFL-Reachability and IFDS
-前排提醒:如果你已经忘记了**数据流分析理论基础**部分的内容,请务必去复习一下再读本文。具体来说,你应该能够回忆起:
+前排提醒:如果你已经忘记了**数据流分析理论基础**部分的内容,请务必去复习一下再读本文具体来说,你应该能够回忆起:
- Meet/Join
- Transfer function
@@ -8,24 +8,14 @@
---
-标题看起来有点吓人,不过我们可以简单地描述一下即将要讲述的内容:
> IFDS是一种分析框架,在这种框架下,分析的数据流是满足CFL-Reachability这一性质的。
-本课主要内容如下:
-
-1. Feasible and Realizable Paths
-2. CFL-Reachability
-3. Overview of IFDS
-4. Supergraph and Flow Functions
-5. Exploded Supergraph and Tabulation Algorithm
-6. Understanding the Distributivity of IFDS
-
-# Feasible and Realizable Paths
+## Feasible and Realizable Paths
实际分析时,JDK中一个方法能产生的CFG是非常复杂的。不过,并非所有的路径都会被执行到,一个很自然的想法是,只分析可能被执行的路径。
-
-## Rule Satety
+## Rule Safety
讲到这里,停下来思考一下,这两条Rules看起来有什么问题吗?
@@ -133,8 +133,8 @@ Datalog使用规则来进行推导(inference),其定义如下:
Datalog的两大重要特性:
-- 单调性。因为事实(facts)不会被删除的。
-- 必然终止。
+- Monotonicity: 因为事实(facts)不会被删除的。
+- Termination:
- 事实的数量是**单调**的。
- 由Rule Safety,所能得到的IDB的大小也是**有限**的。
@@ -150,7 +150,7 @@ Datalog的两大重要特性:
和之前一样,我们把Call放到最后处理。
-## Datalog Model-EDB&IDB
+## Datalog Model-EDB & IDB
我们首先需要对前四条语句建模。输入的EDB代表了4个存储相应类型语句的table,输出为Variable和Field的指向关系。
@@ -252,14 +252,22 @@ e = d.f;
# Key Points
-- Pros
- - **Succinct** and **readable**
- - **Easy** to implement
- - **Benefit from off-the-shelf optimized Datalog engines**
-- Cons
- - **Restricted expressiveness**, i.e., it is impossible or inconvenient to express some logics
- - Cannot fully control **performance**
-- Overall Review
- - **Datalog** language
- - How to implement **pointer analysis via Datalog**
- - How to implement **taint analysis via Datalog**
\ No newline at end of file
+DataLog:
+
+- Pros
+
+ - **Succinct** and **readable**
+ - **Easy** to implement
+ - **Benefit from off-the-shelf optimized Datalog engines**
+
+- Cons
+ - **Restricted expressiveness**, i.e., it is impossible or inconvenient to express some logics
+ - Cannot fully control **performance**
+
+
+
+ Overall Review
+
+ - **Datalog** language
+ - How to implement **pointer analysis via Datalog**
+ - How to implement **taint analysis via Datalog**
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/Static-Analysis/11-CFL-Reachability and IFDS.md b/docs/Static-Analysis/11-CFL-Reachability and IFDS.md
index 9f1a949..7d3578a 100644
--- a/docs/Static-Analysis/11-CFL-Reachability and IFDS.md
+++ b/docs/Static-Analysis/11-CFL-Reachability and IFDS.md
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
# CFL-Reachability and IFDS
-前排提醒:如果你已经忘记了**数据流分析理论基础**部分的内容,请务必去复习一下再读本文。具体来说,你应该能够回忆起:
+前排提醒:如果你已经忘记了**数据流分析理论基础**部分的内容,请务必去复习一下再读本文具体来说,你应该能够回忆起:
- Meet/Join
- Transfer function
@@ -8,24 +8,14 @@
---
-标题看起来有点吓人,不过我们可以简单地描述一下即将要讲述的内容:
> IFDS是一种分析框架,在这种框架下,分析的数据流是满足CFL-Reachability这一性质的。
-本课主要内容如下:
-
-1. Feasible and Realizable Paths
-2. CFL-Reachability
-3. Overview of IFDS
-4. Supergraph and Flow Functions
-5. Exploded Supergraph and Tabulation Algorithm
-6. Understanding the Distributivity of IFDS
-
-# Feasible and Realizable Paths
+## Feasible and Realizable Paths
实际分析时,JDK中一个方法能产生的CFG是非常复杂的。不过,并非所有的路径都会被执行到,一个很自然的想法是,只分析可能被执行的路径。
- +
虽然并非所有的路径都会被执行到。**可是`判断一条路径是否feasible`本身是不可判定(undecidable)的。**
@@ -47,8 +37,7 @@
> The paths in which “returns” are matched with corresponding “calls”.
-- Realizable paths may not be executable, but unrealizable paths
- must not be executable.
+- Realizable paths may not be executable, but unrealizable paths must not be executable.
- 可以把executable/feasible path看作realizable path的真子集
- Our goal is to **recognize realizable paths** so that we could avoid polluting analysis results along unrealizable paths.
- 这个问题和括号匹配问题本质上是一样的。
@@ -57,11 +46,11 @@
+
虽然并非所有的路径都会被执行到。**可是`判断一条路径是否feasible`本身是不可判定(undecidable)的。**
@@ -47,8 +37,7 @@
> The paths in which “returns” are matched with corresponding “calls”.
-- Realizable paths may not be executable, but unrealizable paths
- must not be executable.
+- Realizable paths may not be executable, but unrealizable paths must not be executable.
- 可以把executable/feasible path看作realizable path的真子集
- Our goal is to **recognize realizable paths** so that we could avoid polluting analysis results along unrealizable paths.
- 这个问题和括号匹配问题本质上是一样的。
@@ -57,11 +46,11 @@
 -# CFL-Reachability
+## CFL-Reachability
> A path is considered to connect two nodes A and B, or **B is reachable from A**, only if **the concatenation of the labels on the edges of the path is a word in a specified context-free language.**
-这里默认读者学习过上下文无关语言(context-free language)相关的知识(编译原理和计算理论几乎是每个学校计算机系的必修课)。具体来说,你应该知道:
+这里默认读者学习过上下文无关语言(context-free language)相关的知识。具体来说,你应该知道:
- 终结符(nonterminal)
- 非终结符(terminal)
@@ -69,7 +58,7 @@
- (最左/最右)推导
- 正则文法/上下文无关文法和图灵机之间计算表达能力的差异
-我们进一步定义一个语言`L(realizable)`,右侧黄色框中的4个字符串都是语言L的一部分。
+我们进一步定义一个语言`L(realizable)`,右侧黄色框中的4个字符串都是语言L的一部分
-# CFL-Reachability
+## CFL-Reachability
> A path is considered to connect two nodes A and B, or **B is reachable from A**, only if **the concatenation of the labels on the edges of the path is a word in a specified context-free language.**
-这里默认读者学习过上下文无关语言(context-free language)相关的知识(编译原理和计算理论几乎是每个学校计算机系的必修课)。具体来说,你应该知道:
+这里默认读者学习过上下文无关语言(context-free language)相关的知识。具体来说,你应该知道:
- 终结符(nonterminal)
- 非终结符(terminal)
@@ -69,7 +58,7 @@
- (最左/最右)推导
- 正则文法/上下文无关文法和图灵机之间计算表达能力的差异
-我们进一步定义一个语言`L(realizable)`,右侧黄色框中的4个字符串都是语言L的一部分。
+我们进一步定义一个语言`L(realizable)`,右侧黄色框中的4个字符串都是语言L的一部分
 @@ -83,13 +72,16 @@
@@ -83,13 +72,16 @@
 -# Overview of IFDS
+## Overview of IFDS
> “Precise Interprocedural Dataflow Analysis via Graph Reachability”
>
-> --Thomas Reps, Susan Horwitz, and Mooly Sagiv, POPL’95
+> --Thomas Reps, Susan Horwitz, and Mooly Sagiv, POPL’95
+
+IFDS is for interprocedural data flow analysis with **distributive** flow functions over **finite** domains.
-所谓IFDS,其实是四个单词(Interprocedural, Finite, Distributive, Subset)的缩写。如果一个问题满足这四个性质,则可以用相应的框架来解决问题。
+所谓IFDS,其实是四个单词(Interprocedural, Finite, Distributive, Subset)的缩写。
+如果一个问题满足这四个性质,则可以用相应的框架来解决问题。
复习两个旧概念,介绍一个新概念:
@@ -99,7 +91,7 @@
- 可以理解按照顺序,先后应用一条path上edge/node的transfer function:
- -
-# Overview of IFDS
+## Overview of IFDS
> “Precise Interprocedural Dataflow Analysis via Graph Reachability”
>
-> --Thomas Reps, Susan Horwitz, and Mooly Sagiv, POPL’95
+> --Thomas Reps, Susan Horwitz, and Mooly Sagiv, POPL’95
+
+IFDS is for interprocedural data flow analysis with **distributive** flow functions over **finite** domains.
-所谓IFDS,其实是四个单词(Interprocedural, Finite, Distributive, Subset)的缩写。如果一个问题满足这四个性质,则可以用相应的框架来解决问题。
+所谓IFDS,其实是四个单词(Interprocedural, Finite, Distributive, Subset)的缩写。
+如果一个问题满足这四个性质,则可以用相应的框架来解决问题。
复习两个旧概念,介绍一个新概念:
@@ -99,7 +91,7 @@
- 可以理解按照顺序,先后应用一条path上edge/node的transfer function:
- -  +
+  - `Meet-Over-All-Paths(MOP)`
@@ -119,19 +111,20 @@
---
-接下来要讲一些比较难懂的内容~~战术喝水~~。
-
- `Meet-Over-All-Paths(MOP)`
@@ -119,19 +111,20 @@
---
-接下来要讲一些比较难懂的内容~~战术喝水~~。
-
 -# Supergraph and Flow Functions
+## Supergraph and Flow Functions
+
+### Supergraph
-## Supergraph
+In IFDS, a program is represented by $G^* = (N^*,E^*)$ called a supergraph
-可以理解成IFDS分析体系下的ICFG(Interprocedural Control Flow Graph,即过程间控制流图)。这里只需要了解一下其中的三种edge(图中的G*即指supergraph):
+可以理解成IFDS分析体系下的ICFG(Interprocedural Control Flow Graph,即过程间控制流图)。
+这里只需要了解一下其中的三种edge(图中的G*即指supergraph):
-# Supergraph and Flow Functions
+## Supergraph and Flow Functions
+
+### Supergraph
-## Supergraph
+In IFDS, a program is represented by $G^* = (N^*,E^*)$ called a supergraph
-可以理解成IFDS分析体系下的ICFG(Interprocedural Control Flow Graph,即过程间控制流图)。这里只需要了解一下其中的三种edge(图中的G*即指supergraph):
+可以理解成IFDS分析体系下的ICFG(Interprocedural Control Flow Graph,即过程间控制流图)。
+这里只需要了解一下其中的三种edge(图中的G*即指supergraph):
 -## Design Flow Functions
+### Design Flow Functions
定义`Possibly-uninitialized variables`:
@@ -139,7 +132,7 @@
我们接下来的例子求的就是这样的变量。
-### lambda expression
+#### lambda expression
为了后续叙述方便,这里简单地介绍一下lambda表达式。
@@ -151,7 +144,7 @@
-## Design Flow Functions
+### Design Flow Functions
定义`Possibly-uninitialized variables`:
@@ -139,7 +132,7 @@
我们接下来的例子求的就是这样的变量。
-### lambda expression
+#### lambda expression
为了后续叙述方便,这里简单地介绍一下lambda表达式。
@@ -151,7 +144,7 @@
 -### Example of Flow Functions
+#### Example of Flow Functions
在进入main后,全局变量g和局部变量x一定是没有初始化的。
@@ -177,11 +170,11 @@
-### Example of Flow Functions
+#### Example of Flow Functions
在进入main后,全局变量g和局部变量x一定是没有初始化的。
@@ -177,11 +170,11 @@
 -# Exploded Supergraph and Tabulation Algorithm
+## Exploded Supergraph and Tabulation Algorithm
-## Build Exploded Supergraph
+### Build Exploded Supergraph
-Flow Function对应着二元关系。
+Flow Function对应着二元关系
-# Exploded Supergraph and Tabulation Algorithm
+## Exploded Supergraph and Tabulation Algorithm
-## Build Exploded Supergraph
+### Build Exploded Supergraph
-Flow Function对应着二元关系。
+Flow Function对应着二元关系
 @@ -194,37 +187,35 @@ Flow Function对应着二元关系。
你是否也觉得上面例子中0->0这条边挺奇怪的?它的存在是被刻意设计的。因为IFDS主要依赖于可达性(reachability)做分析。如果没有这样的边,在IFDS中没有办法判断在n4这个点处,a是否满足某种性质。
-
@@ -194,37 +187,35 @@ Flow Function对应着二元关系。
你是否也觉得上面例子中0->0这条边挺奇怪的?它的存在是被刻意设计的。因为IFDS主要依赖于可达性(reachability)做分析。如果没有这样的边,在IFDS中没有办法判断在n4这个点处,a是否满足某种性质。
- +
+ 而加上这条总是存在的Glue Edge之后,就可以满足IFDS分析的要求。
-
而加上这条总是存在的Glue Edge之后,就可以满足IFDS分析的要求。
- +
+ -回到我们之前的例子,用新的二元关系的视角去**手动分析**,将会是这样(视频之后会做的会做的~~吧~~,咕!):
+回到我们之前的例子,用新的二元关系的视角去**手动分析**,将会是这样:
标黄部分比较重要,它的意思是:如果a或g一开始没有被初始化,则a都没有被初始化。
-
-回到我们之前的例子,用新的二元关系的视角去**手动分析**,将会是这样(视频之后会做的会做的~~吧~~,咕!):
+回到我们之前的例子,用新的二元关系的视角去**手动分析**,将会是这样:
标黄部分比较重要,它的意思是:如果a或g一开始没有被初始化,则a都没有被初始化。
- +
+ 最后构造出来的Exploded Supergraph是这样的:
-
最后构造出来的Exploded Supergraph是这样的:
- +
+ 怎样使用这样的分析结果呢?我们来考虑一个问题,全局变量g在程序片段运行结束时,是否可能没有被初始化?
-
怎样使用这样的分析结果呢?我们来考虑一个问题,全局变量g在程序片段运行结束时,是否可能没有被初始化?
- +
+ 结果是,g在这里可能没有被初始化。
-
结果是,g在这里可能没有被初始化。
- +
+ 而之前提到的realizable path在这里也能提供更高的精度。
-
而之前提到的realizable path在这里也能提供更高的精度。
- -
-
-
- +
+
 -## Tabulation Algorithm
+### Tabulation Algorithm
刚才我们是手动分析的,而用Tabulation算法,可以在$$ O(ED^3)$$复杂度(E为Edge的数量,D为Data facts的数量,如在下面的例子中,D为3)下得到MRP的结果:
@@ -234,7 +225,7 @@ Flow Function对应着二元关系。
-## Tabulation Algorithm
+### Tabulation Algorithm
刚才我们是手动分析的,而用Tabulation算法,可以在$$ O(ED^3)$$复杂度(E为Edge的数量,D为Data facts的数量,如在下面的例子中,D为3)下得到MRP的结果:
@@ -234,7 +225,7 @@ Flow Function对应着二元关系。
 -# Understanding the Distributivity of IFDS
+## Understanding the Distributivity of IFDS
这里的Distributivity是指Flow Function的性质,即满足:
diff --git a/docs/Static-Analysis/12-Soundness and Soundiness.md b/docs/Static-Analysis/12-Soundness and Soundiness.md
index 9f29ed3..504837d 100644
--- a/docs/Static-Analysis/12-Soundness and Soundiness.md
+++ b/docs/Static-Analysis/12-Soundness and Soundiness.md
@@ -1,264 +1,151 @@
-# CFL-Reachability and IFDS
+# Soundiness
-前排提醒:如果你已经忘记了**数据流分析理论基础**部分的内容,请务必去复习一下再读本文。具体来说,你应该能够回忆起:
+在时间中很难实现sound的算法,所以专家们提出一个与Soundness不同的概念Soundiness。(关于Soundness,可以回顾B站上的前两节课)。
-- Meet/Join
-- Transfer function
-- Bottom/Top
+本文主要内容如下:
----
+1. Soundness and Soundiness
+2. Hard Language Feature: Java Reflection
+3. Hard Language Feature: Native Code
-标题看起来有点吓人,不过我们可以简单地描述一下即将要讲述的内容:
+# Soundness and Soundiness
-> IFDS是一种分析框架,在这种框架下,分析的数据流是满足CFL-Reachability这一性质的。
+回顾Soundness的定义(没有漏报bug就是sound):
-本课主要内容如下:
+> **Conservative** approximation: the analysis **captures all program behaviors**, or the analysis result **models all possible executions** of the program.
-1. Feasible and Realizable Paths
-2. CFL-Reachability
-3. Overview of IFDS
-4. Supergraph and Flow Functions
-5. Exploded Supergraph and Tabulation Algorithm
-6. Understanding the Distributivity of IFDS
+无论是学术界还是工业界的算法,都是不完全sound的。
-# Feasible and Realizable Paths
+这是由于很多语言拥有的部分高级特性对于静态分析来说是难以分析的:
-实际分析时,JDK中一个方法能产生的CFG是非常复杂的。不过,并非所有的路径都会被执行到,一个很自然的想法是,只分析可能被执行的路径。
+- Java
+ - Reflection, native code, dynamic class loading, etc.
+- JavaScript
+ - eval, document object model (DOM), etc.
+- C/C++
+ - Pointer arithmetic, function pointers, etc.
-
-# Understanding the Distributivity of IFDS
+## Understanding the Distributivity of IFDS
这里的Distributivity是指Flow Function的性质,即满足:
diff --git a/docs/Static-Analysis/12-Soundness and Soundiness.md b/docs/Static-Analysis/12-Soundness and Soundiness.md
index 9f29ed3..504837d 100644
--- a/docs/Static-Analysis/12-Soundness and Soundiness.md
+++ b/docs/Static-Analysis/12-Soundness and Soundiness.md
@@ -1,264 +1,151 @@
-# CFL-Reachability and IFDS
+# Soundiness
-前排提醒:如果你已经忘记了**数据流分析理论基础**部分的内容,请务必去复习一下再读本文。具体来说,你应该能够回忆起:
+在时间中很难实现sound的算法,所以专家们提出一个与Soundness不同的概念Soundiness。(关于Soundness,可以回顾B站上的前两节课)。
-- Meet/Join
-- Transfer function
-- Bottom/Top
+本文主要内容如下:
----
+1. Soundness and Soundiness
+2. Hard Language Feature: Java Reflection
+3. Hard Language Feature: Native Code
-标题看起来有点吓人,不过我们可以简单地描述一下即将要讲述的内容:
+# Soundness and Soundiness
-> IFDS是一种分析框架,在这种框架下,分析的数据流是满足CFL-Reachability这一性质的。
+回顾Soundness的定义(没有漏报bug就是sound):
-本课主要内容如下:
+> **Conservative** approximation: the analysis **captures all program behaviors**, or the analysis result **models all possible executions** of the program.
-1. Feasible and Realizable Paths
-2. CFL-Reachability
-3. Overview of IFDS
-4. Supergraph and Flow Functions
-5. Exploded Supergraph and Tabulation Algorithm
-6. Understanding the Distributivity of IFDS
+无论是学术界还是工业界的算法,都是不完全sound的。
-# Feasible and Realizable Paths
+这是由于很多语言拥有的部分高级特性对于静态分析来说是难以分析的:
-实际分析时,JDK中一个方法能产生的CFG是非常复杂的。不过,并非所有的路径都会被执行到,一个很自然的想法是,只分析可能被执行的路径。
+- Java
+ - Reflection, native code, dynamic class loading, etc.
+- JavaScript
+ - eval, document object model (DOM), etc.
+- C/C++
+ - Pointer arithmetic, function pointers, etc.
- +例如对C/C++中的一个指针p,加上某个经过运算的偏移量x,为了分析的安全,只能假设p+x可以指向内存中的任何一个地方。
-虽然并非所有的路径都会被执行到。**可是`判断一条路径是否feasible`本身是不可判定(undecidable)的。**
+为了解决这一问题,专家们提出一个新的概念Soundiness,对应的形容词是Soundy。
-这并不代表我们束手无策了,我们来看一个例子:
+> A **soundy** analysis typically means that the analysis is mostly sound, with **well-identified** unsound treatments to hard/specific language features.
-
+把新旧词汇放到一起做个比较:
-动态执行时x和y都有确定的值,而上下文不敏感的分析中,x和y的取值都会是NAC,更具体的说,就是`{18,30,-1}`。
+- A **sound** analysis requires to **capture all** dynamic behaviors
+ - 完全理想情况
+- A **soundy** analysis aims to **capture all** dynamic behaviors **with certain hard language features unsoundly handled within reason**
+ - 现实情况
+- An **unsound** analysis **deliberately ignores certain behaviors in its design for better efficiency, precision or accessibility**
+ - 过于现实的情况
-仔细地观察x的两个不精确的分析结果,可以发现-1这个结果在当前框架下是不可避免的:
+# Hard Language Feature: Java Reflection
-
+例如对C/C++中的一个指针p,加上某个经过运算的偏移量x,为了分析的安全,只能假设p+x可以指向内存中的任何一个地方。
-虽然并非所有的路径都会被执行到。**可是`判断一条路径是否feasible`本身是不可判定(undecidable)的。**
+为了解决这一问题,专家们提出一个新的概念Soundiness,对应的形容词是Soundy。
-这并不代表我们束手无策了,我们来看一个例子:
+> A **soundy** analysis typically means that the analysis is mostly sound, with **well-identified** unsound treatments to hard/specific language features.
-
+把新旧词汇放到一起做个比较:
-动态执行时x和y都有确定的值,而上下文不敏感的分析中,x和y的取值都会是NAC,更具体的说,就是`{18,30,-1}`。
+- A **sound** analysis requires to **capture all** dynamic behaviors
+ - 完全理想情况
+- A **soundy** analysis aims to **capture all** dynamic behaviors **with certain hard language features unsoundly handled within reason**
+ - 现实情况
+- An **unsound** analysis **deliberately ignores certain behaviors in its design for better efficiency, precision or accessibility**
+ - 过于现实的情况
-仔细地观察x的两个不精确的分析结果,可以发现-1这个结果在当前框架下是不可避免的:
+# Hard Language Feature: Java Reflection
- +说了这么多抽象的概念,接下来具体说说在Java里给静态分析添乱的特性。
-而30这个不精确的结果则是可以避免的(比如使用我们之前介绍过的上下文敏感指针分析):
+
+说了这么多抽象的概念,接下来具体说说在Java里给静态分析添乱的特性。
-而30这个不精确的结果则是可以避免的(比如使用我们之前介绍过的上下文敏感指针分析):
+ -
- +## Java Reflection
-定义一个新概念`Realizable Paths`:
+首先,右上角Run-time代码块中的前三行的Class、Method和Field都是Metaobject。然后就能够以Metaobject执行一系列操作,如`c.newInstance()`就相当于左下角的`new Person()`。
-> The paths in which “returns” are matched with corresponding “calls”.
+使用Reflection时,无法在编译时确定其行为,只能在运行时确定。
-- Realizable paths may not be executable, but unrealizable paths
- must not be executable.
- - 可以把executable/feasible path看作realizable path的真子集
-- Our goal is to **recognize realizable paths** so that we could avoid polluting analysis results along unrealizable paths.
- - 这个问题和括号匹配问题本质上是一样的。
- - 如果你是计算机系大一的学生,或许会想到用stack来做括号匹配问题。
- - 而如果你刚刚修过计算理论课程,你应该能够想起来使用上下文无关文法能够很好地识别一个匹配的括号串(Balanced-Parenthesis Problem)。
+
+## Java Reflection
-定义一个新概念`Realizable Paths`:
+首先,右上角Run-time代码块中的前三行的Class、Method和Field都是Metaobject。然后就能够以Metaobject执行一系列操作,如`c.newInstance()`就相当于左下角的`new Person()`。
-> The paths in which “returns” are matched with corresponding “calls”.
+使用Reflection时,无法在编译时确定其行为,只能在运行时确定。
-- Realizable paths may not be executable, but unrealizable paths
- must not be executable.
- - 可以把executable/feasible path看作realizable path的真子集
-- Our goal is to **recognize realizable paths** so that we could avoid polluting analysis results along unrealizable paths.
- - 这个问题和括号匹配问题本质上是一样的。
- - 如果你是计算机系大一的学生,或许会想到用stack来做括号匹配问题。
- - 而如果你刚刚修过计算理论课程,你应该能够想起来使用上下文无关文法能够很好地识别一个匹配的括号串(Balanced-Parenthesis Problem)。
+ -
- +## Why Analyze It
-# CFL-Reachability
+可能会**错失检测出某些bug的机会**(忽略`m.invoke`所引入的调用时发生),也可能**导致分析的结果不安全**(忽略`f.set(a,a)`的作用时发生,将会错误地认为箭头指向处的cast可以优化掉)。
-> A path is considered to connect two nodes A and B, or **B is reachable from A**, only if **the concatenation of the labels on the edges of the path is a word in a specified context-free language.**
+
+## Why Analyze It
-# CFL-Reachability
+可能会**错失检测出某些bug的机会**(忽略`m.invoke`所引入的调用时发生),也可能**导致分析的结果不安全**(忽略`f.set(a,a)`的作用时发生,将会错误地认为箭头指向处的cast可以优化掉)。
-> A path is considered to connect two nodes A and B, or **B is reachable from A**, only if **the concatenation of the labels on the edges of the path is a word in a specified context-free language.**
+ -这里默认读者学习过上下文无关语言(context-free language)相关的知识(编译原理和计算理论几乎是每个学校计算机系的必修课)。具体来说,你应该知道:
+## How to Analyze It
-- 终结符(nonterminal)
-- 非终结符(terminal)
-- 空串符号$$ \epsilon$$
-- (最左/最右)推导
-- 正则文法/上下文无关文法和图灵机之间计算表达能力的差异
+一种方法是模拟动态运行过程,只要知道关键调用时的字符串,就能分析出结果:
-我们进一步定义一个语言`L(realizable)`,右侧黄色框中的4个字符串都是语言L的一部分。
+
-这里默认读者学习过上下文无关语言(context-free language)相关的知识(编译原理和计算理论几乎是每个学校计算机系的必修课)。具体来说,你应该知道:
+## How to Analyze It
-- 终结符(nonterminal)
-- 非终结符(terminal)
-- 空串符号$$ \epsilon$$
-- (最左/最右)推导
-- 正则文法/上下文无关文法和图灵机之间计算表达能力的差异
+一种方法是模拟动态运行过程,只要知道关键调用时的字符串,就能分析出结果:
-我们进一步定义一个语言`L(realizable)`,右侧黄色框中的4个字符串都是语言L的一部分。
+ -
- +**吗?**
-还是太抽象了!我们拿两个例子来看看:
+
+**吗?**
-还是太抽象了!我们拿两个例子来看看:
+ -
- +因为有太多的因素(见右边黄框内容)可能会影响到字符串的值,而其中很多是无法静态确定的。基于字符串常量的分析此时并不奏效……
-图中绿色标记的Call Edge和Return Edge分别是字符串中的$$ (_1$$和$$ )_1$$,而其他的边则是字符串中的e。
+## Real research paper
-看完一个属于L的例子,再来一个不属于L的例子:
+
+因为有太多的因素(见右边黄框内容)可能会影响到字符串的值,而其中很多是无法静态确定的。基于字符串常量的分析此时并不奏效……
-图中绿色标记的Call Edge和Return Edge分别是字符串中的$$ (_1$$和$$ )_1$$,而其他的边则是字符串中的e。
+## Real research paper
-看完一个属于L的例子,再来一个不属于L的例子:
+ -
- +这来源于一个巧妙的观察:
-# Overview of IFDS
+> When string arguments cannot be resolved statically, **infer the reflective targets at their usage points**!
-> “Precise Interprocedural Dataflow Analysis via Graph Reachability”
->
-> --Thomas Reps, Susan Horwitz, and Mooly Sagiv, POPL’95
+getClass获得Class的Metaobject。
-所谓IFDS,其实是四个单词(Interprocedural, Finite, Distributive, Subset)的缩写。如果一个问题满足这四个性质,则可以用相应的框架来解决问题。
+这里的cmd是动态的命令,静态时无法分析……
-复习两个旧概念,介绍一个新概念:
+
+这来源于一个巧妙的观察:
-# Overview of IFDS
+> When string arguments cannot be resolved statically, **infer the reflective targets at their usage points**!
-> “Precise Interprocedural Dataflow Analysis via Graph Reachability”
->
-> --Thomas Reps, Susan Horwitz, and Mooly Sagiv, POPL’95
+getClass获得Class的Metaobject。
-所谓IFDS,其实是四个单词(Interprocedural, Finite, Distributive, Subset)的缩写。如果一个问题满足这四个性质,则可以用相应的框架来解决问题。
+这里的cmd是动态的命令,静态时无法分析……
-复习两个旧概念,介绍一个新概念:
+ -- `Path Function`
+但是!在篮圈处的调用中,由于只传入parameter这一个参数,而在155行我们已经知道其类型就是``FrameworkCommandInterpreter`(或其子类/父类)。
- - > Path function for path p, denoted as $$ pf_p$$, is a composition of flow functions for all edges (sometimes nodes) on p
+
-- `Path Function`
+但是!在篮圈处的调用中,由于只传入parameter这一个参数,而在155行我们已经知道其类型就是``FrameworkCommandInterpreter`(或其子类/父类)。
- - > Path function for path p, denoted as $$ pf_p$$, is a composition of flow functions for all edges (sometimes nodes) on p
+ - - 可以理解按照顺序,先后应用一条path上edge/node的transfer function:
+
- - 可以理解按照顺序,先后应用一条path上edge/node的transfer function:
+ - -
- -  +此外也有和动态分析结合的方法:
-- `Meet-Over-All-Paths(MOP)`
+
+此外也有和动态分析结合的方法:
-- `Meet-Over-All-Paths(MOP)`
+ - - > For each node n, MOP n provides a “meet-over-all-paths” solution where Paths(start, n) denotes the set of paths in CFG from the start node to n.
+# Hard Language Feature: Native Code
- - 即对所有的开始点start,都以bottom作为path function的输入,并在终点n处对所有的结果做meet操作。
+## Native Code
- -
- - > For each node n, MOP n provides a “meet-over-all-paths” solution where Paths(start, n) denotes the set of paths in CFG from the start node to n.
+# Hard Language Feature: Native Code
- - 即对所有的开始点start,都以bottom作为path function的输入,并在终点n处对所有的结果做meet操作。
+## Native Code
- -  +在Java中,一句简单的`println`最后会调用**与底层平台相关的C或C++代码**,这些代码就称为Native Code。Java也借此实现了 `Run anywhere`的目标。
-- `Meet-Over-All-Realizable-Paths(MRP)`
+
+在Java中,一句简单的`println`最后会调用**与底层平台相关的C或C++代码**,这些代码就称为Native Code。Java也借此实现了 `Run anywhere`的目标。
-- `Meet-Over-All-Realizable-Paths(MRP)`
+ - - > For each node n, MRP n provides a “meet-over-all-realizable-paths” solution where RPaths(start, n) denotes the set of realizable paths (the path’s word is in the language L(realizable)) from the start node to n.
+### Java Native Interface(JNI)
- - 在前者概念的基础上限制Meet的对象为Realizable-Path
+JNI允许JVM与Native Code写出的Native Lib交互。进而提供与OS交互、提高性能和代码复用(指在Java中使用别的C/C++编写的libraries)的功能。
- -
- - > For each node n, MRP n provides a “meet-over-all-realizable-paths” solution where RPaths(start, n) denotes the set of realizable paths (the path’s word is in the language L(realizable)) from the start node to n.
+### Java Native Interface(JNI)
- - 在前者概念的基础上限制Meet的对象为Realizable-Path
+JNI允许JVM与Native Code写出的Native Lib交互。进而提供与OS交互、提高性能和代码复用(指在Java中使用别的C/C++编写的libraries)的功能。
- -  +
+ ----
+## Why Native Code is Hard
-接下来要讲一些比较难懂的内容~~战术喝水~~。
+为了使用Native Library中的一个Method,需要经过这些步骤:
-
----
+## Why Native Code is Hard
-接下来要讲一些比较难懂的内容~~战术喝水~~。
+为了使用Native Library中的一个Method,需要经过这些步骤:
- +1. 用C/C++按照标准写一个库并编译生成`*.so`文件
+2. 在Java中加载Native Library
+3. 在Java中声明Native Method
+4. 调用Native Method
-# Supergraph and Flow Functions
+然而:
-## Supergraph
+1. 类似的JNI可提供的操作有230种(在2020年如此)
+2. 由此引出紫框中的问题:`如何分析Native Call?`
-可以理解成IFDS分析体系下的ICFG(Interprocedural Control Flow Graph,即过程间控制流图)。这里只需要了解一下其中的三种edge(图中的G*即指supergraph):
+
+1. 用C/C++按照标准写一个库并编译生成`*.so`文件
+2. 在Java中加载Native Library
+3. 在Java中声明Native Method
+4. 调用Native Method
-# Supergraph and Flow Functions
+然而:
-## Supergraph
+1. 类似的JNI可提供的操作有230种(在2020年如此)
+2. 由此引出紫框中的问题:`如何分析Native Call?`
-可以理解成IFDS分析体系下的ICFG(Interprocedural Control Flow Graph,即过程间控制流图)。这里只需要了解一下其中的三种edge(图中的G*即指supergraph):
+ -
- +### Current Practice & More
-## Design Flow Functions
+接下来介绍一个现有的解决方法,然后给新的拓展阅读方向。~~对,本次讲的都是前沿内容。~~
-定义`Possibly-uninitialized variables`:
+
+### Current Practice & More
-## Design Flow Functions
+接下来介绍一个现有的解决方法,然后给新的拓展阅读方向。~~对,本次讲的都是前沿内容。~~
-定义`Possibly-uninitialized variables`:
+ -> **For each node n** ∈ N*, determine **the set of variables that may be uninitialized** before execution reaches n.
+arraycopy(src,3,dest,4,5)就是从src的第三个元素起,拷贝起始位置是dest的第四个元素,总共拷贝5个元素。
-我们接下来的例子求的就是这样的变量。
+如果不分析Native Code,我们就会失去很多信息。而Modeling的分析方法是:
-### lambda expression
+- 先将其副作用用Java代码表示出来(图中第一个方框)
+- 然后用指针分析的方法进一步抽象其副作用(图中第二个方框)
-为了后续叙述方便,这里简单地介绍一下lambda表达式。
+
-> **For each node n** ∈ N*, determine **the set of variables that may be uninitialized** before execution reaches n.
+arraycopy(src,3,dest,4,5)就是从src的第三个元素起,拷贝起始位置是dest的第四个元素,总共拷贝5个元素。
-我们接下来的例子求的就是这样的变量。
+如果不分析Native Code,我们就会失去很多信息。而Modeling的分析方法是:
-### lambda expression
+- 先将其副作用用Java代码表示出来(图中第一个方框)
+- 然后用指针分析的方法进一步抽象其副作用(图中第二个方框)
-为了后续叙述方便,这里简单地介绍一下lambda表达式。
+ -以$$ \lambda$$标识一个lambda表达式,从开头到中间点间的符号代表**参数列表**,从中间点到最后的符号代表**函数体**。如下例子,就代表这样一个函数调用:
+如果对Soundiness感兴趣,推荐网站http://soundiness.org
-- 函数以x作为输入参数
-- 函数返回值为x+1
-- 调用函数时传入的参数为3
+
-以$$ \lambda$$标识一个lambda表达式,从开头到中间点间的符号代表**参数列表**,从中间点到最后的符号代表**函数体**。如下例子,就代表这样一个函数调用:
+如果对Soundiness感兴趣,推荐网站http://soundiness.org
-- 函数以x作为输入参数
-- 函数返回值为x+1
-- 调用函数时传入的参数为3
+ -
- +# Key Points
-### Example of Flow Functions
-
-在进入main后,全局变量g和局部变量x一定是没有初始化的。
-
-
+# Key Points
-### Example of Flow Functions
-
-在进入main后,全局变量g和局部变量x一定是没有初始化的。
-
- -
-随后x被初始化:
-
-
-
-随后x被初始化:
-
- -
-以x来初始化a,a是否被初始化与x一致。
-
-
-
-以x来初始化a,a是否被初始化与x一致。
-
- -
-这个函数比较奇妙,它表达的意思是:如果a和g都被初始化了,则a是被初始化的,否则认为a没有被初始化。
-
-
-
-这个函数比较奇妙,它表达的意思是:如果a和g都被初始化了,则a是被初始化的,否则认为a没有被初始化。
-
- -
-注意左侧以红色标记的函数,这样写能够使得在$$ Ret_p$$处g是否已经被赋值/初始化取决于是否在被调用函数中被赋值。
-
-
-
-注意左侧以红色标记的函数,这样写能够使得在$$ Ret_p$$处g是否已经被赋值/初始化取决于是否在被调用函数中被赋值。
-
- 
-
-这里涉及一个特殊的情况,由于离开了函数,所以要去除函数内部变量a。
-
-

-
-这里涉及一个特殊的情况,由于离开了函数,所以要去除函数内部变量a。
-
- -
-# Exploded Supergraph and Tabulation Algorithm
-
-## Build Exploded Supergraph
-
-Flow Function对应着二元关系。
-
-
-
-# Exploded Supergraph and Tabulation Algorithm
-
-## Build Exploded Supergraph
-
-Flow Function对应着二元关系。
-
- -
-直接从左到右解释例子:
-
-1. 输出和输入完全一致
-2. 无论输入为什么,输出都包含a
-3. 输出一定不包含a,且一定包含b,其他变量(这里是c)则保持不变
-4. 如果输入包含a,则输出一定包含b;否则一定不包含b
-
-你是否也觉得上面例子中0->0这条边挺奇怪的?它的存在是被刻意设计的。因为IFDS主要依赖于可达性(reachability)做分析。如果没有这样的边,在IFDS中没有办法判断在n4这个点处,a是否满足某种性质。
-
-
-
-直接从左到右解释例子:
-
-1. 输出和输入完全一致
-2. 无论输入为什么,输出都包含a
-3. 输出一定不包含a,且一定包含b,其他变量(这里是c)则保持不变
-4. 如果输入包含a,则输出一定包含b;否则一定不包含b
-
-你是否也觉得上面例子中0->0这条边挺奇怪的?它的存在是被刻意设计的。因为IFDS主要依赖于可达性(reachability)做分析。如果没有这样的边,在IFDS中没有办法判断在n4这个点处,a是否满足某种性质。
-
- -
-而加上这条总是存在的Glue Edge之后,就可以满足IFDS分析的要求。
-
-
-
-而加上这条总是存在的Glue Edge之后,就可以满足IFDS分析的要求。
-
- -
-回到我们之前的例子,用新的二元关系的视角去**手动分析**,将会是这样(视频之后会做的会做的~~吧~~,咕!):
-
-标黄部分比较重要,它的意思是:如果a或g一开始没有被初始化,则a都没有被初始化。
-
-
-
-回到我们之前的例子,用新的二元关系的视角去**手动分析**,将会是这样(视频之后会做的会做的~~吧~~,咕!):
-
-标黄部分比较重要,它的意思是:如果a或g一开始没有被初始化,则a都没有被初始化。
-
- -
-最后构造出来的Exploded Supergraph是这样的:
-
-
-
-最后构造出来的Exploded Supergraph是这样的:
-
- -
-怎样使用这样的分析结果呢?我们来考虑一个问题,全局变量g在程序片段运行结束时,是否可能没有被初始化?
-
-
-
-怎样使用这样的分析结果呢?我们来考虑一个问题,全局变量g在程序片段运行结束时,是否可能没有被初始化?
-
- -
-结果是,g在这里可能没有被初始化。
-
-
-
-结果是,g在这里可能没有被初始化。
-
- -
-而之前提到的realizable path在这里也能提供更高的精度。
-
-
-
-而之前提到的realizable path在这里也能提供更高的精度。
-
- -
-
-
- -
-## Tabulation Algorithm
-
-刚才我们是手动分析的,而用Tabulation算法,可以在$$ O(ED^3)$$复杂度(E为Edge的数量,D为Data facts的数量,如在下面的例子中,D为3)下得到MRP的结果:
-
-
-
-## Tabulation Algorithm
-
-刚才我们是手动分析的,而用Tabulation算法,可以在$$ O(ED^3)$$复杂度(E为Edge的数量,D为Data facts的数量,如在下面的例子中,D为3)下得到MRP的结果:
-
- -
-
-
- -
-
-
- -
-# Understanding the Distributivity of IFDS
-
-这里的Distributivity是指Flow Function的性质,即满足:
-
-$$ \forall(x,y). f(x\cdot y)=f(x)\cdot f(y)$$
-
-- 这样的要求使得我们**无法用IFDS来做常量传播(constant propagation)和指针分析(pointer analysis)**
-- 换句话说,在IFDS中,我们**可以表达逻辑或,但无法表达逻辑与**
-- 更广泛地说,**如果我们需要考虑多个输入来决定输出**,那么由于Distributivity性质没有被满足,**无法用IFDS来解决**。
-
-
-
-# Understanding the Distributivity of IFDS
-
-这里的Distributivity是指Flow Function的性质,即满足:
-
-$$ \forall(x,y). f(x\cdot y)=f(x)\cdot f(y)$$
-
-- 这样的要求使得我们**无法用IFDS来做常量传播(constant propagation)和指针分析(pointer analysis)**
-- 换句话说,在IFDS中,我们**可以表达逻辑或,但无法表达逻辑与**
-- 更广泛地说,**如果我们需要考虑多个输入来决定输出**,那么由于Distributivity性质没有被满足,**无法用IFDS来解决**。
-
- -
-上图最后的问题答案是**可以使用IFDS,因为只需要考虑单一的输入即可决定输出**。
-
-再来看看指针分析的例子:
-
-
-
-上图最后的问题答案是**可以使用IFDS,因为只需要考虑单一的输入即可决定输出**。
-
-再来看看指针分析的例子:
-
- -
-注意图中的虚线部分,由于没有别名(alias)信息,这个边是无法被IFDS框架分析出来的。而IFDS是无法处理别名信息的,因为别名信息的另一种意义是“x和y**都**指向同一个对象”——这需要我们同时考虑x和y来决定他们是否指向同一个对象。
-
-> Note: If we want to obtain alias information in IFDS, say alias(x,y), to produce correct outputs, we need to consider multiple input data facts, x and y, which cannot be done in standard IFDS as **flow functions handle input facts independently (one fact per time). Thus pointer analysis is non-distributive.**
-
-## Key Points
-
-- Understand **CFL-Reachability**
-- Understand **the basic idea** of IFDS
- - 大概知道有几个阶段即可
-- Understand **what problems can be solved** by IFDS
\ No newline at end of file
+- Understand **soundiness: its motivation and concept**
+- Understand why **Java reflection and native** code are hard to analyze
\ No newline at end of file
-
-注意图中的虚线部分,由于没有别名(alias)信息,这个边是无法被IFDS框架分析出来的。而IFDS是无法处理别名信息的,因为别名信息的另一种意义是“x和y**都**指向同一个对象”——这需要我们同时考虑x和y来决定他们是否指向同一个对象。
-
-> Note: If we want to obtain alias information in IFDS, say alias(x,y), to produce correct outputs, we need to consider multiple input data facts, x and y, which cannot be done in standard IFDS as **flow functions handle input facts independently (one fact per time). Thus pointer analysis is non-distributive.**
-
-## Key Points
-
-- Understand **CFL-Reachability**
-- Understand **the basic idea** of IFDS
- - 大概知道有几个阶段即可
-- Understand **what problems can be solved** by IFDS
\ No newline at end of file
+- Understand **soundiness: its motivation and concept**
+- Understand why **Java reflection and native** code are hard to analyze
\ No newline at end of file